5G Evolution Explained: Technologies, Spectrum, and Future Applications

5G Evolution Breakdown: Tech, Spectrum, and Future Uses
The launch of 5G networks is a big deal in the telecom world, bringing along unmatched speed, capacity, and low latency. But the thing is, 5G is constantly evolving thanks to ongoing research, fresh standards, and cool new applications.
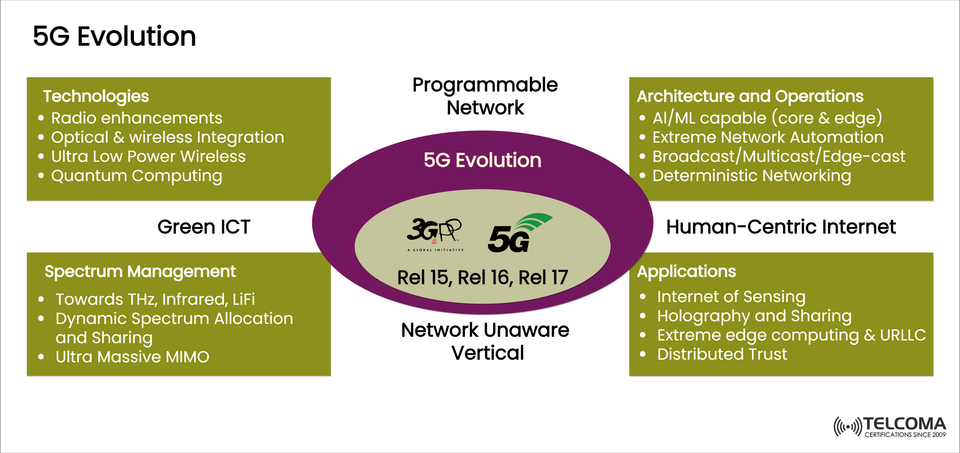
The image above highlights the multi-faceted evolution of 5G across technologies, spectrum management, architectures, and applications, influenced by 3GPP Releases 15, 16, and 17. This article will unpack each of these aspects, helping both pros and enthusiasts grasp the forward-thinking design of 5G.
5G Evolution and 3GPP Releases
At the heart of 5G's development is the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), the worldwide body that sets the standards for 5G.
Release 15: Laid the groundwork for 5G New Radio (NR) and Non-Standalone (NSA) deployment options.
Release 16: Concentrated on ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT), and enhanced vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication.
Release 17: Dived into satellite integration, massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and optimizations for edge computing.
These releases mark a gradual evolution that allows carriers, vendors, and companies to slowly adopt next-gen features.
Tech Innovations Behind 5G Evolution
5G is more than just speeding up the internet; it's about incorporating advanced technologies that lay the groundwork for ultra-connected, smart networks.
Some key advancements include:
Radio Enhancements
Better antenna designs (like Massive MIMO and beamforming)
Improved modulation schemes for boosting throughput.
Optical & Wireless Integration
Merging fiber-optic networks with wireless 5G access to alleviate bottlenecks
Crucial for achieving end-to-end gigabit connectivity.
Ultra Low Power Wireless
Allows IoT and sensor networks to function for years without needing a battery change.
Quantum Computing (Future Perspective)
A longer-term vision of using quantum algorithms for enhanced network optimization, security, and cryptography.
These innovations guarantee that 5G is evolving into a programmable, smart, and scalable network.
Spectrum Management in 5G Evolution
Spectrum is essential for any mobile network, and 5G evolution focuses on flexible, efficient spectrum use to keep up with rising data demands.
Key Elements of Spectrum Management:
Exploring THz, Infrared, and LiFi
Pushing communications beyond standard RF into terahertz (THz) bands, infrared, and light-based (LiFi) technologies
This could lead to ultra-high data rates in specialized environments.
Dynamic Spectrum Allocation and Sharing
5G supports dynamic allocation, allowing spectrum sharing across different services, operators, and cases
For instance, CBRS in the U.S. enables shared access models.
Ultra Massive MIMO
Large-scale antenna arrays boost spectral efficiency
This allows for servicing thousands of devices at once in busy urban areas.
Good spectrum management ensures that 5G networks stay scalable, adaptable, and high-performing, even in crowded areas.
Architecture and Operations in Future 5G
The structure of 5G networks is becoming smarter, more automated, and adaptable. The diagram highlights four important areas:
AI/ML Capable Networks (Core & Edge)
AI/ML algorithms built into both the 5G Core and edge nodes help optimize traffic routing, spotting anomalies, and improving energy efficiency.
Extreme Network Automation
From setup to fault management, networks are moving towards zero-touch automation, cutting down on human involvement.
Broadcast/Multicast/Edge-cast
This enables content delivery to go beyond just one-on-one (unicast) to one-to-many, easing the burden during live streams, software updates, or emergency alerts.
Deterministic Networking
Offers predictable latency and reliability, crucial for industrial automation, remote surgeries, and vehicle networks.
This change is turning 5G into a programmable network fabric, capable of supporting both everyday users and enterprise-level applications.
Applications of 5G Evolution
Beyond just faster downloads, 5G opens the door to transformative applications that are shaping a human-centered internet.
Highlighted in the diagram are:
Internet of Sensing
Takes IoT a step further by embedding sensing abilities into the network
Valuable for smart cities, environmental monitoring, and healthcare IoT.
Holography and Sharing
The ultra-high bandwidth of 5G supports real-time 3D holographic communication for remote meetings, education, and entertainment.
Extreme Edge Computing & URLLC
Processing data closer to the user (at the edge) guarantees ultra-reliable, low-latency communications
This is essential for autonomous driving, industrial robots, and critical systems.
Distributed Trust
By integrating blockchain and distributed ledger technologies with 5G, we can enhance security, trust, and decentralized applications.
These applications point towards a human-centric digital ecosystem where 5G drives real-world change.
Green ICT and Sustainability in 5G Evolution
A key trend in 5G evolution is Green ICT (Information and Communication Technology), which prioritizes energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Ultra Low Power Wireless and dynamic spectrum allocation help cut down on energy waste.
Network automation and AI/ML optimization help decrease resource consumption.
5G-powered smart grids and IoT systems align with global sustainability goals.
Green ICT makes sure that 5G isn't just high-tech but also in sync with climate-conscious innovation.
Comparative Table: 5G Evolution Across Key Domains
Domain Key Features Benefits Technologies Radio Enhancements, Optical Integration, Quantum Computing Faster, smarter, future-proof networks Spectrum THz, LiFi, Dynamic Allocation, Massive MIMO Higher capacity, flexible usage Architecture AI/ML, Automation, Deterministic Networking Intelligent, reliable, zero-touch ops Applications IoS, Holography, URLLC, Distributed Trust Human-centric, immersive, mission-critical Green ICT Energy efficiency, sustainable design Eco-friendly telecom infrastructure
Conclusion: The Path Forward for 5G Evolution
The evolution of 5G is far more than just rolling out high-speed mobile broadband. With advancements in tech, spectrum, architecture, and applications, 5G is becoming the backbone of a genuinely programmable, intelligent, and human-focused internet.
3GPP Releases 15, 16, and 17 have already set the stage, and future releases are likely to explore even deeper into AI-driven networks, terahertz communication, and quantum security.
Applications like holographic communication, distributed trust systems, and industrial automation are set to redefine various industries.
By incorporating Green ICT, the telecom sector is ensuring that 5G is not just powerful but also sustainable.
For telecom experts and fans, grasping these evolving aspects of 5G is essential for gearing up for a future where connectivity fuels every facet of life.
