5G NR RRC Reconfiguration Explained: Complete Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Procedure

5G NR RRC Reconfiguration: The Last Step Before Data Transfer
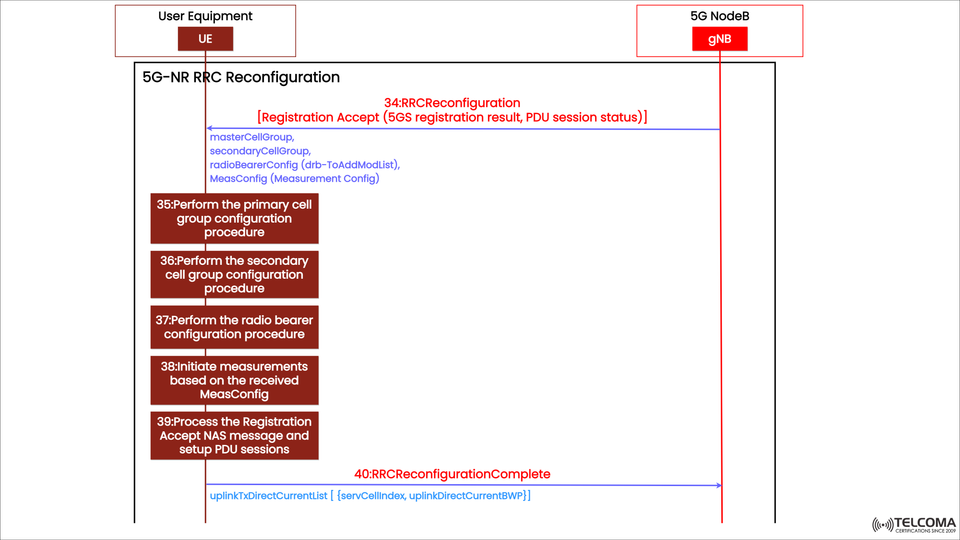
After establishing 5G NR Access Stratum (AS) security, the next major milestone in 5G standalone registration is the RRC Reconfiguration procedure. This step transitions the User Equipment (UE) from just being connected to being fully configured and ready to transfer data. It enables things like active PDU session establishment, mobility management, and radio optimization.
The accompanying image illustrates the interaction between the UE and the gNB (Next Generation NodeB), highlighting how the RRC Reconfiguration sequence prepares the UE for normal operation within the 5G network.
Overview of the RRC Reconfiguration Procedure
The Radio Resource Control (RRC) layer in 5G NR plays a critical role in managing connections between the UE and the gNB. The RRC Reconfiguration process is kicked off by the gNB and carried out by the UE to:
Set up or change radio bearers,
Configure measurement parameters,
Assign primary and secondary cell groups,
Wrap up 5G registration and establish PDU sessions.
In simpler terms, this procedure lays the groundwork for starting uplink and downlink data transmission.
Step 34: RRC Reconfiguration Message
The RRC Reconfiguration message is sent from the gNB to the UE and contains all the info needed to establish or tweak the UE’s configuration.
It consists of:
master Cell Group: Configures the Primary Cell Group (PCG) — typically the main cell that controls radio communication.
secondary Cell Group: Details for Secondary Cell Groups (SCG), used when dual connectivity is in play.
radio Bearer Config: Defines Data Radio Bearers (DRBs) responsible for handling user-plane data.
Meas Config (Measurement Configuration): Outlines measurement parameters for network optimization and mobility management.
Additionally, this message carries NAS messages such as:
Registration Accept, which includes the 5GS registration result and PDU session status.
Overall, the RRC Reconfiguration message acts as the “final configuration command” that brings the UE to a fully operational state.
Step 35: Perform Primary Cell Group Configuration
Once the UE gets the message, it starts by setting up the Primary Cell Group (PCG).
The PCG usually aligns with the Master Cell Group (MCG) under the direct control of the serving gNB. The configuration includes:
Physical layer parameters,
Scheduling configuration,
Logical channel arrangement,
Uplink and downlink frequency settings.
This way, the UE ensures its primary connection to the 5G network is stable and optimized for communication.
Step 36: Perform Secondary Cell Group Configuration
If the UE supports dual connectivity or carrier aggregation, the gNB might assign one or more Secondary Cell Groups (SCG).
These secondary groups improve throughput and coverage since they let the UE connect to more cells. They’re vital for:
High-speed data applications,
Carrier aggregation,
Load balancing, and
Network densification (small cells).
In this step, the UE applies parameters from the secondary Cell Group section in the RRC Reconfiguration message.
Step 37: Perform Radio Bearer Configuration
Next up, the UE goes through the radio bearer configuration procedure. In this part, it sets up the SRBs (Signaling Radio Bearers) and DRBs (Data Radio Bearers):
SRBs manage control-plane signaling (like RRC and NAS messages).
DRBs look after user-plane data transfer (like internet or voice traffic).
The radio Bearer Config field specifies which DRBs need to be added, changed, or dropped (drb-To Add ModList).
This step essentially activates the data paths between the UE and gNB, allowing for real-time communication and data transfer once everything is ready.
Step 38: Initiate Measurements Based on MeasConfig
Next, it’s time for measurement configuration.
The MeasConfig section in the RRC Reconfiguration message gives the UE instructions to:
Check the signal quality of nearby cells,
Track Reference Signal Received Power (RSRP) and Quality (RSRQ),
Report measurements back to the gNB.
These measurements are key for:
Handover decisions,
Cell reselection, and
Network optimization.
By kicking off these measurements, the UE helps the network keep connectivity at its best and support smooth mobility.
Step 39: Process the Registration Accept NAS Message and Setup PDU Sessions
Once the radio and measurement setups are done, the UE processes the embedded NAS Registration Accept message.
This message confirms that the UE registered successfully in the 5G Core Network (5GC) and provides:
5GS Registration Result: Shows whether the registration was successful or not.
PDU Session Status: Lists the status of all requested data sessions (active/inactive).
The UE utilizes this info to:
Set up or resume PDU sessions,
Allocate IP addresses for data communication,
Establish appropriate QoS flows.
In doing so, this step links the RRC layer (access stratum) with the NAS layer (core signaling), finishing the UE’s integration into the 5G system.
Step 40: RRC Reconfiguration Complete
After all configurations are successfully processed, the UE sends the RRC Reconfiguration Complete message back to the gNB.
This message confirms:
The new RRC, bearer, and measurement settings were applied successfully.
Activation of PDU sessions and readiness for uplink/downlink data transfer.
It also includes:
uplink Tx Direct Current List { serv Cell Index, uplink Direct Current BWP }
This part reports the uplink transmission configuration, ensuring everything’s synced up and resources are used efficiently.
With this, the RRC Reconfiguration phase wraps up, and the UE becomes fully connected and ready for data.
Key Functions Enabled by RRC Reconfiguration
Once this process is complete, the UE can:
Exchange user data with the network (internet, voice, video),
Conduct inter-cell measurements for smooth handovers,
Stay in sync with both primary and secondary cells,
Support advanced features like dual connectivity and carrier aggregation.
So, this step is basically the bridge between the setup phase and the active data transfer phase of the 5G connection.
Importance of RRC Reconfiguration in 5G Networks
RRC Reconfiguration is a key step that shifts the UE from “partially connected” to “fully operational.”
Without it:
The UE can't start PDU sessions.
Mobility measurements can’t be taken.
The UE can’t optimize throughput through carrier aggregation or dual connectivity.
In essence, it’s the “final handshake” that gets the UE ready for sustained, secure, and optimized 5G performance.
Conclusion
The 5G NR RRC Reconfiguration procedure is the final and crucial step before the UE dives into full data communication. It ties together radio, measurement, and session configuration into a single, coordinated process, ensuring smooth operation between UE and gNB.
Through steps 34 to 40, the UE sets up solid radio links, activates PDU sessions, and wraps up network integration — enabling the ultra-reliable, high-speed, and low-latency communication that characterizes 5G.
With this procedure in the books, the 5G connection is now fully active, secure, and optimized for the next-gen mobile experience.
