5G Applications Explained: Enterprise, Government, and Consumer Use Cases
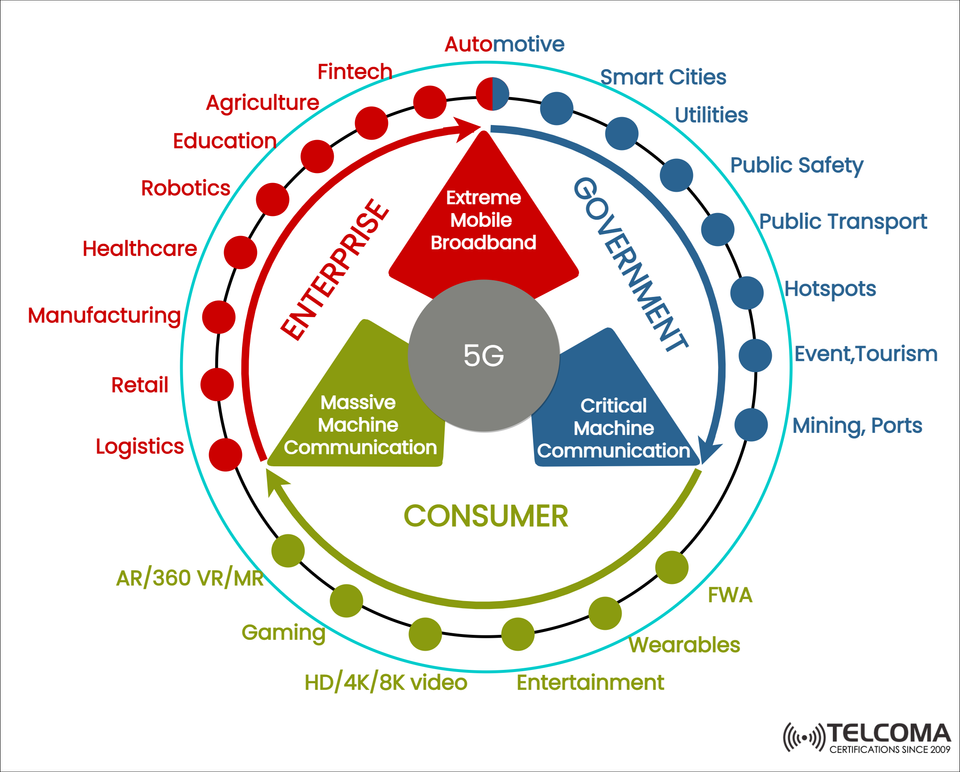

5G isn’t just a step up from 4G—it fundamentally changes how we connect. With features like extreme mobile broadband, critical communications for machines, and support for numerous devices, 5G caters to a host of uses in enterprise, government, and consumer sectors.
The image above from Telcoma shows how these three areas interact with the three main pillars of 5G. Let’s dive deeper to see how 5G influences our interconnected world.
5G in Enterprises: Powering Industry 4.0
Enterprises are among the top winners when it comes to 5G, as it enables automation, data-driven processes, and immediate decision-making.
Main Applications in Enterprises:
Manufacturing: Smart factories that utilize robotics, AI for quality control, and predictive maintenance.
Healthcare: Remote surgeries, telemedicine options, and connected medical devices offering ultra-low latency.
Retail: Improved shopping experiences with AR, real-time inventory updates, and stores without cashiers.
Logistics: Tracking fleets, smart warehousing, and automating supply chain management.
Agriculture: Precision farming using IoT soil sensors, drones, and automated irrigation.
Education: Immersive classrooms using AR/VR tech and platforms for remote learning.
Fintech: Fast, secure transactions and services based on blockchain.
How 5G Benefits Enterprises:
Facilitates Massive Machine Communication (which connects millions of IoT devices).
Provides Extreme Mobile Broadband for rich applications.
Allows for low-latency URLLC suitable for robotics, healthcare, and critical operations.
With these features, 5G speeds up Industry 4.0—bringing together automation, IoT, and AI in the business landscape.
5G in Government: Creating Smarter, Safer Communities
Worldwide, governments are turning to 5G to improve public infrastructure, safety, and services.
Main Applications in Government:
Smart Cities: Intelligent systems for managing traffic, waste, and energy-efficient grids.
Utilities: Remote monitoring for power, water, and gas services to boost efficiency and reliability.
Public Safety: Real-time video surveillance, emergency response systems, and effective disaster management.
Public Transport: Connected buses, trains, and autonomous shuttles providing real-time information.
Mining and Ports: Remote-controlled machines, autonomous vehicles, and sensor safety systems.
Tourism and Events: AR tours, immersive experiences at events, and managing crowds effectively.
Hotspots: Reliable high-speed internet access for both rural and urban areas.
How 5G Benefits Governments:
Critical Machine Communication supports vital tasks like emergency responses.
Network slicing guarantees dedicated lines for public safety, keeping them clear of congestion.
IoT integration permits large-scale monitoring and smart urban planning.
By adopting 5G, governments are building the path to safer, more efficient, and sustainable communities.
5G in Consumer Applications: Transforming Daily Experiences
For everyday users, 5G brings exciting possibilities in entertainment, mobility, and immersive experiences.
Main Applications in Consumer Space:
AR/VR/MR: Augmented, virtual, and mixed reality for gaming, training, and immersive media.
Gaming: Cloud gaming with nearly no lag and ultra-high frame rates.
Video Streaming: Smooth 4K, 8K, or even 360° video without interruptions.
Entertainment: Holographic concerts, interactive sports viewing, and smart home features.
Wearables: Devices for health monitoring, smart glasses, and connected fitness trackers.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): High-speed wireless internet as a substitute for fiber for homes and businesses.
How 5G Benefits Consumers:
Offers extreme mobile broadband for high-quality entertainment.
Lowers latency for real-time applications like gaming and AR.
Supports IoT wearables and smart homes, making daily life more connected.
In conclusion, consumers are set to enjoy faster, smarter, and more engaging digital lives thanks to 5G.
Comparing 5G Use Cases Across Sectors
Sector Key 5G Enablers Example Applications Enterprise eMBB, URLLC, mMTC Smart factories, remote surgeries, AR retail Government URLLC, mMTC, Network Slicing Smart cities, public safety, transport, ports Consumer eMBB, URLLC Gaming, 8K video, wearables, AR/VR
This table highlights how the same 5G pillars function differently in various sectors, ensuring tailored performance for each specific need.
The Core Pillars Behind These Applications
At the core of these applications are three main pillars of 5G:
Extreme Mobile Broadband (eMBB) – Lightning-fast speeds for streaming, gaming, and immersive media.
Critical Machine Communication (URLLC) – Reliable low-latency connections for autonomous driving, healthcare, and public safety.
Massive Machine Communication (mMTC) – Capable of connecting millions of IoT devices for smart cities, agriculture, and industrial IoT.
Every use case—be it in enterprise, government, or consumer markets—depends on one or more of these pillars.
Challenges in 5G Adoption Across Domains
Even with all its potential, 5G rollout isn't without hurdles that telecom experts and policymakers need to tackle:
Infrastructure costs: Installing small cells and fiber backhaul requires significant investment.
Spectrum allocation: Governments have to efficiently manage and license frequency bands.
Security and privacy: With billions of devices connected, the risks to cybersecurity rise.
Interoperability: Making sure different networks and devices can communicate smoothly.
Digital divide: Closing the gaps in connectivity for rural and underserved areas.
These challenges necessitate collaboration among telecom operators, businesses, and government agencies.
The Three Key Aspects of 5G
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
You can expect peak speeds of up to 20 Gbps and a minimum of 100 Mbps at the edge of the cell.
This enables super high-definition streaming, cloud gaming, and engaging VR/AR experiences.
Main applications include 8K streaming, AR/VR/MR, cloud-based productivity tools, and large content delivery networks.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC)
Aiming for 1 ms latency, with an error rate of 10⁻⁹.
It guarantees real-time responses and almost zero packet loss.
Key applications feature remote surgeries, self-driving vehicles, smart energy grids, and industrial robots.
- Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC)
Can handle up to 1 million device connections per square kilometer.
It's designed for energy efficiency, especially for long-term IoT use.
Key applications include smart cities, industrial IoT, agriculture, logistics, and wearable tech.
Conclusion: A Hyperconnected Future with 5G
The image really drives home a key point: 5G impacts every part of society. It helps businesses automate and improve efficiency, allows governments to enhance infrastructure, and gives consumers richer digital experiences.
For enterprises, 5G is essential for Industry 4.0.
For governments, it enables smart cities and better public services.
For consumers, it offers the immersive, connected experiences that are the future.
Understanding these specific applications in different sectors is vital for telecom professionals as they plan networks, innovate services, and gear up for a fully connected future.
5G isn’t just a step forward in telecommunications—it’s the foundation for the digital economy and the intelligent world to come.
