5G IoT: Tailored Solutions for Different Use Cases – From NB-IoT to RedCap and 5G NR
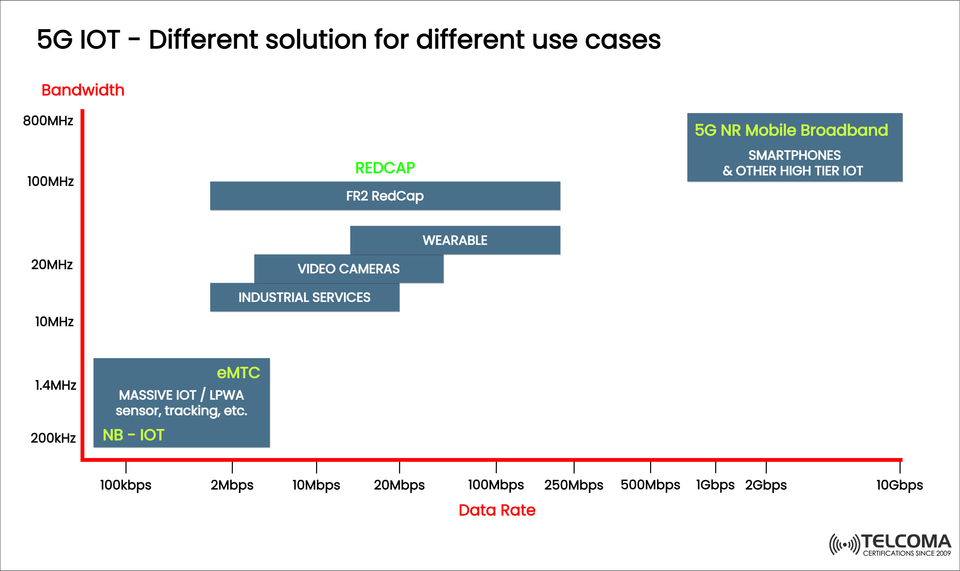

5G IoT – Various Solutions for Different Use Cases
The fifth generation of mobile networks, 5G, goes beyond just faster speeds; it’s all about smarter and more adaptable connectivity. One of the biggest changes is how it supports IoT (Internet of Things) across an array of industries and devices. From low-power sensors to high-bandwidth mobile broadband, 5G lays out various connectivity options designed for specific performance, power, and budget needs.
The visual above gives an overview of how each 5G IoT category—NB-IoT, eMTC, RedCap, and 5G NR Mobile Broadband—fits into the larger ecosystem, based on data rate (horizontal axis) and bandwidth (vertical axis).
Understanding the 5G IoT Landscape
Unlike earlier network generations, 5G doesn’t stick to just one connectivity model. Instead, it takes a flexible and scalable approach to cater to everything from tiny battery-operated devices to data-heavy industrial applications.
Chart Key Dimensions:
Data Rate (x-axis): Shows how much data a device can send or receive per second—ranging from kilobits to gigabits.
Bandwidth (y-axis): Reflects the spectrum range each technology uses to meet its target data rate.
These factors help define how each 5G IoT tech serves a specific niche.
- NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT): Efficient Connectivity for Large IoT Networks
NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things) is found at the lower-left corner of the chart, indicating its low bandwidth (200 kHz) and low data rate (up to hundreds of kbps). It’s tailored for massive IoT (mIoT) applications that involve a lot of low-power devices sending small data packets from time to time.
NB-IoT Key Features:
Bandwidth: ~200 kHz
Data Rate: Up to 250 kbps
Power Efficiency: Super high (battery life can reach up to 10 years)
Coverage: Excellent indoor and rural reach
Latency: Great for applications that can tolerate delays
NB-IoT Applications:
Smart meters (for electricity, gas, and water)
Environmental monitoring
Smart parking and waste management
Tracking for agriculture and livestock
Low-frequency industrial sensors
NB-IoT uses a licensed spectrum, which means security, reliability, and consistent performance—a big plus for critical infrastructure.
eMTC (Enhanced Machine-Type Communication): Flexibility and Mobility
Moving up the scale, we have eMTC (Enhanced Machine-Type Communication), also known as LTE-M. It operates with wider bandwidth (1.4 MHz) and accommodates higher data rates (up to 2 Mbps), filling the gap between low-power NB-IoT and the quicker RedCap.
eMTC Key Features:
Bandwidth: ~1.4 MHz
Data Rate: Up to 2 Mbps
Mobility: Supports cell handovers, perfect for moving devices
Latency: Lower than NB-IoT, good for interactive uses
Power Efficiency: High, but a bit less than NB-IoT
eMTC Applications:
Fleet management and asset tracking
Health monitoring devices and wearables
Connected vehicles
Industrial IoT (sensors, actuators, control systems)
eMTC balances mobility, coverage, and performance, making it a popular option for mobile IoT operations.
RedCap (Reduced Capability NR): Connecting IoT to Full 5G
In the center of the image is RedCap (Reduced Capability NR)—an important step in the journey of 5G IoT. Launched with 3GPP Release 17, RedCap is a simplified version of 5G NR (New Radio), tailored for mid-range IoT applications.
The Importance of RedCap
While full 5G NR modems are powerful, they can be complex and pricey. RedCap cuts down on this complexity—offering the benefits of 5G (like low latency, better spectral efficiency, and scalability) while keeping costs and power consumption manageable.
RedCap Technical Profile:
Parameter RedCap SpecificationBandwidth5–20 MHz (FR1), up to 100 MHz (FR2)Data Rate10 Mbps – 500 MbpsLatency<10 msDuplexFDD/TDD supportedComplexity~50% less than full 5G NR devices
RedCap Applications:
Industrial Services: For automation, robotics, and monitoring manufacturing processes
Video Cameras: Medium-bitrate streaming for surveillance and analytics
Wearables: Smartwatches, AR/VR glasses, and fitness trackers
FR2 RedCap: Advanced tasks at mmWave frequencies, like ultra-HD sensors
RedCap successfully links low-power IoT (NB-IoT/eMTC) with high-performance 5G broadband, paving the way for new possibilities with mid-tier connected devices.
5G NR Mobile Broadband: The High-Performance Category
At the far right of the chart, we find 5G NR Mobile Broadband (MBB)—the top-tier option meant for smartphones, high-end IoT devices, and data-heavy applications. It provides multi-gigabit speeds and ultra-low latency, accommodating advanced uses demanding a lot of throughput.
Key Features:
Bandwidth: Up to 800 MHz (especially in mmWave frequencies)
Data Rate: Multi-Gbps (up to 10 Gbps)
Latency: <1 ms (in URLLC setups)
Spectral Efficiency: Much higher than LTE
5G NR Applications:
Smartphones and tablets
High-end IoT (autonomous vehicles, drones, AR/VR)
Smart manufacturing and robotics
Real-time control systems
Immersive media (8K streaming, holographic communication)
5G NR symbolizes the “evolution path as usual”—carrying on the tradition of mobile broadband while integrating IoT applications that require top-notch reliability and performance.
Comparative Overview of 5G IoT Technologies
Technology Bandwidth Data Rate Latency Power Efficiency Key ApplicationsNB-IoT200 kHz<250 kbps High Ultra High Sensors, smart meters eMTC (LTE-M)1.4 MHz Up to 2 Mbps Medium High Wearables, trackers RedCap (FR1/FR2)5–100 MHz Up to 500 Mbps Low Moderate Industrial IoT, video, AR5G NR MBB100–800 MHz Up to 10 Gbps Ultra Low Low Smartphones, AR/VR, automation
The 5G IoT Evolution
5G introduces a layered IoT framework that grows over time:
NB-IoT and eMTC keep supporting massive and low-power IoT applications.
RedCap broadens the landscape by targeting mid-tier devices that need extra bandwidth without the full 5G complexity.
5G NR MBB caters to premium, high-data-rate applications like autonomous systems and engaging media.
This organized approach ensures that no device or application gets left out. Every use case—from a simple sensor to a self-driving vehicle—has an ideal connectivity layer within the 5G setup.
The Importance of 5G IoT Diversity
The versatility of 5G IoT brings several benefits to industries:
Efficient Resource Use: Each tech utilizes spectrum and power smartly.
Scalability: Networks can handle billions of devices all at once.
Cost-Effectiveness: RedCap and LPWAN solutions lower hardware and subscription costs.
Future-Ready Design: Supports a smooth transition as device needs evolve.
Wrapping Up: One Network, Many Opportunities
The 5G IoT landscape marks a major shift from one-size-fits-all connectivity to customized network designs. By blending NB-IoT, eMTC, RedCap, and 5G NR, operators can offer a continuum of connectivity—from tiny sensors to ultra-fast smart devices—all within the same 5G infrastructure.
For those in telecom, this variety highlights the need for smart spectrum planning, network slicing, and aligning device ecosystems.
