5G Capabilities Explained: eMBB, mIoT, and Mission-Critical Services

The launch of 5G networks is a major turning point for the telecommunications sector. Unlike earlier generations that mainly aimed for faster mobile internet, 5G is intended to cater to a broader range of applications. It brings in exciting features like ultra-low latency, massive IoT connectivity, and incredible data speeds, paving the way for new technologies such as self-driving cars, smart cities, and automated industries.
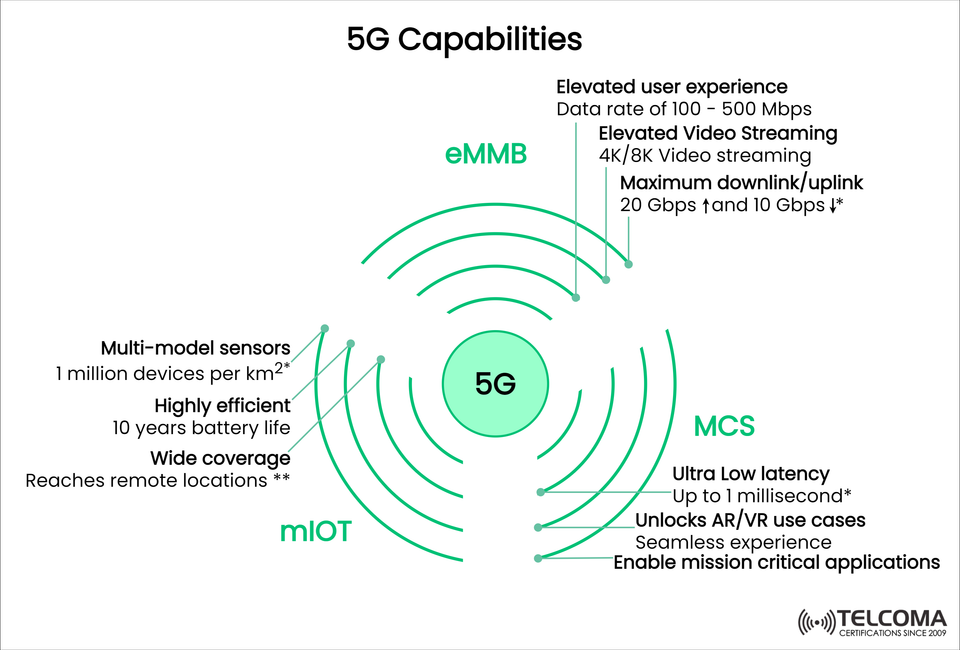
The diagram above showcases the three main pillars of 5G capabilities:
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) – lightning-fast speeds and improved capacity.
mIoT (Massive Internet of Things) – connecting billions of devices.
MCS (Mission-Critical Services) – ultra-reliable communication with low latency.
Let’s dive deeper into each of these to see how 5G is changing the landscape of telecommunications.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
One of the most noticeable upgrades with 5G is the improvement in mobile broadband performance. Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) increases network capacity and provides data rates that are significantly higher than what 4G LTE can offer.
Key Capabilities of eMBB
Improved User Experience: Average data speeds between 100 Mbps and 500 Mbps, making streaming, browsing, and downloads much smoother.
Ultra-HD Video Streaming: Can handle 4K and 8K video streaming with minimal buffering, creating rich media experiences.
Peak Data Rates: Maximum 20 Gbps downlink and 10 Gbps uplink, perfect for demanding applications like cloud gaming, AR/VR, and remote teamwork.
Real-World Applications
Immersive Gaming: Cloud-based gaming experiences with zero lag.
Smart Cities: High-definition video surveillance for safety and traffic management.
Remote Education & Work: Smooth video conferencing and collaborative tools.
In a nutshell, eMBB fuels the data-hungry applications we see in today’s world.
Massive Internet of Things (mIoT)
The second pillar of 5G capabilities is massive IoT (mIoT), allowing connections of billions of low-power devices over large areas. Unlike traditional mobile broadband, mIoT emphasizes scale, efficiency, and range.
Key Capabilities of mIoT
High Device Density: Can support up to 1 million devices per km², making it ideal for crowded urban areas or large industrial sites.
Energy Efficiency: Devices can run for up to 10 years on a single battery, cutting down on maintenance and promoting long-term use.
Wide Coverage: Extends to remote and hard-to-reach areas, improving connectivity in rural regions and enabling extensive sensor networks.
Real-World Applications
Smart Agriculture: Soil sensors, weather monitors, and livestock trackers to enhance crop yield.
Smart Homes: Connected devices, wearables, and energy-efficient solutions.
Industry 4.0: IoT devices and sensors that facilitate predictive maintenance and automation.
Healthcare: Remote monitoring tools that constantly gather patient information.
Through mIoT, 5G connects not just people but also the digital ecosystem of devices.
Mission-Critical Services (MCS)
One of the most groundbreaking features of 5G is its capacity to support mission-critical services that require ultra-reliable, low-latency communications (URLLC).
Key Capabilities of MCS
Ultra-Low Latency: Latency can go down to as low as 1 millisecond, guaranteeing almost instantaneous communication.
Reliability: High reliability makes it suitable for critical applications in healthcare and self-driving technologies.
Support for AR/VR: Enables immersive augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) with smooth interaction.
Mission-Critical Applications: Ideal for cases where failure is not an option, like remote surgeries, autonomous driving, and robotic automation.
Real-World Applications
Autonomous Vehicles: Real-time communication between cars and infrastructure to avert accidents.
Remote Surgery: Surgeons can operate using robotic tools from afar.
Smart Grids: Dependable communication for energy management and distribution.
Public Safety: Real-time video streaming for emergency and disaster response services.
With MCS, 5G goes beyond just entertainment, enabling vital and mission-critical innovations.
Comparison of 5G Capabilities
Capability | eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) | mIoT (Massive IoT) | MCS (Mission-Critical Services)
Focus | Speed and capacity | Device density and efficiency | Reliability and low latency
Data Rate | Up to 20 Gbps | Low | Variable (depends on application)
Latency | 10–20 ms | Non-critical | ~1 ms
Use Cases | Streaming, gaming, cloud services | Smart cities, agriculture, IoT sensors | Autonomous vehicles, healthcare, robotics
Why 5G Capabilities Matter
The strength of 5G lies in its ability to meet various needs all at once:
Consumers get faster internet and immersive media experiences.
Businesses gain from IoT-driven efficiencies.
Critical sectors like healthcare, transport, and energy benefit from dependable, real-time connectivity.
This adaptability makes 5G not just an upgrade but a transformative platform for innovation across multiple industries.
Challenges in Realizing 5G Capabilities
Even with all its potential, rolling out 5G brings some hurdles:
Infrastructure Costs: Significant investment in small cells, fiber backhaul, and spectrum is needed.
Device Ecosystem: Ensuring a wide availability of 5G-compatible devices is essential.
Spectrum Allocation: Balancing high-band (mmWave) and low-band frequencies for optimal coverage and performance.
Security: Protecting billions of IoT devices from cyber threats is a major consideration.
Tackling these challenges is crucial for fully unleashing 5G’s potential.
Future Outlook
Looking forward, 5G is expected to evolve with 6G advancements. Features such as AI-driven networks, terahertz frequencies, and holographic communications will build on the foundation of 5G capabilities.
eMBB will likely deliver even faster speeds with 6G.
mIoT will grow to support trillions of devices worldwide.
MCS will cater to even more demanding uses, like fully automated smart cities.
The combination of these capabilities will transform our digital society, industry, and economy.
Conclusion
The three pillars of 5G capabilities—eMBB, mIoT, and MCS—signify a significant leap forward in connectivity.
eMBB offers lightning-fast data rates and immersive media experiences.
mIoT connects billions of devices while being efficient and widely accessible.
MCS provides ultra-reliable, low-latency communication for essential applications.
Together, they make 5G a versatile platform that caters to consumers, businesses, and critical sectors alike.
