5G Advanced in 3GPP Release 18: The Next Evolution Beyond 5G

5G Advanced in 3GPP Release 18: The Next Phase of 5G Evolution
The 5G journey is moving beyond just faster speeds and reduced latency. With 3GPP Release 18, the telecom sector is stepping into the 5G Advanced era — a crucial evolution that connects our current 5G networks to a future that's all about intelligence, energy efficiency, and being ultra-connected, which will eventually lead to 6G.
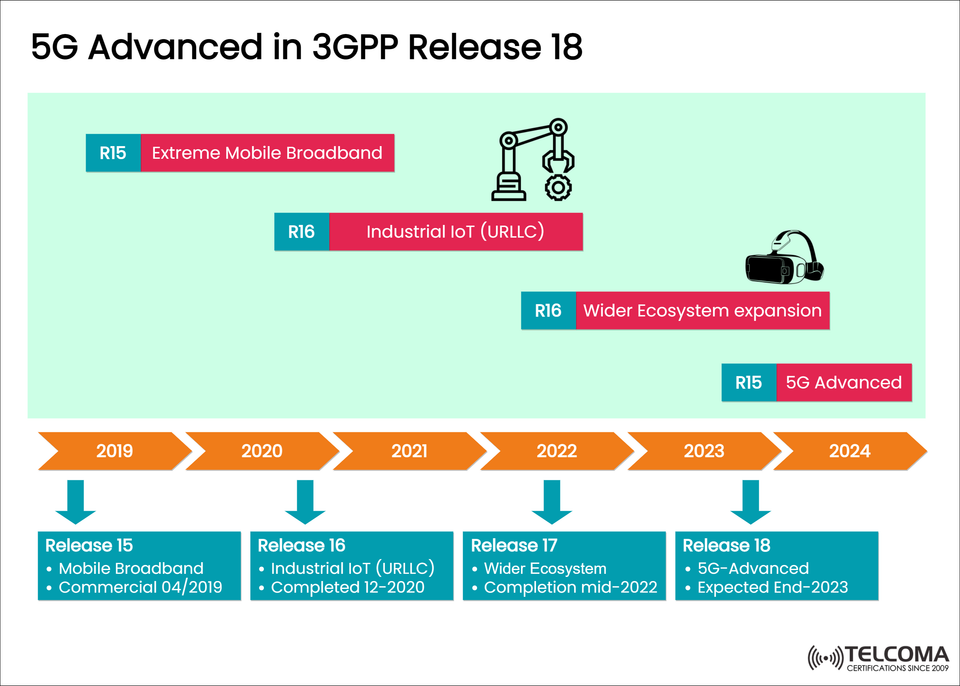
The image above illustrates a roadmap of the 5G evolution from 3GPP Releases 15 to 18, highlighting significant milestones like Extreme Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Industrial IoT (URLLC), ecosystem growth, and the onset of 5G Advanced. Let’s dive into each phase to get a clearer picture of what 5G Advanced really means for the telecom world.
Understanding 3GPP Releases: The Foundation of 5G Evolution
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is the global standards body that defines the specs steering 5G development. Each release brings upgrades, fresh features, and extended capabilities that advance mobile communications.
Here’s how this evolution has played out:
3GPP Release | Key Focus Areas | Timeline
Release 15 | Mobile Broadband (eMBB) | 2019
Release 16 | Industrial IoT (URLLC) | 2020
Release 17 | Wider Ecosystem Expansion | 2022
Release 18 | 5G Advanced | 2023–2024
Release 15: The Foundation – Extreme Mobile Broadband
Release 15, wrapped up in 2019, was the beginning of the commercial rollout of 5G networks around the globe. It set the stage for Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), which brought a significant boost in data speeds and capacity compared to LTE.
Key Features of 3GPP Release 15:
Launch of eMBB: Offered peak data speeds reaching up to 20 Gbps.
Support for Massive MIMO and Beamforming: Enhanced spectral efficiency.
OFDMA-based 5G NR Air Interface: Allowed more flexible spectrum use.
Standalone (SA) and Non-Standalone (NSA) Architectures: Facilitated dual connectivity with LTE.
Impact:
Release 15 was a game changer for global 5G adoption, enabling high-speed internet, HD video streaming, AR/VR applications, and super-fast mobile broadband experiences.
Release 16: Expanding to Industrial IoT (URLLC)
3GPP Release 16, completed in December 2020, took 5G further by moving into industrial applications. This marked the start of 5G’s role in Industry 4.0.
Key Focus – URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication):
URLLC guarantees extremely low latency (down to 1 ms) and high reliability, which is crucial for critical operations like factory automation, self-driving cars, and remote surgeries.
Enhancements in Release 16:
Industrial IoT (IIoT): Support for time-sensitive networking (TSN).
Private 5G Networks: Customized for businesses and industrial applications.
V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) Communication: Enabled cooperative and self-driving technology.
Enhanced Positioning: Boosted location accuracy to within centimeters.
Energy Efficiency Improvements: New power-saving features were introduced.
Impact:
Release 16 shifted 5G from a consumer-focused tech to a robust industrial-grade network, driving automation and smart manufacturing.
Release 17: Wider Ecosystem Expansion
3GPP Release 17, completed in mid-2022, aimed at broadening the 5G ecosystem and increasing flexibility for new devices and environments.
This phase was all about inclusivity — extending 5G into non-traditional sectors, including satellite communications, non-terrestrial networks (NTN), and massive IoT applications.
Key Features of Release 17:
Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN): Merging satellite links with 5G for global coverage.
RedCap (Reduced Capability) Devices: Introduced cost-effective IoT devices suitable for wearables and sensors.
Better Positioning and Mobility: Enhanced management for drones and connected vehicles.
Multicast and Broadcast Services: Aimed at public safety and entertainment.
Network Energy Efficiency: Emphasis on sustainable operation and reducing carbon output.
Impact:
Release 17 expanded the 5G ecosystem by connecting more devices — from satellites to smart sensors — creating a more seamless communication landscape that covers land, sea, and air.
Release 18: The Dawn of 5G Advanced
3GPP Release 18, expected to wrap up by the end of 2023, signifies the shift from “5G” to 5G Advanced — a significant leap forward that enhances intelligence, efficiency, and network flexibility.
5G Advanced isn’t a new generation; rather, it’s an evolutionary step within 5G, laying the groundwork for 6G. It builds upon the previous releases to offer smarter, more energy-efficient, AI-driven capabilities.
Key Pillars of 5G Advanced (Release 18):
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB++)
Multi-Gbps speeds and vast capacity.
Improved spectral efficiency through advanced MIMO and beam management.
Integration of sub-6 GHz and mmWave for smooth performance.
- Intelligent Network Automation and AI Integration
AI/ML-driven optimization for network slicing, scheduling, and beamforming.
Predictive resource management that cuts down on latency and energy use.
- Advanced Positioning and Sensing
Sub-centimeter-level accuracy in positioning.
5G-based radar and sensing for indoor navigation and autonomous functions.
- Expanded Support for XR and Metaverse Applications
Ultra-low latency and high-throughput for Extended Reality (XR), AR/VR, and holographic communication.
Optimized coordination for uplink and downlink to enhance user experiences.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Smarter sleep modes for base stations and devices.
AI-based load balancing to lessen the carbon footprint.
- Integration with Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN)
Better integration of satellite and 5G for global coverage in hard-to-reach areas.
Smooth handover between terrestrial and non-terrestrial systems.
Key Objectives of 5G Advanced
Objective | Description
AI-driven Networks | Dynamic optimization utilizing real-time data and ML models
Energy Efficiency | Greener and more sustainable 5G deployments
Immersive Media | Support for AR/VR and metaverse-level connectivity
Industrial Automation | Expansion of URLLC and IIoT capabilities
Global Coverage | Integration of satellite networks for universal access
Timeline of 5G Evolution (Releases 15–18)
Year | 3GPP Release | Highlights
2019 | Release 15 | Commercial 5G launch, eMBB
2020 | Release 16 | Industrial IoT, URLLC, private networks
2022 | Release 17 | Broader ecosystem, NTN, RedCap IoT
2023–2024 | Release 18 | 5G Advanced – AI, XR, energy efficiency
5G Advanced vs. Early 5G: What’s Different?
Feature | Early 5G (R15–R17) | 5G Advanced (R18)
Focus | Connectivity & speed | Intelligence & efficiency
Latency | ~5 ms | <1 ms (URLLC enhanced)
AI/ML Integration | Minimal | Deep integration for automation
Energy Efficiency | Limited | Optimized network power control
Coverage | Terrestrial | Global (Terrestrial + NTN)
XR/Metaverse Support | Experimental | Fully optimized
Why 5G Advanced Matters
The shift to 5G Advanced isn’t just about improving performance; it's about changing network intelligence, flexibility, and sustainability. This shift will bring gains for telecom operators, equipment vendors, and businesses all around:
Smarter automation through AI/ML-driven network management.
Sustainability with reduced energy consumption.
Enhanced experiences with XR, holographic communication, and real-time interactivity.
Global reach enabled by terrestrial-satellite integration.
Conclusion
The journey from 3GPP Release 15 to 18 shows how 5G has developed from simple broadband into a smart, adaptable, and industrial-grade communication platform.
With 5G Advanced, we’re stepping into a new age of intelligent connectivity — where networks do more than just connect devices. They learn, adapt, and evolve in real-time.
This release lays the groundwork for 6G, merging AI, IoT, satellite capabilities, and extended reality into one cohesive, sustainable ecosystem. For telecom professionals and innovators, Release 18 isn’t just another point on a timeline — it’s the gateway to the future of connected intelligence.
