5G Technology Explained: Enhanced Mobile Broadband, Ultra-Low Latency, and Massive IoT

Introduction: Why 5G is a Game Changer
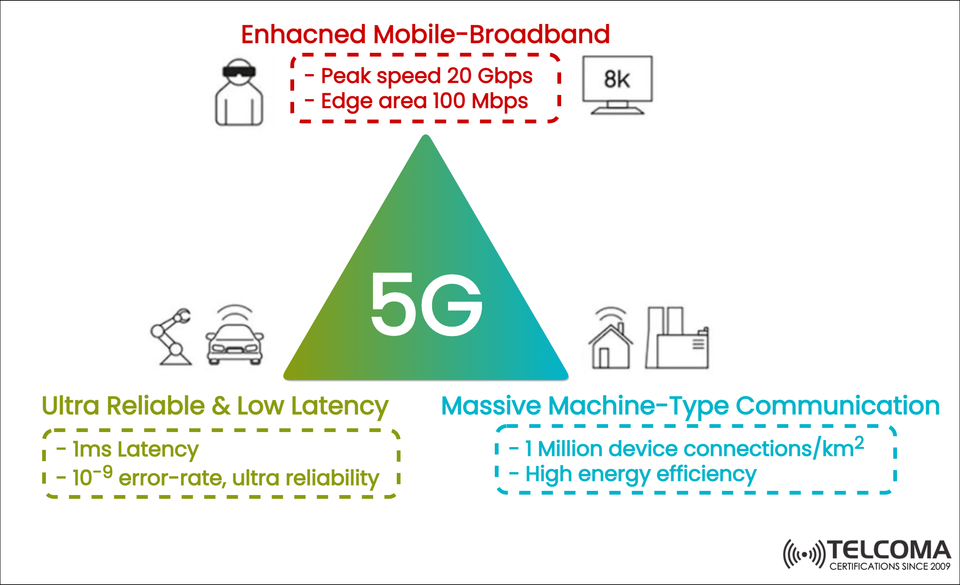
Moving from 4G LTE to 5G is about more than just faster speeds—it's a whole new way of thinking about mobile connectivity. 5G is built to handle the needs of future applications, and it stands on three key pillars: Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), and Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC).
These three aspects are changing how we connect and interact, paving the way for advancements in smart cities, self-driving cars, healthcare, industrial automation, and experiences like VR and AR.
Let’s dive deeper into each of these components.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): The Foundation of Speed and Immersion
Enhanced Mobile Broadband is probably the most noticeable part of 5G, aimed at significantly boosting data rates and overall user experience.
Peak speed of 20 Gbps: That’s a big leap from the 1 Gbps max of 4G LTE, allowing you to download ultra-high-definition movies in just seconds.
100 Mbps at the cell edge: Even those on the outskirts of the network can enjoy high-speed connections, helping to eliminate those annoying “dead zones.”
Immersive experiences: It supports 8K video streaming, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed-reality applications.
Key Applications of eMBB:
8K UHD streaming without any pesky buffering.
VR headsets that offer real-time interaction.
Mobile cloud gaming with almost no lag.
Remote collaboration tools that enhance communication with 3D holographic calls.
For everyday users, eMBB means incredibly fast entertainment. For businesses, it allows them to use bandwidth-intensive tools like digital twins and AR training without hitting network snags.
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC): Powering Critical Missions
Latency is how long it takes for data to move between devices. While 4G networks have an average latency of around 50 milliseconds, 5G URLLC cuts that down to just 1 millisecond, making it perfect for mission-critical applications.
1 ms latency: This kind of speed is essential where every single millisecond matters.
Ultra-high reliability (error rate of 10⁻⁹): Basically, this means nearly error-free communication, which is vital for systems where lives or safety are at stake.
Key Applications of URLLC:
Self-driving cars: Vehicles that can communicate in real-time with each other and their surroundings to avoid accidents.
Remote robotic surgery: Surgeons performing operations on patients located miles away with no noticeable delay.
Smart manufacturing: Real-time coordination among robots that ensures a smooth automated production process.
Power grids: Quick control measures to prevent failures from spreading.
URLLC makes sure that 5G isn’t just about speed; it’s also reliable enough for industries where a delay can have serious consequences.
Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC): The Backbone of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) relies on a ton of connected devices, from smart home devices to industrial sensors. 5G’s mMTC is specifically designed to handle the incredible increase in the number of devices.
1 million device connections per km²: Unlike 4G, which struggled with dense device environments, 5G can easily connect smart homes, factories, and entire cities.
High energy efficiency: This means IoT devices can last for years without needing a battery change.
Key Applications of mMTC:
Smart cities: Managing everything from traffic lights to waste management systems and energy networks.
Smart homes: Seamless integration of various appliances, meters, and security systems.
Industrial IoT: Using sensors to monitor equipment, which cuts downtime and boosts productivity.
Agriculture: Smart irrigation systems and crop monitoring thanks to connected sensors.
mMTC helps industries and governments create smarter, more sustainable, and more connected environments.
Comparing the Three Pillars of 5G
Featuree MBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband)URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency)mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication)Peak Speed Up to 20 Gbps Not speed-focused Not speed-focusedLatency~10 ms1 ms Moderate Reliability High Ultra-high (10⁻⁹ error rate)High Device Density Tens of thousands per km²Thousands per km²1 million per km²Key Applications Streaming, VR/AR, cloud gaming Self-driving cars, surgery, robotics Smart cities, IoT, industrial automation
Why 5G Matters for Telecom Professionals
For those in the telecom field, getting a grip on these three pillars is essential for planning and rolling out networks:
Spectrum utilization: High-frequency millimeter waves offer tremendous capacity, while low-band signals ensure broad coverage.
Infrastructure needs: Things like small cells, beamforming, and Massive MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) are key to fulfilling 5G’s promises.
Network slicing: This lets operators dedicate resources for eMBB, URLLC, or mMTC, tailoring services for different use cases.
Telecom providers need to navigate strategies that balance user desires (like high-speed streaming), industry needs (such as low-latency automation), and national goals (like IoT-powered smart cities).
Challenges Ahead in 5G Deployment
While the potential of 5G is exciting, there are some bumps in the road for deployment:
High infrastructure costs: Setting up dense small-cell networks requires a big investment.
Spectrum allocation: Governments have to balance many competing needs for limited spectrum access.
Security concerns: With so many connected devices, the risk of vulnerabilities goes up.
Interoperability: Devices, apps, and networks have to work together seamlessly.
Tackling these hurdles will need cooperation among telecom operators, governments, and tech firms.
Conclusion: A Connected Future Powered by 5G
Visualize 5G as a triangle supported by three pillars—eMBB, URLLC, and mMTC—to grasp its transformative capabilities. It’s not just about faster internet; it’s about building a robust, reliable, and interconnected ecosystem.
For consumers: Expect immersive experiences with lightning-fast connectivity.
For industries: Work will become smarter and safer, thanks to ultra-low latency.
For cities and governments: Resource management will improve with a vast IoT network.
For telecom experts and tech fans alike, 5G symbolizes the start of a new digital era. The groundwork laid today will guide innovations for years ahead—from self-driving vehicles to fully automated smart factories.
5G isn’t merely a leap in connectivity; it’s the foundation for the intelligent, hyperconnected world we’re heading towards.
