5G Core Network Automation: Inside NWDAF, AnLF, and MTLF for Intelligent 5G Analytics

Introduction: Entering the Era of Autonomous 5G Networks
5G isn’t just about faster speeds and lower latency—it's a whole new level of network intelligence and automation. With the surge of connected devices, varied network slices, and the demand for real-time services, operators really need some AI-driven automation integrated into the 5G Core.
This automation is powered by the Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF), which is a critical part laid out by 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) in Release 17 and 18.
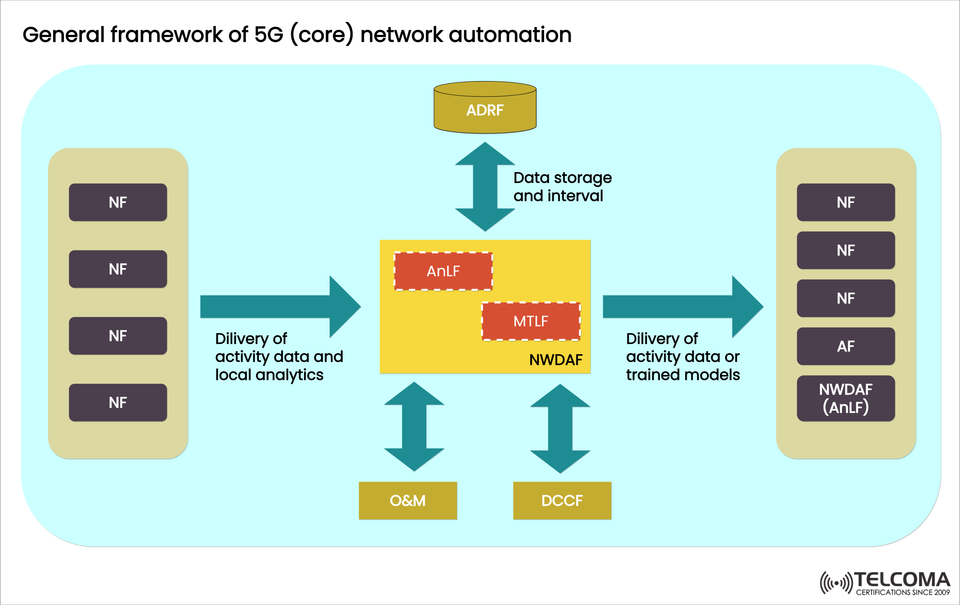
The illustration from Telcoma above gives a clear view of the General Framework for 5G Core Network Automation, showing how NWDAF links up with various data sources, analytics functions, and management systems to provide real-time insights and smart control.
What is 5G Network Automation?
5G network automation is about leveraging AI/ML analytics, policy control, and orchestration to manage network operations automatically.
The goals here are pretty straightforward:
Cut down on manual setup and human mistakes.
Boost network efficiency and resource usage.
Create self-healing, self-optimizing, and self-configuring networks.
This automation happens in a closed-loop system where data is gathered, analyzed, and acted on—with NWDAF at the heart of it all.
Getting to Know NWDAF (Network Data Analytics Function)
Definition
NWDAF is a standardized function from 3GPP that provides data analytics services to other Network Functions (NFs) and Application Functions (AFs) within the 5G Core.
Think of it as the brain behind 5G network automation, processing raw data, doing analytics, and providing actionable insights.
Core Responsibilities
Gathering activity and performance data from different NFs.
Conducting AI/ML-based analytics on that data.
Delivering analytics results or trained models back to other NFs or external systems.
Facilitating real-time decision-making and network optimization.
NWDAF’s Internal Components
Inside NWDAF, there are two key sub-functions that keep everything running smoothly:
Component Full Form Primary Function An LF Analytics Logical Function Handles data analysis, statistical aggregation, and model execution. MTLF Model Training Logical Function Trains AI/ML models using historical or real-time data for forecasting.
a) AnLF (Analytics Logical Function)
The AnLF focuses on:
Running AI/ML models to extract insights.
Doing both predictive and descriptive analytics.
Providing analytics results like KPIs, congestion forecasts, or mobility trends to other NFs or AFs.
Some examples of what it does:
Predicting where users (UEs) are likely to move.
Spotting unusual traffic patterns.
Forecasting how network slices will be used.
b) MTLF (Model Training Logical Function)
The MTLF is all about training and fine-tuning machine learning models. It pulls data from the Analytics Data Repository Function (ADRF) and real-time inputs from network functions to build solid predictive models.
Key tasks include:
Training AI/ML models based on past data.
Sharing those trained models with AnLF for inference.
Continually updating models to keep them precise and relevant.
This teamwork between AnLF and MTLF allows for ongoing learning and dynamic analytics, which are essential for real-time network intelligence.
The Role of ADRF (Analytics Data Repository Function)
The ADRF serves as the data hub for NWDAF. It keeps raw network data, interim analytics results, and trained AI/ML models.
In the diagram, ADRF is positioned above NWDAF, connected through data storage and retrieval systems to support:
Historical data analysis.
Model retraining and tracking.
Long-term correlation of analytics.
This integration lets NWDAF access both real-time data streams and archived information for thorough analytics.
NWDAF’s External Interactions
NWDAF isn’t working alone—it connects with several entities in the 5G Core and management systems:
EntityInteraction with NWDAFPurposeNetwork Functions (NF)Supply raw activity data and local analyticsFor gathering data and generating insightsApplication Functions (AF)Get analytics or models from NWDAFTo optimize services and applicationsO&M (Operations and Maintenance)Accesses analytics insightsAids in fault detection and network optimizationDCCF (Data Collection and Coordination Function)Manages data streamsFor efficient data aggregationADRFStores and retrieves data/modelsEnsures continuity in analyticsExternal NWDAFsShare analytics and modelsFor collaborative learning and coordination
Data and Analytics Flow in the NWDAF Framework
The overall workflow in 5G Core Network Automation looks like this:
Data Collection: * Network Functions (NF) send in activity data (usage metrics, performance stats, faults). * Local analytics or event logs might also be part of this.
Data Coordination: * The DCCF brings together and manages various data sources for NWDAF.
Data Storage and Model Management: * The ADRF keeps collected data and trained models for future use.
Model Training: * The MTLF trains AI/ML models using ADRF data.
Analytics Execution: * The AnLF runs the trained models to produce insights or forecasts.
Insight Delivery: * NWDAF sends back analytics results or trained models to NFs, AFs, and O&M systems for automation and optimization.
This closed-loop system allows for ongoing feedback and improvement, which is crucial for achieving a self-optimizing network.
Key Use Cases for NWDAF in 5G Core Automation
Use CaseDescriptionBenefitCongestion PredictionAnticipates network load and smoothly reroutes traffic.Stops service issues before they start.UE Mobility AnalyticsPredicts user movement patterns to manage sessions better.Boosts QoS and reliability.Network Slice OptimizationAnalyzes how slices are used to adjust resources on the fly.Maximizes efficiency and meets SLAs.Anomaly DetectionIdentifies unusual KPIs or behaviors using ML models.Improves fault response and enhances security.QoE EnhancementKeeps an eye on user experience metrics to optimize them.Ensures consistent service quality.
Distributed NWDAF and Multi-Level Analytics
In more advanced 5G setups, multiple NWDAFs might be at work across various network domains. The diagram hints at this distributed operation:
Local NWDAFs take care of edge or regional analytics.
Central NWDAFs gather global insights for coordination.
This model allows for:
Scalable solutions for larger networks.
Low latency for quick decisions at the edge.
Federated learning, where trained models are shared instead of raw data, enhancing privacy.
How NWDAF Integrates with O&M and DCCF
O&M (Operations and Maintenance)
Gains real-time analytics to:
Identify anomalies.
Automate fault management.
Optimize resource distribution.
DCCF (Data Collection and Coordination Function)
Acts as a data broker, ensuring NWDAF only receives relevant, organized, and time-aligned data, which boosts efficiency and data integrity.
Advantages of NWDAF-Driven 5G Network Automation
Operational Efficiency
Cuts back on manual operations.
Facilitates AI-driven decision-making loops.
Automates KPI tracking and alerts.
Predictive Intelligence
Spots and solves network problems before they impact users.
Dynamically optimizes traffic and slice usage.
Scalable Automation
Supports distributed NWDAFs across core and edge levels.
Encourages federated AI/ML analytics.
Enhanced QoE and Reliability
Ensures stable user experiences, no matter the network conditions.
The Future of NWDAF in 5G and Beyond
With 3GPP Release 18 and beyond, NWDAF’s capabilities are set to level up:
Closed-loop automation alongside PCF (Policy Control Function).
Cross-domain data sharing among RAN, Core, and Edge NWDAFs.
Linkages with Non-3GPP networks and 6G intelligent automation frameworks.
As we move into the 6G era, NWDAF’s successors will probably morph into AI-native network management systems, capable of autonomous service orchestration and intelligent decision-making.
Conclusion
The general framework of 5G Core Network Automation—driven by NWDAF, AnLF, and MTLF—marks a significant step forward in telecom intelligence. By blending data analytics, AI model training, and automated decision-making, NWDAF is turning the 5G Core into a self-aware, self-optimizing network.
This automation framework not only boosts operational efficiency and service reliability but also sets the stage for AI-driven 6G networks—where automation isn't just an add-on but the very essence of the network.
