3GPP 5G Timeline Explained: Releases 15, 16, 17 and the Evolution of 5G

Get to Know the 3GPP 5G Timeline: Releases 15, 16, 17 and the Evolution of 5G
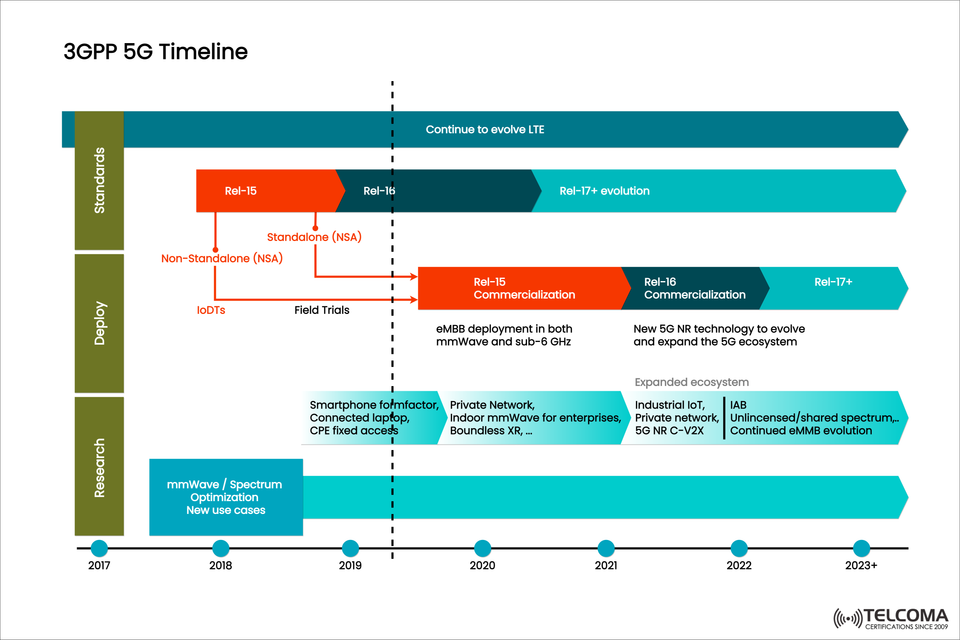
The evolution of 5G has been largely driven by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), which is the global group that sets the standards for cellular technology. Starting from initial research back in 2017 to the commercialization and growth of the ecosystem by 2023 and beyond, the 3GPP 5G timeline showcases a collective global effort aimed at building the most advanced mobile network we have today.
In this post, we’ll break down the timeline shown above, discuss the significance of Releases 15, 16, and 17, and explain how 5G continues to develop through ongoing research, deployment, and expanding use cases.
Understanding the 3GPP Timeline
The journey of 5G development through 3GPP can be broken down into three major phases:
Research (2017–2018): Focus on spectrum optimization, looking into mmWave, and testing new use cases.
Deployment (2018–2020): Rolling out Non-Standalone (NSA) and Standalone (SA) setups, conducting field trials, and launching initial devices.
Commercialization (2019–2023+): Seeing mass adoption, broadening the ecosystem's use cases, and continually evolving standards.
These phases link directly to the 3GPP releases:
Release 15: The base for 5G NR (New Radio).
Release 16: Expanding into new industries and enhancing efficiency.
Release 17+: Preparing for future scalability, unlicensed spectrum, IoT applications, and advanced XR.
Release 15: The Foundation of 5G
Release 15 (Rel-15) was the first official standard for 5G, wrapping up in 2018. It rolled out 5G NR (New Radio) and set the groundwork for the first deployments.
Key Highlights:
Non-Standalone (NSA): This allows 5G to work alongside existing 4G LTE networks for quicker deployment.
Standalone (SA): A fully 5G core network that supports new features beyond LTE.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Offers high-speed data through both mmWave and sub-6 GHz spectrum.
Field Trials and IoDTs: Early testing for interoperability with various vendors and operators.
Commercialization:
Adoption of 5G smartphones grows.
Urban areas see deployments using mmWave for capacity, with sub-6 GHz for better coverage.
Introduction of CPE (Customer Premises Equipment) for fixed wireless access.
Rel-15 really laid down the groundwork for what 5G is today.
Release 16: Expanding the Ecosystem
Release 16 (Rel-16), finalized in 2020, broadened 5G’s potential beyond just consumer uses. This release brought features aimed at enterprise, industrial, and high-stakes applications.
Key Highlights:
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC): Vital for autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote surgeries.
Private Networks: Secure, localized 5G setups specifically for businesses and factories.
Indoor mmWave: Enhancing 5G coverage for enterprise applications.
Boundless XR: Facilitating advanced Extended Reality (AR/VR/MR) applications.
V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything): Connecting cars with other systems for smart transport.
Commercialization:
Networks focused on enterprise applications are expanding.
Industrial IoT is gaining traction with reliability.
The ecosystem is growing to include laptops, IoT gadgets, and wearables.
Rel-16 shifted 5G’s focus from just consumers to also empowering industry and enterprise.
Release 17+: Evolving 5G for the Future
Release 17 and beyond (Rel-17+) is pushing 5G further into new areas, concentrating on scalability, flexibility, and global inclusivity. This release, which wrapped up in 2022, and future advancements are designed to meet both consumer demands and the needs of emerging industries.
Key Highlights:
Unlicensed/Shared Spectrum: Creating flexibility for both operators and businesses.
Integrated Access and Backhaul (IAB): Expanding coverage without needing new fiber installations.
Industrial IoT Enhancements: Improving automation and communication for machines.
Extended XR Support: High-performance VR/AR for gaming, education, and businesses.
Ongoing eMBB Development: Higher speeds, improved efficiency, and broader coverage.
Rel-17+ positions 5G to transition smoothly into 6G by supporting future research and deployment strategies.
Research Phase: Spectrum and Use Cases
Before the 5G rollout, there was extensive research and trials:
mmWave Spectrum: Testing millimeter-wave frequencies to evaluate their potential for ultra-fast data rates.
Spectrum Optimization: Making the best use of available spectrum bands.
New Use Cases: Exploring smart cities, connected vehicles, and immersive media as early 5G drivers.
These research activities helped inform the standards finalized in Rel-15 and beyond.
Deployment Timeline: Step-by-Step
The rollout of 5G followed a clear timeline:
2018: Conducting IoDTs and field trials.
2019: Launch of commercial networks and entry of smartphones and CPE devices into the market.
2020: Start of private networks and enterprise solutions.
2021: Expansion of industrial IoT and V2X use cases.
2022: Broader ecosystem growth with unlicensed spectrum and IAB for rural connectivity.
2023+: Ongoing development with Release 17 and future versions.
Expanded 5G Ecosystem
The 5G ecosystem has grown well beyond just smartphones. As shown in the timeline, it now encompasses:
Consumer Devices: Smartphones, laptops, and fixed wireless access.
Enterprise Solutions: Private networks, XR applications, and indoor mmWave.
Industrial Applications: IoT, C-V2X, and automation.
Advanced Infrastructure: IAB, shared spectrum, and enhanced eMBB.
This diversification makes sure that 5G meets both consumer needs and drives industry innovation.
Key Differences Between Releases
Here’s a quick look at the main features of the three major 5G releases:
Release Focus Key FeaturesRel-15FoundationNSA/SA, eMBB, mmWave + sub-6 GHz, field trialsRel-16ExpansionURLLC, private networks, industrial IoT, XR, V2XRel-17+EvolutionUnlicensed spectrum, IAB, enhanced XR, ongoing eMBB
Conclusion
The 3GPP 5G timeline reveals how collaborative research, standard-setting, and deployment have shaped our current mobile networks.
Release 15 set the foundational elements for 5G.
Release 16 broadened its applications for enterprises, industries, and low-latency needs.
Release 17+ focuses on ongoing evolution and lays the groundwork for what’s next with 6G.
For those in telecom, this roadmap is essential for grasping how 5G continues to evolve through each release. For tech fans, it shows how innovations like XR, IoT, and private networks are reshaping industries and everyday life.
The journey of 5G is just getting started—additional releases will keep enhancing capabilities as we head toward a 6G era of hyper-connectivity.
