3GPP SA1 Verticals in 5G Release 18: Exploring 5GET, 5GSEI, RAILSS, OFFNETRAIL & eFRMCS Innovations

3GPP SA1 Verticals in Release 18: The Next Wave of 5G Evolution
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is actively mapping out the future of mobile communication standards, guiding the transition from LTE to 5G and beyond. With Release 18, 3GPP takes a significant leap towards 5G-Advanced, broadening its focus to include a variety of industry verticals beyond just traditional networks.
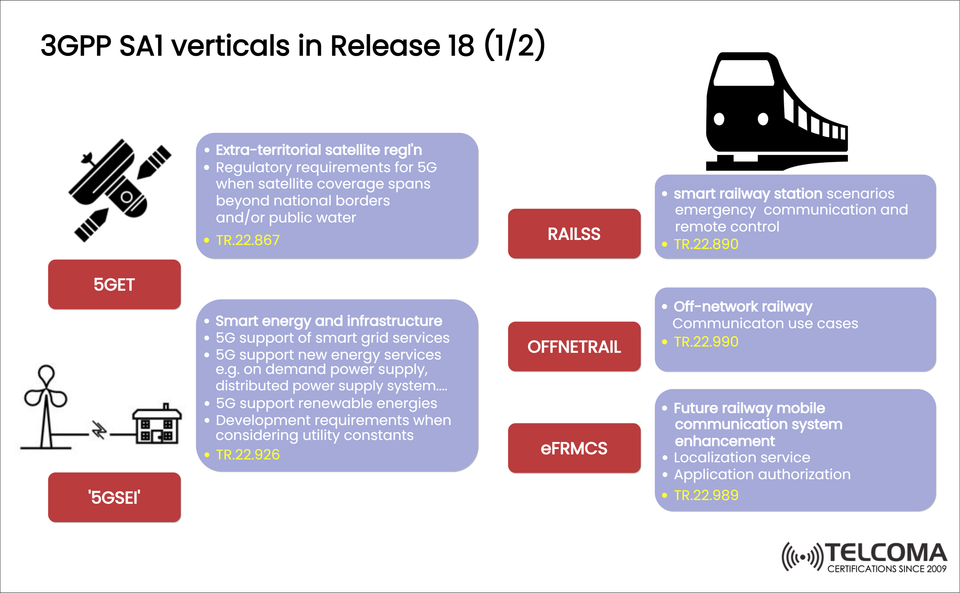
The SA1 (Service and System Aspects 1) working group zeroes in on determining service requirements for upcoming 5G applications. Release 18 unveils several new verticals like 5GET, 5GSEI, RAILSS, OFFNETRAIL, and eFRMCS. Each one is tailored to meet unique connectivity and regulatory challenges in fields such as satellite communications, smart energy, and railway systems.
Let’s dive into these verticals to see how 3GPP SA1 is laying the groundwork for smart, cross-domain connectivity.
5GET – Extra-Territorial Satellite Regulation
Technical Report: TR 22.867
Focus: Cross-border 5G satellite coverage and regulatory guidelines
Overview
The 5GET (5G Extra-Territorial) initiative is designed to tackle the challenges of 5G satellite communications that cross national borders. As satellite networks become key to the 5G landscape, it’s crucial to ensure all regulatory requirements are met across various jurisdictions.
Key Objectives
Outline regulatory needs for 5G when satellite services extend beyond national boundaries or public waters.
Allow smooth global communication for maritime, aviation, and remote areas.
Encourage harmonized spectrum management between nations.
Technical Impact
Incorporating non-terrestrial networks (NTN) with traditional 5G boosts global connectivity, which enables services like:
Global IoT connectivity for logistics and fleet management.
Real-time communication in remote or oceanic areas.
Support for international emergency communication frameworks.
To sum up, 5GET connects space and ground communication, creating a unified global 5G experience.
5GSEI – Smart Energy and Infrastructure
Technical Report: TR 22.926
Focus: 5G applications for smart grids, renewable energy, and infrastructure enhancement
Overview
The 5G Smart Energy and Infrastructure (5GSEI) initiative looks into how 5G can transform the energy landscape. The energy sector is quickly embracing IoT, automation, and edge computing, and 5G’s low latency and massive connectivity can really help connect the dots.
Key Objectives
Provide 5G support for smart grid services, aiding real-time monitoring and control.
Enable on-demand power supply and distributed power systems via 5G networks.
Assist with renewable energy integration through better communication among solar, wind, and storage systems.
Create utility-compliant frameworks for reliability and safety.
Use Cases
Application5G Role Benefit Smart Grids URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) Real-time fault detection Distributed Energy Resources m MTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication)Connects thousands of smart meters Renewable Integration Edge Computing Dynamically balances energy load
By facilitating real-time energy management, 5GSEI promotes sustainability, cuts down power losses, and builds a resilient energy network for smart cities.
RAILSS – Smart Railway Station Scenarios
Technical Report: TR 22.890
Focus: 5G-enabled smart operations in railway stations, emergency comms, and remote control
Overview
The RAILSS (Railway Smart Station Scenarios) vertical expands 5G capabilities into the railway arena, emphasizing station environments. It covers emergency communication, automation, and passenger safety, contributing to the creation of smarter, safer transport hubs.
Key Objectives
Establish emergency communication protocols for alerting passengers and staff in real time.
Allow remote control of station devices and security systems.
Promote IoT-based monitoring for passenger flow, ticketing, and crowd management.
Use Cases
Automated train scheduling and platform coordination.
Real-time surveillance and AI-driven incident detection.
IoT sensors for smart lighting and environmental controls.
The end result? Railway stations that are smart, secure, and seamlessly connected.
OFFNETRAIL – Off-Network Railway Communication
Technical Report: TR 22.990
Focus: Communication systems for railway operations in off-network or remote areas
Overview
The OFFNETRAIL (Off-Network Railway Communication) initiative addresses one of transportation’s biggest hurdles: maintaining communication when network connections aren’t available. It sets out requirements and use cases for autonomous, resilient communication systems in railway operations that go beyond typical network coverage.
Key Objectives
Guarantee constant communication for railway systems in isolated locations.
Support direct device-to-device (D2D) or relay-based communication for critical operations.
Improve operational safety even when networks are down.
Technical Innovations
ProSe (Proximity Services): This allows train units or track workers to talk directly to each other.
Edge caching and local processing: This keeps things running without needing a constant network connection.
OFFNETRAIL makes sure that railway operations can keep running smoothly, boosting safety and reliability even in tough terrains.
eFRMCS – Future Railway Mobile Communication System Enhancement
Technical Report: TR 22.989
Focus: Upgrading the 5G-based FRMCS (Future Railway Mobile Communication System)
Overview
The eFRMCS project builds on the Future Railway Mobile Communication System, which is set to replace older GSM-R systems. This initiative focuses on improvements in localization services, application authorization, and service reliability.
Key Objectives
Enhance localization accuracy for trains and trackside equipment.
Establish authorization processes for mission-critical railway applications.
Boost interoperability and standardization across different regions.
Use Cases
Real-time tracking of trains with sub-meter positioning accuracy.
Secure communications for railway control centers.
AI integration for predictive maintenance and resource management.
By incorporating 5G features such as URLLC and network slicing, eFRMCS sets the stage for a next-gen railway communication infrastructure.
Interconnected Vertical Synergy in Release 18
3GPP’s Release 18 doesn’t view these verticals as stand-alone entities; they collectively form a unified ecosystem that contributes to the wider 5G vision:
5GET provides global coverage, connecting rail and energy systems even in hard-to-reach areas.
5GSEI supports infrastructure that powers electric trains and renewable-powered transport systems.
RAILSS, OFFNETRAIL, and eFRMCS work together to redefine smart mobility through the reliability and real-time capabilities of 5G.
This interconnected approach ensures that 5G-Advanced isn’t just faster; it's also smarter and more adaptable across various industries.
Why Release 18 Matters
Release 18 marks a shift from 5G Phase 2 to 5G-Advanced, with a focus on intelligence, resilience, and enabling various industries. These SA1 verticals contribute directly to:
Industrial automation and digitization
Global interoperability of communication networks
Sustainability through energy efficiency
Enhanced safety and reliability for transport and utilities
In short, 3GPP SA1’s efforts are driving the evolution of 5G from merely a communication standard to a key enabler for digital transformation.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for 5G-Advanced
The launch of new verticals in 3GPP Release 18 highlights how 5G is broadening its reach beyond just smartphones and urban networks into space, energy, and mobility ecosystems. Each initiative — whether it’s 5GET’s satellite regulation or eFRMCS’s advanced railway systems — illustrates 3GPP’s commitment to providing connectivity that is universal, reliable, and ready for the future.
As we look forward to 5G-Advanced and beyond to 6G, these verticals will play a crucial role in linking industries, infrastructures, and nations with a cohesive communication framework — where data flows seamlessly, securely, and sustainably across all boundaries.
