5G NR Diverse Deployments: Spectrum, Services, and Network Topologies Explained

5G NR Diverse Deployments: Spectrum, Services, and Topologies
5G New Radio (5G NR) isn't just a step up from 4G LTE; it’s a total reimagining of wireless connectivity. It's built to handle everything from smartphones to self-driving cars and IoT devices, allowing for varied deployments across different spectrums, services, and network structures.
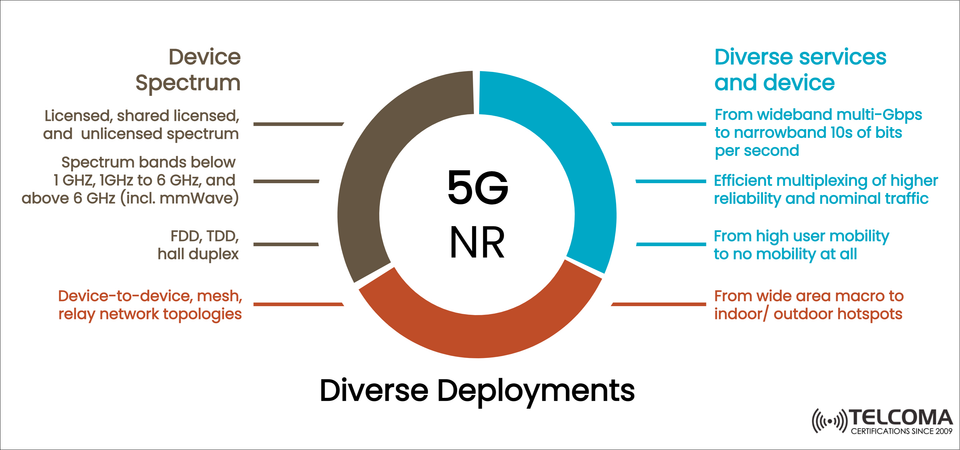
The diagram included shows the key components of 5G NR deployments:
Device Spectrum (flexible frequency usage)
Wide Range of Services and Devices (supporting many applications)
Network Structures (device-to-device, mesh, relay)
In this blog, we’ll unpack each element, aiming to provide both technical depth and a reader-friendly approach.
- Device Spectrum in 5G NR
One of the standout features of 5G NR is its capability to function over a broad spectrum range, from sub-1 GHz to millimeter-wave (mmWave) bands above 6 GHz. This flexibility is key for addressing various deployment needs.
Spectrum Bands in 5G NR:
Sub-1 GHz: * Great coverage with good penetration (perfect for rural areas and indoor connections). * Ideal for massive IoT (mMTC) applications like smart meters, logistics, and farming.
1 GHz – 6 GHz (Mid-band): * Strikes a good balance between coverage and capacity. * Used for enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) offering higher speeds.
Above 6 GHz (mmWave): * Offers incredibly high capacity with super low latency. * Perfect for dense urban areas, AR/VR, and fixed wireless access.
Spectrum Licensing in 5G:
Licensed spectrum: Dedicated to carriers, ensuring reliability and quality of service.
Shared licensed spectrum: Lets multiple operators share resources on the fly.
Unlicensed spectrum: Gives flexibility to businesses and private networks.
This spectrum agility allows 5G NR to be deployed in urban, suburban, and rural environments, ensuring customized connectivity.
- Diverse Services and Devices in 5G NR
Unlike earlier generations that focused mainly on mobile broadband, 5G NR caters to a broad spectrum of services for both consumer and business applications.
Service Flexibility in 5G NR:
From wideband multi-Gbps to narrowband: * Multi-Gbps speeds allow for high-res video, holographic calls, and AR/VR experiences. * Narrowband supports low-power IoT sensors.
Efficient multiplexing: * Ensures coexistence of ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) traffic. * Allows both mission-critical and normal services on the same network.
Mobility spectrum: * Supports everything from high-speed trains and vehicles to stationary IoT gadgets. * Smooth transitions across cells guarantee continuous connectivity.
Coverage range: * From wide area macro cells providing large-scale coverage * To indoor/outdoor hotspots for places like stadiums, shopping malls, and offices.
With this kind of flexibility, 5G NR becomes a universal platform, capable of enabling varied ecosystems from consumer tech to industrial IoT.
Network Topologies: Device-to-Device, Mesh, and Relay
5G NR doesn't just depend on traditional base station-to-device communication. It also introduces new network structures that enhance adaptability, resilience, and efficiency.
a) Device-to-Device (D2D) Communication
Lets devices connect directly without needing a base station.
Lowers latency and takes some load off the core network.
Crucial for public safety communications and proximity-based services.
b) Mesh Topologies
Devices create a multi-hop mesh network, relaying data between themselves.
Extends coverage in tough environments like mines, disaster-hit areas, or rural locations.
Guarantees network resilience even if some nodes go down.
c) Relay Networks
Expand base station coverage by using relay nodes.
Improve connectivity in hard-to-reach places (indoors, tunnels).
Boost cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for closely packed base stations.
These topologies ensure that 5G NR isn't just for urban areas but can also thrive in remote, rural, and critical-use environments.
The Technical Foundation of 5G NR
To support these varied deployments, 5G NR brings together several core technologies:
FDD (Frequency Division Duplex): * Separate channels for uplink and downlink. * Great for wide-area coverage.
TDD (Time Division Duplex): * Shares the same channel for uplink and downlink but alternates in time. * Efficient for data-heavy traffic in urban settings.
Full Duplex: * Lets simultaneous transmission and reception on the same frequency. * Boosts spectral efficiency and cuts down on latency.
These duplexing options give operators the flexibility to deploy based on spectrum availability and traffic demands.
Practical Examples of 5G NR Diverse Deployments
Let’s tie the theory to some real-world scenarios:
Deployment Scenario Spectrum Used Services Enabled Topology Used Smart City IoT NetworkSub-1 GHz Smart meters, traffic sensors, surveillance Mesh/D2DUrban Mobile Broadband1-6 GHz Mid-band eMBB, AR/VR, cloud gaming Macro + hotspots Stadium or Event Venues mmWave > 6 GHzUltra-HD streaming, AR navigation Hotspot + relay Industrial Automation Mid-band + mmWave URLLC for robotics, remote machineryD2D + private 5GRural Broadband AccessSub-1 GHz Fixed wireless, tele-education, telemedicine Relay + mesh
This table illustrates how 5G NR tailors spectrum, services, and topology to fit deployment needs.
Why 5G NR Diverse Deployments Matter
Telecom operators and businesses gain from unparalleled flexibility:
Operators can fine-tune deployments by blending spectrum bands and setups for urban, rural, and industrial applications.
Businesses can establish private 5G networks tailored for factories, hospitals, and campuses.
Consumers enjoy seamless services, from fast streaming to low-latency gaming.
By allowing one platform for many uses, 5G NR guarantees scalability and cost effectiveness.
Conclusion
The diverse deployments of 5G NR—spanning spectrum flexibility, service variety, and innovative structures—position it as the foundation of next-generation connectivity.
Device Spectrum ensures 5G adapts to various settings, from rural IoT to urban mmWave.
Diverse Services and Devices allow it to support high-speed broadband and ultra-low-bandwidth IoT sensors without a hitch.
Topologies like D2D, mesh, and relay enhance resilience, coverage, and adaptability.
