5G and IoT: Four Connectivity Segments Driving Industry Digitalization

Introduction: 5G – The Core of IoT
5G is shaking things up across industries with its super-fast, low-latency, and reliable connectivity. Unlike 4G LTE that mainly focused on mobile internet, 5G is built to be a versatile network. It’s structured to support a range of Internet of Things (IoT) applications, from low-energy sensors to critical automation systems.
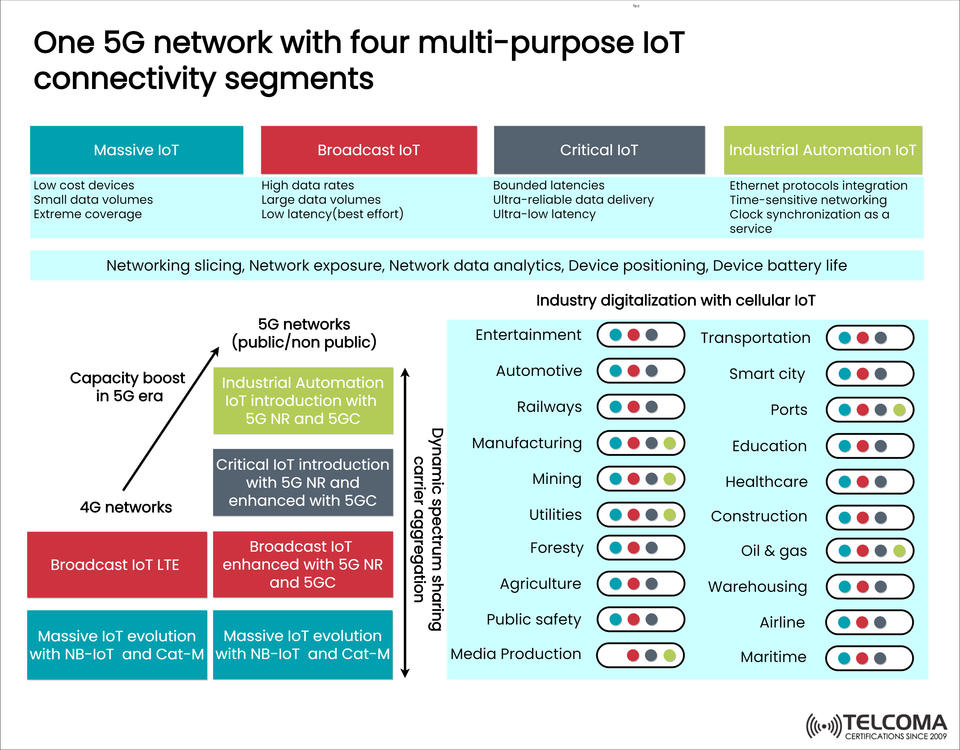
The graphic above shows how one 5G network can manage four different IoT connectivity segments:
Massive IoT
Broadcast IoT
Critical IoT
Industrial Automation IoT
Each of these segments serves its own purpose and helps meet the growing need for digital transformation across sectors like healthcare, transport, utilities, and smart urban development.
The Four IoT Connectivity Segments in 5G
Massive IoT
Massive IoT is all about connecting a huge number of devices, often sending small data packets. It builds on tech like NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) and Cat-M (LTE-M), which are already part of 4G networks.
Key Features: * Affordable devices * Small data requirements * Broad coverage and scalability
Use Cases: * Smart farming (soil sensors, irrigation) * Utility meters (for water and electricity) * City sensors (waste management, parking)
Massive IoT is crucial for scenarios where billions of devices need to stay connected while using as little power as possible.
Broadcast IoT
Broadcast IoT takes advantage of 5G’s capacity to send high data rates to multiple devices at once. Unlike one-to-one communication, broadcast allows info to go out to big groups of devices simultaneously.
Key Features: * High-speed data transfers * Large amounts of data * Low latency (best effort)
Use Cases: * Media distribution and live broadcasts * Software updates for vehicles and IoT devices * Emergency notifications for public safety
5G boosts Broadcast IoT with 5G NR (New Radio) and 5GC (5G Core), making content distribution smoother across various sectors.
Critical IoT
Critical IoT is aimed at applications where reliability and quick response times are key. This is also known as Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), supporting life-critical and real-time industrial needs.
Key Features: * Highly reliable data delivery * Very low latency (as low as 1 ms) * Guaranteed response times
Use Cases: * Remote surgeries and health monitoring * Self-driving vehicles and transport safety * Robotics and factory automation
With 5G NR and advanced 5GC capabilities, Critical IoT ensures that networks are up to the task where failure just isn't an option.
Industrial Automation IoT
Industrial Automation IoT dives deep into critical industries, blending time-sensitive networking (TSN) with Ethernet protocols. This creates the reliable communication needed for industrial control.
Key Features: * Integration with Ethernet protocols * Time-sensitive networking * Clock synchronization services
Use Cases: * Smart factories with robotic assembly lines * Oil and gas monitoring * Smart ports and logistics automation * Coordinating power grids
This segment ensures Industry 4.0 applications thrive on a solid, synchronized, and dependable communication structure.
Transition from 4G to 5G IoT
The diagram also shows how networks are evolving from 4G to 5G:
4G Networks supported: * Massive IoT (via NB-IoT and Cat-M) * Broadcast IoT LTE
5G Enhancements: * Enhanced Broadcast IoT with 5G NR and 5GC * Introduction of Critical and Industrial IoT with 5G NR and 5GC * Ongoing evolution of Massive IoT propelled by 5G’s scalability
This transition ensures that backward compatibility is maintained while significantly boosting capabilities in the 5G landscape, like dynamic spectrum sharing and carrier aggregation.
Industry Digitalization with Cellular IoT
The combination of these four IoT segments paves the way for complete industry digitalization.
Industries benefiting from 5G IoT:
Entertainment & Media: Using Broadcast IoT for premium streaming and live production.
Automotive & Railways: Implementing Critical IoT for self-driving technology, signaling, and safety.
Manufacturing & Mining: Utilizing Industrial Automation IoT for robotic management and real-time monitoring.
Utilities & Agriculture: Relying on Massive IoT for smart grids, water management, and crop surveillance.
Smart Cities & Public Safety: Applying Broadcast IoT for emergency notifications and Massive IoT for environmental monitoring.
Healthcare: Leveraging Critical IoT for telehealth, surgeries, and patient observation.
Transportation & Ports: Using Industrial IoT for logistics, navigation, and smart port operations.
Supporting Technologies in 5G IoT
To enable these various IoT segments, 5G uses a range of advanced technologies:
Network Slicing: Sets up virtual networks tailored for specific IoT services.
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS): Efficiently shares spectrum between 4G and 5G.
Network Exposure & APIs: Allows businesses access to network capabilities.
Data Analytics: Boosts IoT insights through real-time data analysis.
Device Positioning: Enhances location-based services with high precision.
Extended Battery Life: Optimized for IoT devices needing long-term functionality.
Summary Table: Four IoT Connectivity Segments in 5G
IoT Segment Features Typical Use Cases Massive IoT Low cost, small data, extensive coverage Smart agriculture, utilities, smart cities Broadcast IoT High data rates, large data, low latency Media streaming, software updates, public alerts Critical IoT Ultra-low latency, ultra-reliable Remote surgeries, autonomous driving, robotics Industrial Automation IoT TSN, Ethernet integration, synchronization Smart factories, ports, oil & gas, power grids
Why One 5G Network is Enough for IoT
The beauty of 5G is in its multi-use design. Instead of having to create separate networks for each use case, a single 5G network can accommodate all four IoT segments at the same time.
Scalable: From billions of low-energy sensors to high-definition video streaming.
Reliable: Guarantees ultra-low latency for critical needs.
Flexible: Works for both public and private 5G setups.
Future-Proof: Sets the stage for Industry 4.0 and future digital advances.
Conclusion
The 5G IoT connectivity model shows how one network can serve Massive IoT, Broadcast IoT, Critical IoT, and Industrial Automation IoT. This approach caters to varied needs across industries—5G isn’t just faster internet; it lays the groundwork for digital transformation.
For telecom professionals, understanding these connectivity segments is key to designing, optimizing, and rolling out next-gen IoT solutions. As industries move toward automation, AI, and real-time data, 5G will continue to be the backbone of our connected world.
