5G Use Cases Explained: eMBB, mMTC, and URLLC for the Future of Telecom

Introduction: The 5G Revolution
5G, or the fifth generation of mobile networks, is a lot more than just speeding up your smartphone internet. It’s really about transforming how wireless communication works, paving the way for new applications, services, and business models across various sectors. With features like 20 Gbps peak speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive device connectivity, 5G is setting the stage for smart cities, self-driving cars, industrial automation, and digital healthcare.
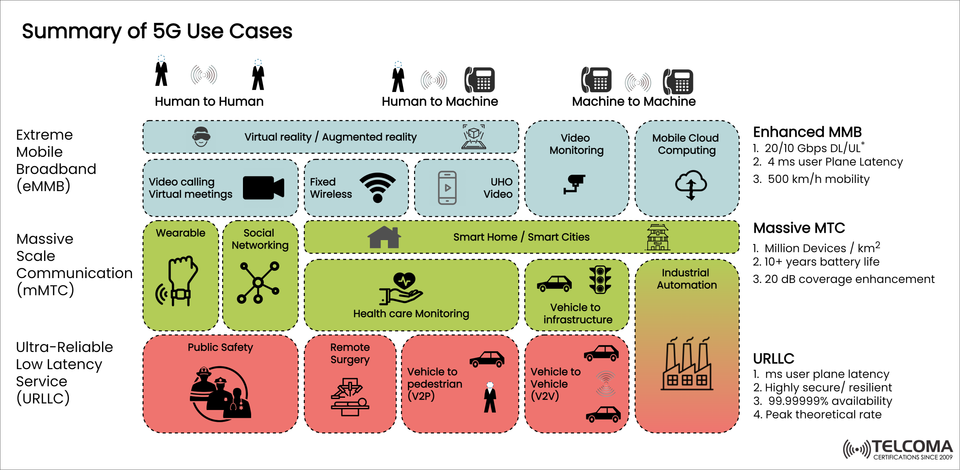
The image above shows three main categories of 5G use cases:
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband)
mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication)
URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication)
Let’s dive into each category, look at real-world applications, and see why 5G is a significant step forward for telecom experts and tech fans alike.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
eMBB focuses on delivering superior data speeds and greater capacity, making user interactions in data-heavy apps much better.
Key Features of eMBB
20/10 Gbps Download/Upload Speeds
4 ms User Plane Latency
500 km/h Mobility Support (perfect for high-speed trains and transport)
Use Cases for eMBB
Virtual Reality (VR) / Augmented Reality (AR): Creating seamless immersive experiences in gaming, education, and remote training.
Video Calling & Virtual Meetings: Ensuring crystal-clear communication, even in crowded areas.
Fixed Wireless Access: Providing high-speed internet to rural areas or places without fiber optics.
Ultra-High Definition (UHD) Video Streaming: Offering smooth 4K/8K viewing on mobile devices.
Video Monitoring: Delivering high-quality live feeds for both public safety and private security.
Mobile Cloud Computing: Allowing heavy applications to run on the cloud with minimal lag, freeing devices from hardware limits.
Impact:
eMBB improves user experience, helps close the digital gap, and opens up new business avenues in entertainment, education, and collaboration.
Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC)
mMTC is all about efficiently connecting billions of devices to support the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape.
Key Features of mMTC
1 Million Devices per km² Connectivity
10+ Years Battery Life (for low-power IoT devices)
20 dB Coverage Enhancement (improved reach indoors and in rural areas)
Use Cases for mMTC
Wearables: Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and health monitors that provide real-time data.
Social Networking for IoT Devices: Devices that can communicate and share data on their own.
Smart Homes & Smart Cities: Energy-efficient lighting, waste management, and interconnected infrastructure.
Healthcare Monitoring: Tools for remote patient care, chronic disease management, and elderly support.
Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I): Smart traffic systems that interact directly with vehicles.
Industrial Automation: Factories using IoT sensors for operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
Impact:
mMTC drives the IoT revolution, creating affordable and scalable smart ecosystems in healthcare, urban planning, and manufacturing.
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC)
URLLC aims for ultra-low latency (as low as 1 ms) and near-perfect reliability, making it essential for mission-critical applications where failure isn't an option.
Key Features of URLLC
1 ms User Plane Latency
Highly Secure & Resilient
99.999999% Availability (seven nines reliability)
Peak Theoretical Data Rates
Use Cases for URLLC
Public Safety: Real-time communications for emergency responders, ensuring guaranteed reliability.
Remote Surgery: Enabling doctors to perform operations with robotic help from distances far away.
Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P): Enhancing safety by allowing vehicles and pedestrians to communicate instantly.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V): Facilitating autonomous driving through seamless car-to-car communication.
Industrial Automation: Using precision robotics and real-time controls in manufacturing settings.
Impact:
URLLC provides dependability and trust in essential services, ensuring that critical and high-risk applications operate without fail.
5G Use Cases at a Glance
Here’s a quick overview of how the three key areas of 5G apply across different sectors:
Category | Key Features | Use Cases
eMBB | High speed (20 Gbps), low latency (4 ms), high mobility | VR/AR, UHD video, cloud gaming, video surveillance, mobile broadband
mMTC | 1M devices/km², long battery life, coverage enhancement | IoT, smart cities, healthcare monitoring, wearables, industrial automation
URLLC | 1 ms latency, high reliability (99.999999%), secure | Remote surgery, self-driving cars (V2V, V2P, V2I), public safety, robotics
Why 5G Use Cases Matter for Telecom Professionals
For telecom operators and network engineers, getting a grip on these use cases is crucial because:
Network Planning: You need infrastructure that can handle different needs (speed vs. density vs. reliability).
Revenue Models: Operators can find ways to profit from 5G through enterprise solutions, IoT platforms, and critical services.
Spectrum Utilization: Different uses require specific frequency bands (e.g., mmWave for eMBB, sub-6 GHz for mMTC).
Business Transformation: From smart factories to connected vehicles, telecom players will be key players in the digitization of various industries.
Conclusion: Building the Connected Future
5G isn’t just a step up from 4G—it’s a driving force behind digital transformation. With eMBB providing high-speed broadband, mMTC linking billions of IoT devices, and URLLC delivering mission-critical reliability, 5G is reshaping the future of healthcare, transport, smart cities, entertainment, and manufacturing.
Telecom pros face challenges in updating networks, innovating new business models, and guaranteeing secure, dependable infrastructure. For tech enthusiasts, 5G presents a realm of possibilities, from immersive experiences to smart automation.
5G as the Backbone of Tomorrow 5G goes beyond just faster downloads—it’s a game-changing technology that helps industries transition into connected, intelligent systems.
* eMBB will transform entertainment, education, and cloud computing.
* mMTC will drive the Internet of Things and the development of smart cities.
* URLLC will make sure essential services stay safe, dependable, and instantaneous.
For telecom experts, this is the time to innovate, lead in infrastructure, and explore new ways to make money. As for tech fans, with 5G, you can experience cutting-edge technologies right now. The future is faster, smarter, and more connected—and it’s all thanks to 5G.
