5G NR RRC Setup and NAS Registration Request Explained: UE to gNB Signaling Flow

5G NR RRC Setup and NAS Registration Request: Connecting to the 5G Core
In a 5G Standalone (SA) network, the access registration process is key to how a User Equipment (UE) connects with the 5G Core (5GC). After the initial Random Access and RRC Connection Setup steps are completed, the UE enters the next important phase — RRC Setup and NAS Registration Request.
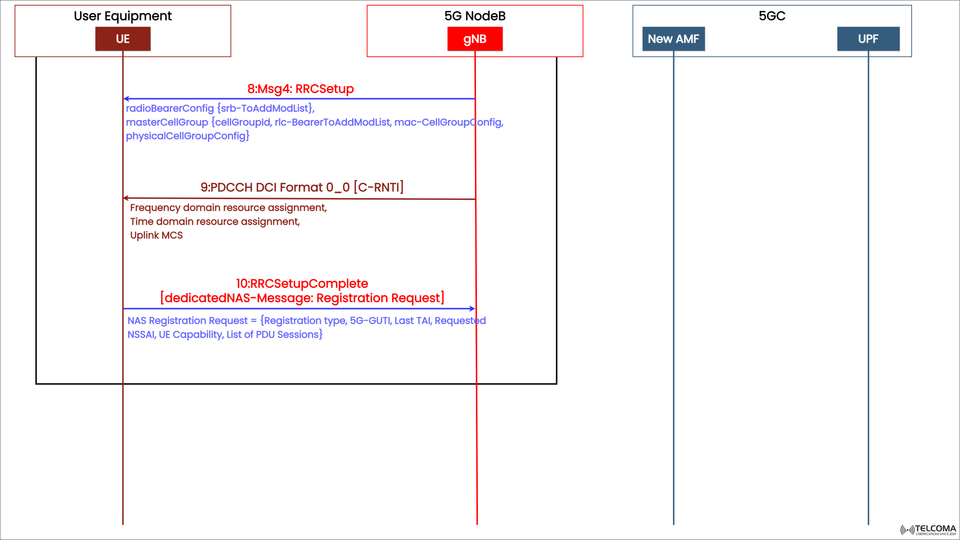
The diagram uploaded illustrates this specific part of the signaling exchange involving the UE, gNB (5G NodeB), and components of the 5GC (AMF and UPF). It showcases steps 8 to 10 of the entire 5G SA registration sequence, which deal with the configuration of RRC parameters and the initiation of NAS-level registration.
Overview: Moving from RRC Connection Setup to NAS Registration
Once the UE finishes the Random Access Procedure (Msg1–Msg4) and syncs with the gNB, the next step is the RRC Setup process. This ensures that the UE has the right configurations to communicate with the network effectively.
At this point:
The UE is assigned a C-RNTI (Cell Radio Network Temporary Identifier).
A Signaling Radio Bearer (SRB1) gets established.
The gNB is all set to send detailed radio and cell group configurations.
Next, the UE sends an RRC Setup Complete message, which includes the NAS Registration Request — the UE's first message meant for the 5G Core (5GC).
Key Players and Their Roles
Component Full Name Role UE User Equipment Starts RRC setup and NAS registration.gNB5G Node B Manages RRC signaling and passes on NAS messages. AMF Access and Mobility Management Function Oversees UE registration, authentication, and mobility. UPF User Plane Function Takes care of user data after sessions are set up.
At this point, the AMF in the 5GC gets activated for the first time, receiving NAS messages from the UE via the gNB.
Step-by-Step Message Flow Breakdown
The diagram highlights three key signaling steps:
Step 8: Msg4 – RRC Setup
Direction: gNB → UE
Purpose: Sends radio bearer and cell group configurations to the UE.
After the UE’s RRCSetupRequest (Msg3) is received, the gNB responds with the RRCSetup message. This message is crucial for completing the RRC connection and setting various parameters needed for data exchange.
Content of Msg4 – RRCSetup:
radioBearerConfig: Outlines SRB0/SRB1 along with any additional or modified DRB (Data Radio Bearer) settings.
masterCellGroup: Lists master cell parameters, including:
cellGroupId
rlc-BearerToAddModList
mac-CellGroupConfig
physicalCellGroupConfig
These settings allow the UE to accurately interpret scheduling, timing, and physical layer configurations from the gNB.
Once the UE gets this message, it applies these configurations locally, setting up an operational RRC link with the gNB.
Step 9: PD-CCH DCI Format 0_0 [C-RNTI]
Direction: gNB → UE
Purpose: Allocates uplink scheduling resources for the UE’s next transmission.
Before the UE can send its RRCSetupComplete message, it requires uplink resources. The gNB allocates these through a Downlink Control Information (DCI) message sent over the PDCCH (Physical Downlink Control Channel).
DCI Format 0_0 carries:
Frequency domain resource assignment
Time domain resource assignment
Uplink Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS)
Using the C-RNTI (Cell RNTI) as the message identifier ensures that the UE now has a stable logical identity within the cell.
This setup tells the UE exactly when and where to send its next uplink message (RRCSetupComplete).
Step 10: RRCSetupComplete (with NAS Registration Request)
Direction: UE → gNB
Purpose: Wraps up RRC setup and kicks off NAS registration with the 5GC.
Once the UE gets the uplink scheduling details, it sends the RRCSetupComplete message using the assigned uplink resources.
This message does two main things:
It lets the gNB know that the UE has successfully finished the RRC setup.
It contains the NAS Registration Request that the gNB will forward to the AMF in the 5G Core.
NAS Registration Request includes:
Registration Type (Initial Registration or Mobility Update)
5G-GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary Identifier)
Last TAI (Tracking Area Identifier)
Requested NSSAI (Network Slice Selection Assistance Information)
UE Capability Information
List of PDU Sessions that the UE is requesting to set up
This message marks the first NAS (Non-Access Stratum) communication in the 5G SA registration process, signifying the shift from access-level signaling (RRC) to core-level signaling (NAS).
Importance of Each Configuration Parameter
Parameter Function radio Bearer Config Specifies RLC/MAC setup for signaling bearers (SRB1).master Cell Group Delivers cell-level configuration, including scheduling and physical parameters. C-RNTI Identifies the UE uniquely for scheduling and data transmission. NAS Registration Type Indicates the registration purpose (initial, periodic, or mobility update).5G-GUTITemporary ID that helps protect the UE’s identity. Requested NSSAI Assists the UE in requesting specific network slices for differentiated services. UE Capability Describes the UE’s supported features (bands, modulation schemes, etc.).PDU Session List Shows which user data sessions the UE wants to establish later.
These parameters ensure the UE smoothly transitions from basic access setup to full service connectivity.
Collaboration Between gNB and AMF During This Phase
While the gNB mainly handles RRC-level control, it also acts as a bridge for NAS messages. When the RRCSetupComplete (NAS Registration Request) comes in, the gNB sends the embedded NAS message to the AMF using the NGAP (Next Generation Application Protocol).
The AMF then:
Authenticates the UE.
Allocates security parameters.
Begins network registration and mobility management.
This transition marks the handover of control from the RAN (Radio Access Network) to the Core Network.
Technical Highlights
RRC Setup Completes Access Stratum Configuration: It wraps up the UE’s radio settings and enables SRB1-based control-plane communication.
NAS Registration Kicks Off Core Communication: The NAS layer sets up a logical link between the UE and AMF in the 5GC.
DCI Scheduling Is Dynamic: The gNB dynamically assigns uplink grants, optimizing radio resource use and reducing latency.
Security Setup Comes Next: After RRC Setup Complete, the Security Mode Command (SMC) is initiated by the AMF through the gNB.
Comparing LTE and 5G RRC Setup & NAS Registration
FeatureLTE5G NR (Standalone)Core Network EPC (MME, SGW, PGW)5GC (AMF, SMF, UPF)
Registration Message Attach Request NAS Registration Request
Bearer Setup Sequential Parallel (config + NAS in RRCSetupComplete)
IdentifierGUTI5G-GUTI
Slicing SupportNoYes (via NSSAI)
5G NR brings flexibility, modularity, and network slicing capabilities at this stage, setting it apart from LTE.
Conclusion
The RRC Setup and NAS Registration Request process represents the UE’s official entry into the 5G Core ecosystem. It begins with Msg4: RRCSetup from the gNB and wraps up with RRCSetupComplete, allowing the UE to not just configure its radio resources but also signal its desire to register with the 5GC.
By integrating RRC and NAS in this phase, 5G achieves a streamlined, low-latency access setup that’s both flexible and scalable. This combination lays the foundation for secure registration, slicing, and PDU session management — the essential pillars of 5G Standalone operations.
