3GPP RAN3 Release 17: Enhancements for QoE, NTN, and Network Architecture

3GPP Release 17 is a major leap forward for 5G networks, with the RAN3 working group playing a key role in its protocol and architecture development. While RAN1 is all about the physical layer and RAN2 deals with MAC/RLC/PDCP protocols, RAN3 tackles the higher-level architecture, focusing on mobility, QoE, SON/MDT, and the split between control and user planes.
In this blog post, we’re breaking down the RAN3 Release 17 timeline and exploring how these updates enhance 5G rollout, boost user experiences, and provide scalability for operators.
🔹 Key Focus Areas in RAN3 Release 17
- NR QoE (Quality of Experience)
One of the standout features is the NR QoE Study and Enhancements. Unlike QoS, which centers on the network, QoE shines a light on user-focused performance metrics.
Study phase: Identified crucial QoE metrics for various services like video streaming, XR, and gaming.
Outcome: Protocol upgrades that help networks dynamically adjust according to users' perceived service quality.
🔑 Impact: Operators can offer experience-based SLAs, paving the way for models that tie monetization to user satisfaction instead of just throughput.
- SON/MDT Enhancements
Self-Organizing Networks (SON) and Minimization of Drive Tests (MDT) are vital for cutting down on operational expenses.
SON Enhancements: Automation improvements in cell configuration and fault recovery.
MDT Enhancements: Enable networks to gather performance and coverage data straight from UEs, which minimizes the need for pricey manual drive tests.
🔑 Impact: Leads to reduced OPEX, quicker troubleshooting, and better network optimization.
- Multicast for NR
RAN3 has expanded multicast support, making broadcast-style services more efficient:
Software updates can be sent to thousands of IoT devices all at once.
Live video streams or public alerts can be disseminated on a large scale.
🔑 Impact: Conserves spectrum, eases the load on the core, and enhances efficiency for large-scale IoT and media applications.
- Non-Public Network Enhancements (SA2-led, supported by RAN3)
Private 5G networks are vital for enterprise adoption. RAN3 tweaks ensure protocol-level optimizations for NPNs:
Smooth handovers between private and public networks.
Secure connectivity models designed for enterprise requirements.
🔑 Impact: Boosts the adoption of Industry 4.0, healthcare, and smart campus networks.
- IAB (Integrated Access and Backhaul) Enhancements
RAN3 helps standardize IAB alongside RAN2, which is essential for dense urban deployments.
Supports wireless backhaul links, reducing reliance on fiber.
Facilitates multi-hop relaying with low latency.
🔑 Impact: Makes for a cost-effective 5G rollout, particularly in metro areas and developing regions.
- NR over NTN and NB-IoT over NTN
Satellite integration is a significant breakthrough in Release 17.
NR over NTN: Brings 5G NR coverage to remote locations via satellite links.
NB-IoT over NTN: Guarantees global IoT coverage with lightweight, low-power devices.
🔑 Impact: Crucial for logistics, agriculture, maritime, and emergency connectivity, ensuring true global 5G access.
- NR Positioning Enhancements
Building on the work from RAN1/RAN2, RAN3 guarantees protocol support for precise positioning.
Achieves cm-level accuracy through multi-antenna NR.
Provides protocols for quick reporting and handover support.
🔑 Impact: Unlocks precision navigation, asset tracking, and AR/VR overlays.
- LTE UP/CP Split
RAN3 refines the split between Control Plane (CP) and User Plane (UP) in LTE aligning it to 5G dual connectivity models.
🔑 Impact: Smoother interworking between LTE and 5G, supporting transitional networks.
- Corrections and TEI (Tracking Area Enhancements)
Release 17 also brings corrections and improvements in architecture to ensure interoperability and stability.
🔑 Impact: Enhances standard consistency, making it easier for operators and vendors to deploy.
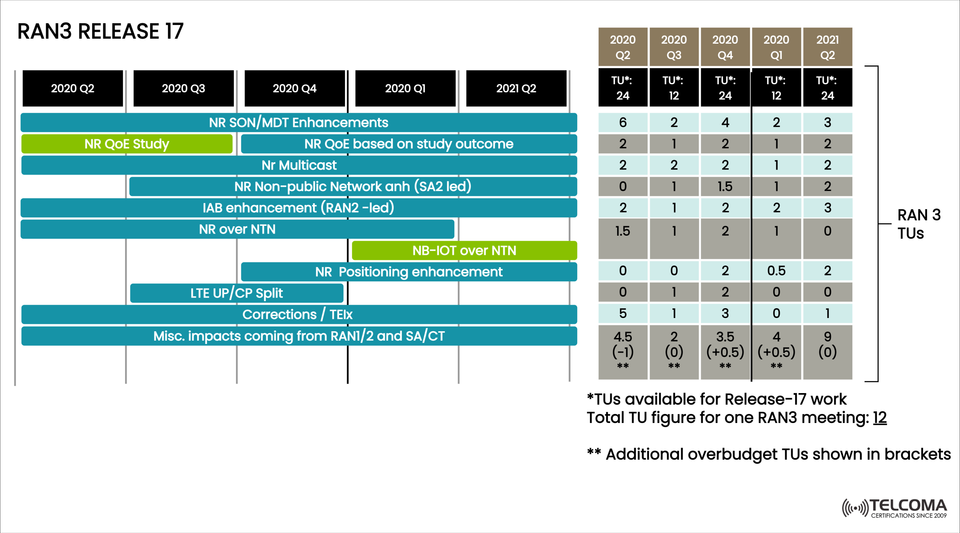
📊 RAN3 Release 17 Timeline and TU Allocation
The timeline details phased work from Q2 2020 to Q2 2021. Each feature received specific Technical Units (TUs), which measures resource allocation for the standardization process.
Feature Key Work Item TU Allocation (avg)Impact NR QoE Study & Enhancements User-centric quality metrics2-3 TUs Experience-based SLAs SON/MDT Enhancements Network automation & drive test reduction6-3 TUs Lower OPEX, improved optimization NR Multicast Efficient broadcast2 TUs Firmware updates, media Non-Public Networks Private 5G optimizations1-2 TUs Enterprise adoption IAB Enhancements Wireless backhaul2-3 TUs Cost-effective densification NR over NTN5G via satellites1.5-2 TUs Rural/remote connectivity NB-IoT over NTN IoT via satellites1-2 TUs Global IoT coverage NR Positioning Protocol support0.5-2 TUs Precise location services LTE UP/CP Split LTE/5G interworking1-2 TUs Smooth migration Corrections/TEI Standard refinements1-5 TUs Stability & consistency
🔹 Industry-Wide Implications of RAN3 Release 17
For Operators
Cuts down on deployment and O&M costs thanks to SON/MDT.
Opportunity to monetize QoE-based services.
Expands rural access with satellite NTN support.
For Enterprises
Eases integration of private 5G networks.
Strengthened support for mission-critical applications.
For IoT Ecosystem
NB-IoT over NTN ensures global scale for asset tracking, agriculture, and logistics.
For Consumers
Improved service consistency in remote regions.
QoE-driven enhancements for streaming, XR, and gaming.
🔹 RAN3 vs. RAN1/RAN2: Complementary Roles
RAN1: Concentrates on air-interface and spectrum improvements.
RAN2: Handles lower-layer protocols and slicing.
RAN3: Supplies the architecture and protocol backbone — facilitating interworking, automation, and QoE management.
Together, these efforts make Release 17 the most comprehensive evolution of 5G to date.
🔹 Cross-Group Synergies in Release 17
Each RAN group has its own set of tasks, but the real strength of Release 17 comes from how well they work together.
RAN1 (air interface) + RAN2 (protocols): Take RAN1’s cm-level positioning accuracy, for instance—it’s only useful if RAN2’s protocols can effectively handle signaling and manage mobility.
RAN2 (protocols) + RAN3 (architecture): Improvements in protocols, like RAN slicing, need some adjustments in RAN3’s architecture to make sure those slices are isolated, scalable, and aware of the user experience.
RAN1 + RAN3: Features such as IoT over NTN rely on insights from RAN1’s spectrum and waveform studies, while RAN3 ensures these functionalities mesh smoothly with operator networks and enterprise setups.
This integration across layers is what makes Release 17 a holistic evolution of the system, not just a set of separate upgrades.
🔹 Conclusion
3GPP RAN3 Release 17 is pivotal in defining how 5G networks function in the real world. By enhancing QoE management, automating SON/MDT, integrating satellite NTN, and supporting private networks, RAN3 is taking 5G beyond just speed — creating a platform that delivers reliability, efficiency, and scalability.
With these architectural advancements, Release 17 marks a significant milestone on the path to 5G-Advanced (Release 18), where we can expect AI-driven optimizations, integrated sensing, and advanced XR services to shape the next chapter.
