5G IoT: Exploring RedCap, eMTC, and NB-IoT Solutions for Diverse Use Cases

5G IoT: Tailored Solutions for Various Use Cases
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing the game for how industries, cities, and people interact with technology. With the rise of IoT devices, there’s a growing need for connectivity solutions that juggle data rate, bandwidth, power efficiency, and latency.
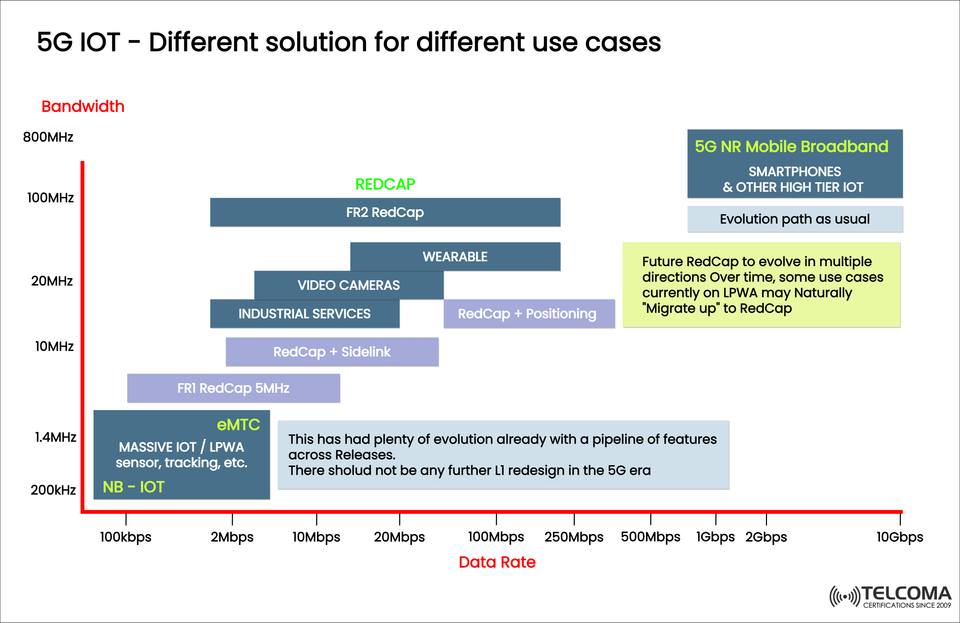
Take a look at the image from Telcoma Global; it beautifully demonstrates how 5G IoT provides multiple connectivity options designed for different scenarios—from massive IoT sensors to wearables, industrial automation, and mobile broadband.
In this blog, we’ll dive into how 5G IoT offers this flexibility through NB-IoT, eMTC, RedCap, and 5G NR broadband, highlighting where each technology fits in the broader 5G ecosystem.
The 5G IoT Landscape: One Network, Many Needs
A major challenge for 5G IoT is catering to its varied use cases. On one side, you’ve got simple sensors that send small data packets now and then (think smart meters), while on the other, there are industrial robots and wearables that need high reliability and decent throughput.
5G IoT tackles this variety with a layered connectivity model, where each tech segment serves a unique purpose based on bandwidth and data rate.
Key Parameters Defining 5G IoT Categories
Bandwidth: The radio spectrum the device uses (ranging from 200 kHz to hundreds of MHz).
Data Rate: How much data can be sent in a second.
Power Consumption: Extremely important for devices that run on batteries.
Coverage and Range: How far the signal can reach in rural, indoor, or densely populated areas.
These considerations are foundational in shaping different IoT categories under 5G.
- NB-IoT and eMTC: The Backbone of Massive IoT
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
Bandwidth: ~200 kHz
Data Rate: Up to 100 kbps
Use Case: Massive IoT, sensors, and LPWA (Low Power Wide Area) devices
NB-IoT was crafted for massive, low-throughput devices like:
Smart meters
Asset trackers
Environmental sensors
Utility monitoring
NB-IoT stands out with its ability to penetrate deep and maintain ultra-low power consumption, making it perfect for devices that only send small data packets sporadically.
eMTC (Enhanced Machine-Type Communication)
Bandwidth: Up to 1.4 MHz
Data Rate: Up to 1 Mbps
Use Case: Tracking, telemetry, and moderate data IoT devices
eMTC strikes a balance between NB-IoT and broadband, providing support for mobility, voice, and firmware updates, which NB-IoT doesn’t offer.
Typical Applications:
Fleet tracking
Smart city lighting
Wearable health monitors
As noted in the image, both NB-IoT and eMTC have advanced significantly with features evolving across multiple 3GPP releases.
As stated by Telcoma, “There shouldn’t be any more L1 redesign in the 5G era,” emphasizing that these technologies are stable and standardized now.
RedCap: Bridging IoT and Broadband
What is RedCap?
Reduced Capability (RedCap), introduced in 3GPP Release 17, is the link between massive IoT (NB-IoT/eMTC) and high-performance 5G NR broadband.
It’s designed for devices that:
Require higher throughput than NB-IoT,
But don’t need full 5G NR capabilities (like smartphones).
Key Characteristics of RedCap
Parameter RedCap (FR1)RedCap (FR2)Bandwidth5–20 MHzUp to 100 MHz Data Rate10 Mbps – 250 Mbps100 Mbps – 1 Gbps Latency<10 ms<5 ms Target Devices Wearables, cameras, sensors AR/VR devices, advanced IoT
Use Cases Highlighted in the Image
Industrial Services: RedCap enhances connected machinery with real-time control and monitoring.
Video Cameras: It supports video streaming for surveillance or automation without high data rates.
Wearables: Fitness trackers, medical monitors, and AR/VR headsets benefit from RedCap’s energy efficiency and low latency.
Positioning and Sidelink: 5G-Advanced takes RedCap further to include RedCap + Positioning and RedCap + Sidelink, supporting device-to-device communication and location accuracy.
This positions RedCap as a versatile solution for mid-tier IoT devices going forward.
5G NR Mobile Broadband: Premium IoT and Smartphones
At the high-end of the spectrum is 5G NR Mobile Broadband, which powers smartphones, laptops, and high-performance IoT devices.
Key Features
Bandwidth: Up to 800 MHz
Data Rate: Up to 10 Gbps
Latency: <1 ms
Use Cases: AR/VR, 8K streaming, connected vehicles, industrial robotics
This segment is following the “evolution path as usual,” focusing on increasing bandwidth and throughput instead of making things simpler.
In the context of IoT, high-end robotics, AI-driven analytics, and real-time video systems rely heavily on these broadband capabilities.
Evolution Path: RedCap as the Logical Migration Point
The diagram includes an important note:
“Future RedCap to evolve in multiple directions. Over time, some use cases currently on LPWA may naturally ‘migrate up’ to RedCap.”
This signals a strategic evolution:
As IoT needs grow (like higher video resolution, lower latency), devices on NB-IoT or eMTC might phase into RedCap.
RedCap acts as a scalable bridge, handling diverse mid-tier IoT scenarios without overloading the network.
This transition ensures continuity and spectrum efficiency in the 5G era, preventing fragmentation.
Why RedCap is a Game-Changer for 5G IoT
a) Balanced Performance
RedCap sits right between low-cost IoT and full 5G NR, perfect for applications that need medium data rates and long battery life.
b) Simplified Hardware
Devices using RedCap have fewer antennas, reduced MIMO layers, and lower power amplifiers, which helps keep manufacturing costs down.
c) Spectrum Efficiency
It works with both FR1 and FR2 bands, ensuring smooth deployment across current 5G infrastructure.
d) Future Scalability
With 5G-Advanced (Release 18), RedCap will see enhancements, including positioning, sidelink, and AI-driven optimization, ensuring it stays adaptable for the future.
The Road Ahead: 5G-Advanced and Beyond
As we move toward 5G-Advanced (Release 18 and beyond), we’ll see several upgrades that could reshape IoT connectivity:
RedCap Evolution: Integration with sidelink and positioning for cooperative sensing.
LPWA Coexistence: NB-IoT and eMTC will still support low-cost sensors.
AI-Based Resource Management: Smarter allocation of spectrum for IoT traffic.
6G Outlook: Hybrid RedCap and NTN (Non-Terrestrial Networks) for worldwide IoT coverage.
These advancements promise to bring together terrestrial, aerial, and satellite IoT systems under one cohesive intelligent network.
Conclusion
The 5G ecosystem isn’t one-size-fits-all; it’s a multi-layered architecture designed to meet diverse IoT needs.
From NB-IoT’s ultra-low-power sensors to RedCap’s high-performance industrial IoT and full 5G broadband applications, each layer has its own crucial role.
The diagram from Telcoma captures this evolution well, showing how bandwidth, data rate, and device complexity come together to serve various IoT cases.
As 5G-Advanced and RedCap develop further, we can expect a seamless integration of massive, critical, and broadband IoT, leading towards a truly connected intelligent world.
