5G Private Network Architecture Explained: Models, Deployment & Use Cases

The emergence of 5G private networks is changing the way companies set up connectivity for their mission-critical applications. Unlike public mobile networks, private 5G offers dedicated coverage, ultra-low latency, and better security, which allows sectors like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and smart cities to take full advantage of digital transformation.
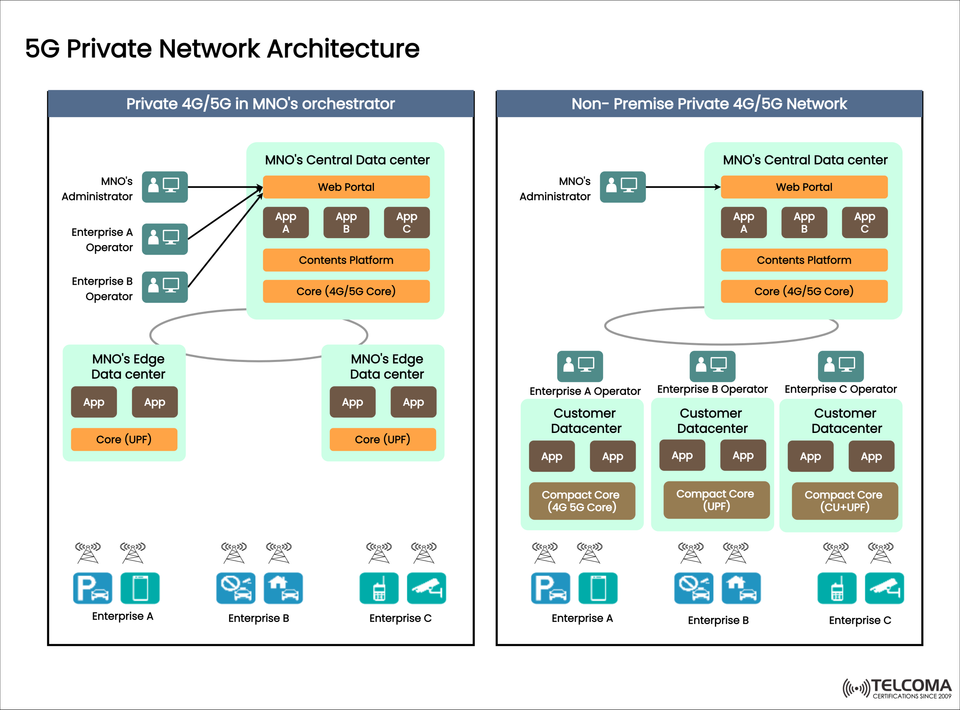
The image above shows two primary models of 5G Private Network Architecture:
Private 4G/5G in MNO’s Orchestrator
Non-Premise Private 4G/5G Network
Each model has its own advantages, deployment strategies, and levels of operational control for businesses. Let's take a closer look at them.
What is a 5G Private Network?
A 5G private network is a mobile network that’s specifically set up for a business or organization, separate from public mobile operators. It provides:
Dedicated resources (like spectrum, compute, and storage)
Enhanced security by keeping enterprise traffic isolated
Reliable connectivity tailored for critical IoT and automation tasks
Custom performance tuning for latency, bandwidth, and coverage
These private 5G networks can either be managed by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) or set up on-premises by the companies themselves.
5G Private Network Architecture Models
The uploaded image outlines two architectural models:
- Private 4G/5G in MNO’s Orchestrator
In this setup, the Mobile Network Operator (MNO) takes care of managing the private network from its central data center.
Key Components:
MNO’s Central Data Center:
Web portal for enterprise operators and admins
Core Network (4G/5G Core)
Platforms for application hosting and content
MNO’s Edge Data Centers:
Hosts applications and the User Plane Function (UPF)
Provides localized processing to ensure low-latency services
Enterprise Operators (A, B, C):
Access through the web portal
Deploy their own apps and services using the MNO’s orchestrator
Benefits:
Less complexity in deployment for companies
Centralized orchestration by MNO boosts efficiency
Supports multiple enterprises through shared infrastructure
Strong integration with MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing)
Example Use Cases:
Smart parking solutions (Enterprise A)
Automated industrial facilities (Enterprise B)
Smart city services like healthcare and transport (Enterprise C)
- Non-Premise Private 4G/5G Network
In this model, companies set up and manage their own on-premises private network, with backing from the MNO’s central infrastructure.
Key Components:
Customer Datacenters (Enterprise A, B, C):
Each business runs its own compact 4G/5G core (control and user plane functions)
Locally hosts applications for low latency and data sovereignty
MNO’s Central Data Center:
Provides the web portal, orchestration, and content platforms
Allows connectivity to broader networks if needed
Enterprise Operators:
Directly manage their private core and applications
Enjoy maximum control and flexibility
Benefits:
Enhanced data sovereignty since enterprise traffic remains on-site
Better latency performance due to local processing
Customized network solutions tailored to enterprise needs
Higher security since traffic doesn’t unnecessarily traverse MNO’s infrastructure
Example Use Cases:
Healthcare facilities with strict compliance needs
Automotive plants utilizing autonomous robotic systems
Logistics hubs needing extremely reliable low-latency connectivity
Comparison of Deployment Models
Aspect MNO-Orchestrated Private 5GNon-Premise Private 5GControlManaged mainly by the MNO Managed by the enterprise Deployment Complexity Lower, as MNO manages orchestration Higher, requires in-house expertise Latency Dependent on MNO’s edge infrastructure Ultra-low latency with local processing Security & Data Sovereignty Data may go through MNO’s infrastructure Data stays on-premises, thus more secure Cost Lower CAPEX, subscription-based Higher CAPEX, long-term ROI Customization Limited by MNO’s offers Fully customizable for enterprise use Use Cases Shared services (smart cities, utilities)Mission-critical industries (healthcare, manufacturing, logistics)
Advantages of 5G Private Networks
Reliability & Performance: Dedicated spectrum offers stable, interference-free connections.
Security: Isolated data protects sensitive enterprise information.
Low Latency: On-premises cores and MEC ensure quick response times.
Scalability: Networks can expand as the needs of the enterprise grow.
Custom SLAs: Businesses define their own service quality standards.
Use Cases of 5G Private Networks
Manufacturing: Smart factories, predictive maintenance, robotic automation
Healthcare: Remote surgeries, patient monitoring, secure medical data transfers
Logistics & Transportation: Smart warehouses, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), port operations
Smart Cities: Traffic management, surveillance, emergency response
Energy & Utilities: Smart grids, remote monitoring, predictive maintenance
Challenges in Deploying Private 5G
Spectrum Availability: Companies need access to licensed or shared spectrum.
High Initial Investment: Non-premise models need considerable CAPEX.
Operational Expertise: Businesses must handle the complexities of telecom infrastructure.
Interoperability: Merging private networks with public MNO infrastructure can be tricky.
Security Risks: Connecting devices expands the potential attack surfaces.
Best Practices for Private 5G Deployment
Choose the Right Model: Businesses need to think about whether MNO-orchestrated or non-premise deployment fits their needs.
Ensure Spectrum Access: Secure spectrum through regulatory or shared licensing options.
Adopt Cloud-Native Cores: Containerized 5G core solutions provide agility and scalability.
Integrate with MEC: For low latency, align private 5G with edge computing frameworks.
Implement Zero-Trust Security: Safeguard all endpoints and network functions.
Plan for Interoperability: Ensure compatibility with public 5G for mobility and roaming.
Conclusion
The 5G Private Network Architecture discussed above focuses on two main deployment models—MNO-orchestrated private 5G and non-premise private 5G networks. Both models equip businesses with dedicated connectivity, yet they differ in control, complexity, security, and cost.
MNO-orchestrated networks make deployment easier, which is great for companies looking for managed services.
Non-premise networks give full control and data sovereignty, making them perfect for mission-critical sectors with stringent needs.
As businesses dive into Industry 4.0, smart cities, and digital transformation, private 5G networks will be essential for building a secure, high-performance, and customizable wireless infrastructure.
Visual Summary: 5G Private Network Deployment Models
Here's a straightforward look at the two architectures shown in the image:
Feature Private 4G/5G in MNO’s Orchestrator Non-Premise Private 4G/5G Network Control Centralized and managed by the MNO Decentralized, managed by the enterprise Core Placement Hosted in the MNO’s central and edge data centers Housed within the enterprise’s own data centers Latency Low (depends on how close the MNO's edge is)Ultra-low (thanks to local processing)Data Sovereignty Partial (data might pass through MNO infrastructure)Full (data stays on-site at the enterprise)Deployment Complexity Low (outsourced to the MNO)High (managed by the enterprise itself)Cost Model OPEX (subscription-based, lower initial cost)CAPEX (higher upfront cost but better long-term ROI)Best For Enter prises looking for managed services Enterprises with critical and sensitive workloads
