4G vs 5G: Key Differences in Speed, Latency, Spectrum Efficiency, and Connectivity

Mobile communication has come a long way, evolving from 2G voice calls to 3G internet access, then to 4G LTE, and now we’re diving into the 5G era of hyper-connectivity. Each generation has reshaped our daily lives, our work environments, and how we connect with each other. But 5G is a whole new ballgame, moving us beyond just small improvements.
When we compare 4G and 5G, it’s not just about faster speeds; it’s about a whole new network structure that can manage a lot more devices, provide ultra-reliable low-latency communications, and support developments like IoT, self-driving cars, smart cities, and Industry 4.0.
The chart I uploaded really brings out the key performance indicators (KPIs) of both technologies, and we’re going to dig into those.
Peak Data Rate
4G LTE: Can hit a peak downlink data rate of 1 Gbps under perfect conditions.
5G NR (New Radio): Steps that up to 20 Gbps, which is a 20-fold improvement.
This huge leap allows for:
Super-fast downloads (like getting a 4K movie in just seconds).
Enhanced video streaming at 8K or experiences in VR/AR.
High-throughput applications like cloud gaming and industrial automation.
User-Experienced Data Rate
Peak rates are great and all, but what really counts is the average user experience:
4G: About ~10 Mbps.
5G: Around ~100 Mbps.
This tenfold increase means:
Smooth video calls and conferences.
Reliable cloud services and SaaS platforms.
Steady connections in crowded places like stadiums and airports.
Spectrum Efficiency
4G: Has limited efficiency when it comes to spectrum.
5G: Offers a 3x boost in spectrum efficiency, allowing for better use of radio frequencies.
Why does this matter?
Helps make the most of limited spectrum resources.
Cuts down on congestion in busy urban areas.
Lets more users connect per MHz, which helps lower costs per bit.
Areal Traffic Capacity
This metric shows how much data can be moved per square meter:
4G: Roughly ~0.1 Mbps/m².
5G: About ~10 Mbps/m².
That’s a 100-fold increase, and it’s crucial for:
Smart cities filled with thousands of IoT devices.
Factories with a dense network of sensors.
Large public events where many people are using mobile networks at once.
Latency
This is where things get really interesting:
4G: Has a latency of ~10 ms.
5G: Can bring latency down to as low as 1 ms.
Low latency impacts include:
Enabling self-driving cars to respond almost instantly.
Supporting remote surgeries with surgical precision.
Making cloud gaming and AR/VR experiences seamless and responsive.
Connection Density
Another game-changing aspect of 5G is its ability to handle massive IoT (mIoT):
4G: Can manage about ~100,000 devices per km².
5G: Can handle up to 1 million devices per km².
This allows for:
Industrial IoT (like smart factories and predictive maintenance).
Smart agriculture with connected sensors covering large areas.
Connected vehicles and V2X communication in modern transport systems.
Network Energy Efficiency
4G: Has moderate energy efficiency.
5G: Achieves up to a 100x improvement in energy efficiency.
Why is this important?
Lowers the cost for each bit transmitted.
Supports sustainable practices and greener telecom infrastructures.
Ensures better battery life for devices, especially IoT ones that need to last for years without being replaced.
Mobility
4G: Offers smooth connectivity at speeds up to 350 km/h (perfect for high-speed trains).
5G: Extends that to 500 km/h, making it perfect for ultra-fast travel scenarios.
That makes 5G ideal for:
High-speed rail connections.
Air-to-ground communications.
Future supersonic or hyperloop systems.
Bandwidth
4G: Features bandwidth up to 20 MHz.
5G: Can go up to 1 GHz.
This broader bandwidth means:
Access to millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies for really high data rates.
Better network slicing options for different services.
Support for massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) antennas.
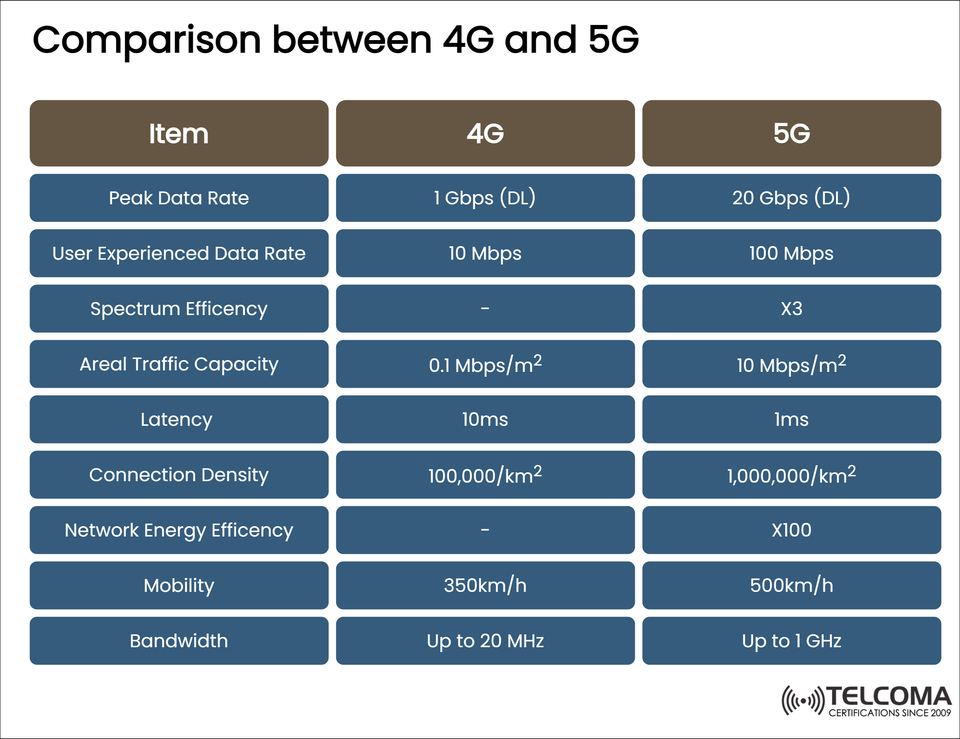
Comparative Table: 4G vs 5G
Item 4G 5G
Peak Data Rate: 1 Gbps (DL) 20 Gbps (DL)
User-Experienced Data Rate: 10 Mbps 100 Mbps
Spectrum Efficiency: - 3x
Areal Traffic Capacity: 0.1 Mbps/m² 10 Mbps/m²
Latency: 10 ms 1 ms
Connection Density: 100,000 devices/km² 1,000,000 devices/km²
Network Energy Efficiency: - 100x
Mobility: Up to 350 km/h Up to 500 km/h
Bandwidth: Up to 20 MHz Up to 1 GHz
Applications Enabled by 5G
While 4G ushered in the mobile broadband age, 5G opens up a whole new realm of possibilities across three main areas:
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB):
Super-fast speeds for users.
8K streaming, AR/VR, immersive media.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC):
Critical services requiring less than 1 ms latency.
Self-driving cars, remote surgeries, industrial automation.
Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC):
Supports billions of IoT devices.
Smart cities, agriculture, logistics, and connected industries.
Challenges in 5G Deployment
Despite the exciting potential, there are several bumps in the road for 5G adoption:
Spectrum availability: Millimeter-wave spectrum has a limited range and needs a lot of infrastructure.
Infrastructure costs: Setting up small cells, fiber backhaul, and massive MIMO raises CAPEX.
Security concerns: With so many IoT devices and APIs, there’s a larger attack surface.
Energy trade-offs: Even though it’s efficient per bit, mmWave base stations can consume more overall power.
Conclusion
The leap from 4G LTE to 5G NR is more than just a new generation; it’s a big change in mobile networking. While 4G brought us mobile broadband, 5G makes way for a hyper-connected, low-latency, and scalable digital world.
For those in telecom, the numbers in the comparison table really tell the story: 10x faster user speeds, 100x more device capacity, 100x greater efficiency, and 10x lower latency. These advancements are going to change industries, enable smart cities, and offer experiences that go far beyond what mobile broadband has provided.
As we see 5G roll out across the globe, it’s clear that 5G will be the backbone for future innovations, from self-driving cars to the Internet of Everything (IoE).
