5G KPI System Explained: Key Performance Indicators for Next-Gen Networks

Understanding the 5G KPI System: Key Performance Indicators for Next-Gen Networks
The 5G KPI (Key Performance Indicator) system lays out the measurable goals that make fifth-generation mobile networks a game changer. In contrast to 4G LTE, which mostly concentrated on speed and coverage, 5G KPIs cover various dimensions, supporting everything from enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) to Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) and Mission-Critical Communications (MCC).
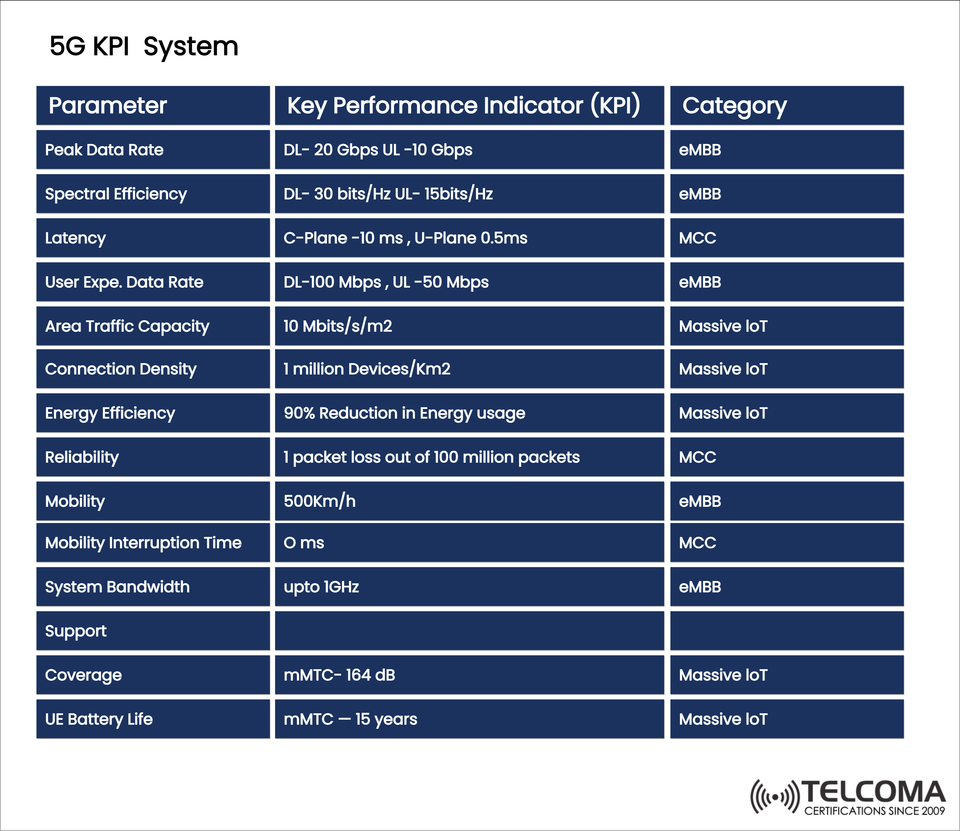
The table in the image you’ll find shows 5G’s performance standards across these categories. In this post, we'll explore each KPI, clarify why it’s important, and see how it relates to real-world applications.
Breakdown of 5G KPIs
Before we get into the specifics, it’s key to highlight the three main service pillars of 5G, each having its own KPI stipulations:
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband): Focused on high data rates, broad bandwidth, and smooth mobility.
mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communications): Aimed at extensive IoT connectivity, energy savings, and greater coverage.
MCC (Mission-Critical Communications / URLLC): Prioritizes ultra-low latency, reliability, and uninterrupted mobility.
Each KPI aligns with one or more of these categories.
Explanation of Key 5G KPIs
- Peak Data Rate
DL: 20 Gbps | UL: 10 Gbps
Category: eMBB
Why It’s Important: Sets the maximum potential throughput under optimal conditions. It’s crucial for data-heavy services like 8K video streaming, VR/AR, and cloud gaming.
- Spectral Efficiency
DL: 30 bits/Hz | UL: 15 bits/Hz
Category: eMBB
Why It’s Important: This measures how well the spectrum is utilized. Higher efficiency means operators can cater to more users without needing extra bandwidth.
- Latency
Control Plane (C-Plane): ≤ 10 ms
User Plane (U-Plane): ≤ 0.5 ms
Category: MCC
Why It’s Important: Latency is vital for autonomous driving, remote surgeries, and industrial automation, where even minor delays can be critical.
- User Experienced Data Rate
DL: 100 Mbps | UL: 50 Mbps
Category: eMBB
Why It’s Important: Unlike peak data rate, this measures the average experience for users. It ensures that even in crowded spots, users get solid speeds consistently.
- Area Traffic Capacity
10 Mbit/s per m²
Category: Massive IoT
Why It’s Important: This indicates the network’s capability to handle a high density of devices, which is crucial for smart cities and IoT-focused industrial areas.
- Connection Density
1 million devices per km²
Category: Massive IoT
Why It’s Important: With billions of IoT devices on the horizon, 5G needs to support this massive connectivity without compromising network quality.
- Energy Efficiency
90% reduction in energy usage
Category: Massive IoT
Why It’s Important: This helps to prolong the battery life of IoT devices and cut down on operator costs, ensuring sustainability over time.
- Reliability
1 packet loss in 100 million packets
Category: MCC
Why It’s Important: High reliability is vital for mission-critical applications like emergency services and connected healthcare.
- Mobility
Up to 500 km/h
Category: eMBB
Why It’s Important: Ensures connectivity for high-speed trains and possibly planes, providing seamless service while moving at such fast speeds.
- Mobility Interruption Time
0 ms
Category: MCC
Why It’s Important: It’s crucial that service isn’t interrupted during cell handovers, especially for autonomous vehicles and real-time applications.
- System Bandwidth
Up to 1 GHz
Category: eMBB
Why It’s Important: Greater system bandwidth means wider channels and support for high-throughput services.
- Coverage
mMTC: 164 dB
Category: Massive IoT
Why It’s Important: Ensures that devices can connect even in challenging locations like deep buildings or rural areas.
- UE Battery Life
Up to 15 years (mMTC devices)
Category: Massive IoT
Why It’s Important: Many IoT sensors are deployed in hard-to-reach places. Longer battery life allows for practical use without needing frequent battery swaps.
Summary Table of KPIs
Parameter KPI Target Category Peak Data Rate DL: 20 Gb ps, UL: 10 Gb ps e MBB Spectral Efficiency DL: 30 bits/Hz, UL: 15 bits/Hz e MBB Latency C-Plane: 10 ms, U-Plane: 0.5 ms MCC User Experienced Data Rate DL: 100 Mb ps, UL: 50 Mb ps e MBB Area Traffic Capacity 10 Mbit/s/m² Massive IoT Connection Density 1 million devices/km² Massive IoT Energy Efficiency 90% reduction in usage Massive IoT Reliability 1 loss in 100 million packets MCC Mobility 500 km/h e MBB Mobility Interruption Time 0 ms MCC System Bandwidth Up to 1 GHz e MBB Coverage m MTC: 164 dB Massive IoT UE Battery Life 15 years (m MTC) Massive IoT
Real-World Impacts of 5G KPIs
Smart Cities: High connection density and coverage enable IoT-driven solutions for traffic management, waste collection, and energy efficiency.
Healthcare: Ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) allows for remote surgeries and ongoing patient monitoring.
Transportation: High mobility and seamless handovers keep autonomous vehicles and high-speed trains connected.
Industry 4.0: Energy efficiency and reliability facilitate predictive maintenance and automated industrial systems.
User Experience: Faster connections and low latency enhance entertainment, gaming, and cloud services.
Challenges in Achieving 5G KPIs
Fronthaul and Backhaul Capacity: Meeting the high throughput and latency needs demands significant investment in fiber optic infrastructure.
Spectrum Availability: Spectral efficiency hinges on regulatory factors and smart utilization of both licensed and unlicensed bands.
Device Limitations: Not all user equipment (UE) can meet the peak KPI goals just yet.
Energy Balancing Act: Striking a balance between high performance and energy efficiency can be tricky.
Looking Forward: Moving Toward 6G KPIs
While 5G sets new standards for KPIs, 6G is set to raise the bar even higher:
Terabit-per-second peak rates.
Sub-millisecond end-to-end latency.
AI-powered resource management.
Global reach through non-terrestrial networks (NTN).
Wrap-Up
The 5G KPI system is more than just a set of technical metrics—it’s a roadmap for future digital experiences. By outlining peak speeds, latency, reliability, coverage, and efficiency, these KPIs enable 5G to cater to a variety of applications, ranging from entertainment to industrial automation and smart cities.
For professionals in telecom, getting a grip on KPIs is essential for network design and optimization. And for tech fans, it provides a clearer view of how 5G delivers on its promises.
As 5G continues to evolve and we start looking at 6G, KPIs will keep adapting, pushing mobile networks to achieve even more remarkable levels of performance and innovation.
