5G Key Performance Indicators Explained: How 5G Surpasses 4G IMT-Advanced

5G Key Performance Indicators: Shaping the Future of Telecom
Moving from IMT-Advanced (4G) to IMT-2020 (5G) is more than just speeding up mobile internet; it’s a major shift in how we connect. This new technology supports enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (mMTC).
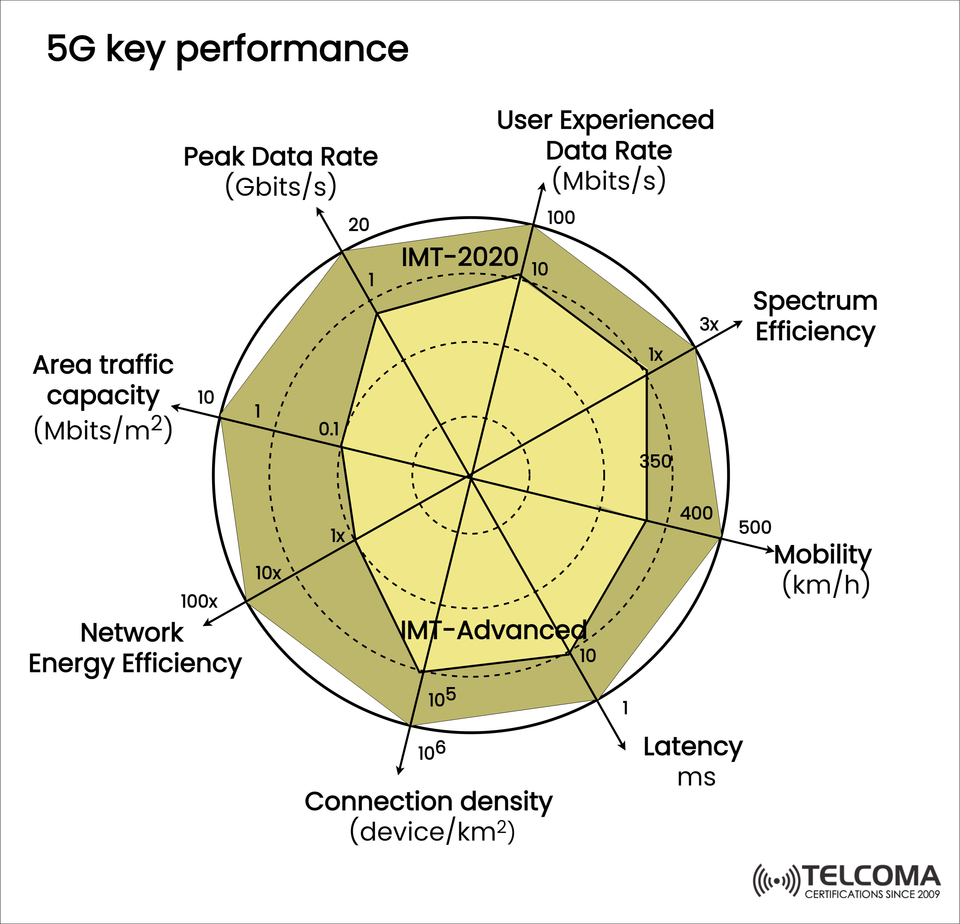
The radar chart you’ll find shows how the key performance metrics for 5G surpass those of 4G across several areas, like peak data rates, latency, spectrum efficiency, connection density, and energy efficiency of networks.
For those in the telecom field or tech fans, getting a handle on these KPIs is vital to understanding how 5G fuels innovations such as smart cities, driverless cars, Industry 4.0, and much more.
What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in 5G?
KPIs are the measurable targets set by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) that help assess what 5G can do compared to 4G. These benchmarks are crucial for ensuring that 5G networks can meet the needs of both consumers and businesses alike.
Some of the main KPIs for 5G include:
Peak Data Rate
User Experience Data Rate
Spectrum Efficiency
Mobility
Latency
Connection Density
Network Energy Efficiency
Area Traffic Capacity
Comparing 5G (IMT-2020) vs 4G (IMT-Advanced)
The radar chart really shows the jump in performance from IMT-Advanced to IMT-2020. Here’s a quick look at each KPI:
- Peak Data Rate (Gbit/s)
4G (IMT-Advanced): ~1 Gbps
5G (IMT-2020): Up to 20 Gbps
Impact: This means you can enjoy ultra-HD streaming, AR/VR experiences, and extensive cloud services.
- User Experienced Data Rate (Mbit/s)
4G: ~10 Mbps
5G: ~100 Mbps
Impact: Even in busy areas, users get fast internet.
- Spectrum Efficiency
4G: Baseline (1x)
5G: Up to 3x improvement
Impact: More effective use of limited spectrum.
- Mobility (km/h)
4G: ~350 km/h
5G: Up to 500 km/h
Impact: Keeps things connected for high-speed trains and future transport systems.
- Latency (ms)
4G: ~10 ms
5G: ~1 ms
Impact: Critical for things like self-driving cars, remote surgeries, and gaming.
- Connection Density (devices/km²)
4G: ~100,000 devices
5G: Up to 1 million devices
Impact: Supports IoT ecosystems in smart cities and factories.
- Network Energy Efficiency
4G: Baseline
5G: 10x to 100x more efficient
Impact: Lowers energy costs for providers while making networks greener.
- Area Traffic Capacity (Mbit/s/m²)
4G: ~0.1 Mbit/s/m²
5G: ~10 Mbit/s/m²
Impact: More capacity for handling large data traffic in crowded urban areas.
Why These KPIs Matter
5G isn’t just about faster phones. Each KPI is crucial for addressing real-world challenges:
Peak and User Data Rates: Vital for mobile broadband and immersive entertainment.
Latency: Important for operations that rely on split-second timing, like remote surgeries and self-driving vehicles.
Connection Density: Fuels IoT networks with millions of sensors in urban settings and factories.
Energy Efficiency: Aids in the sustainable expansion of telecom infrastructure.
Mobility: Keeps users connected even when traveling at high speeds, like those on trains or hyperloops.
Use Cases Driven by 5G KPIs
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
High-speed 5G enables 4K/8K streaming, VR/AR gaming, and cloud services.
KPIs for peak data rates and user experience are key here.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC)
Essential for important services such as self-driving cars, drones, remote healthcare, and industrial robots.
The latency KPI (<1 ms) guarantees consistency and safety.
Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC)
Designed for IoT applications featuring millions of devices.
The connection density KPI (10⁶ devices/km²) supports smart factories and urban environments.
Challenges in Meeting 5G KPIs
Even with its potential, hitting these KPIs is tough:
Spectrum Allocation: Limited availability of spectrum bands and high costs involved.
Infrastructure Costs: Huge investments needed for small cells and fiber infrastructure.
Energy Management: Despite improvements in efficiency, more base stations can actually raise overall power consumption.
Latency in Real Deployments: Consistently achieving that 1 ms latency across wide areas is challenging.
Interoperability: Global standards need to align across different regions and vendors.
Telecom Enablers Behind 5G KPIs
Several key technologies are driving the performance advancements in 5G:
Technology Contribution to KPIs Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output)Improves spectrum efficiency and data speeds Beamforming Enhances coverage and decreases interference mmWave Spectrum Supports ultra-fast data rates Small Cells Boosts capacity and reduces latency Edge Computing (MEC)Cuts down latency by processing data close to users Network Slicing Offers dedicated resources for different use cases Cloud-Native Core Networks Increases scalability and energy efficiency
The Road Ahead: From 5G to 6G
While 5G is a significant advancement, future 6G networks (IMT-2030) aim to push these KPIs even higher:
Data Rates: Targeting terabit-per-second (Tbps) speeds.
Latency: Aiming for microsecond delays.
AI-Integrated Networks: Creating self-optimizing and predictive network capabilities.
Sustainability: A goal for carbon-neutral telecom operations.
Holographic and Multisensory Communication: Opening up immersive interactions between humans and machines.
Challenges to Tackle
Even with its great potential, telecom-powered Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) run into some challenges:
Coverage Gaps: There are still areas where 5G isn't fully rolled out.
Cost: Upgrading infrastructure like small cells and edge computing nodes can really add up.
Cybersecurity: Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) systems can be susceptible to spoofing and hacking.
Standardization: We need to get everyone on the same page with V2X protocols globally.
Public Acceptance: People have to feel confident in automated warnings and platooning systems.
Conclusion
The radar chart that compares IMT-Advanced (4G) and IMT-2020 (5G) clearly shows why 5G is a real game-changer. With its remarkable improvements in speed, latency, energy efficiency, spectrum usage, and IoT density, 5G is on track to completely transform industries, cities, and daily life.
For telecom professionals, these KPIs aren’t just technical markers—they lay the foundation for next-gen services, from smart healthcare and autonomous vehicles to immersive entertainment and industrial automation.
The key performance indicators of 5G make sure that networks are faster and smarter, greener, and ready to support the digital environments of the future.
