5G vs 4G: Performance Goals Compared Across Key Measures

Moving from 4G/LTE to 5G is a big step for mobile communication technology. While 4G did a great job making mobile broadband accessible, 5G takes it a whole lot further by aiming to create a super-connected environment. This includes super-fast data speeds, minimal latency, the ability to connect a ton of devices, and better energy efficiency.
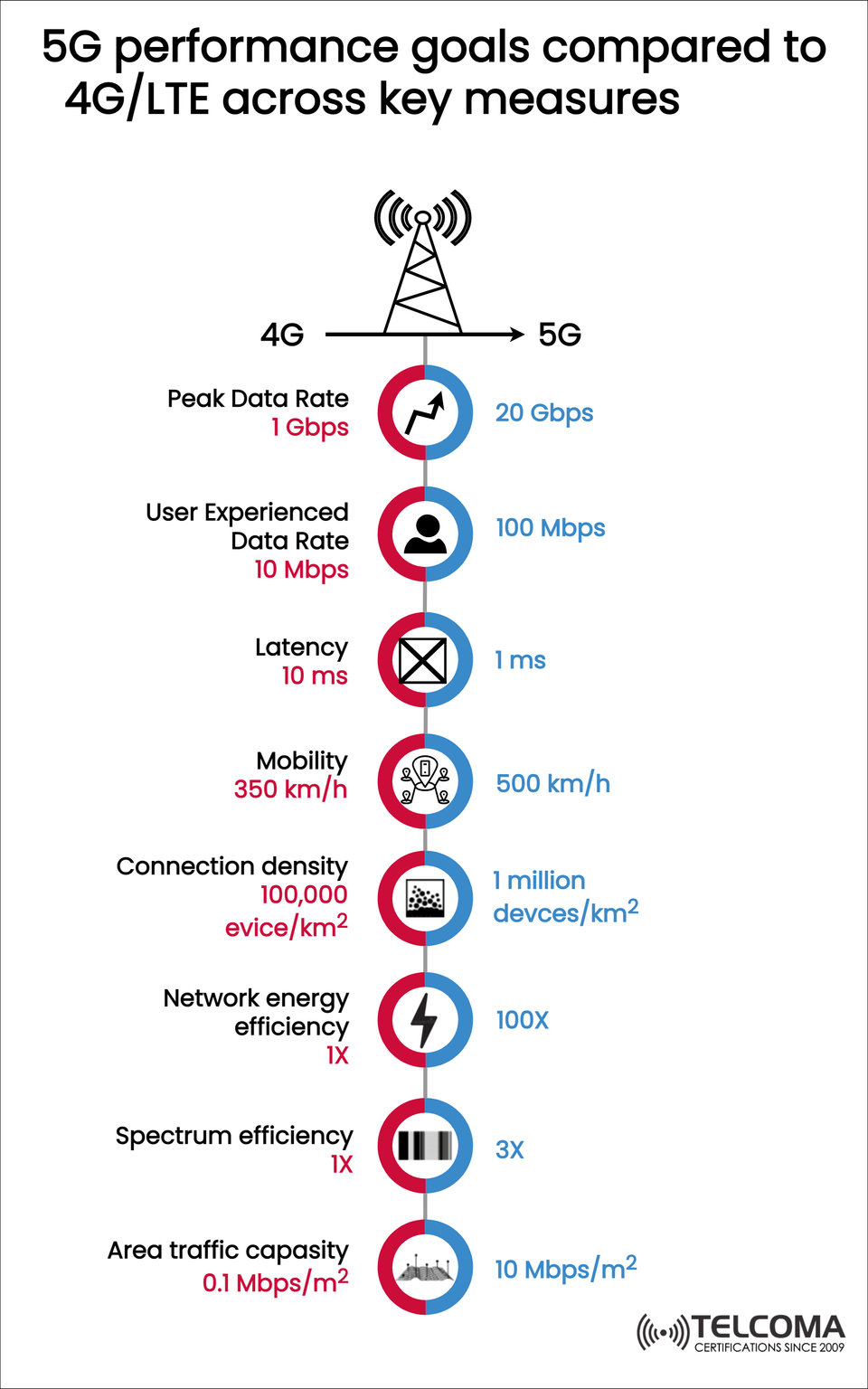
The uploaded infographic shows how 5G stacks up against 4G in key performance areas like peak data rates, latency, mobility, connection density, and spectrum efficiency. In this blog post, we'll dive into each of these performance metrics, discussing their technical significance, real-world applications, and why 5G is really something special for both industries and everyday users.
Peak Data Rate: 1 Gbps (4G) vs. 20 Gbps (5G)
The peak data rate is the highest speed a network can reach under perfect conditions.
4G LTE: Up to 1 Gbps in top-tier LTE setups.
5G NR: Aims for 20 Gbps, which means super-fast downloads and smooth high-res video streaming.
Why it matters:
Supports 8K video streaming without any annoying buffering.
Enables real-time AR/VR experiences.
Cuts down file download times from minutes to just seconds.
User Experienced Data Rate: 10 Mbps (4G) vs. 100 Mbps (5G)
This rate shows the actual speeds people experience in everyday situations.
4G LTE: Average around 10 Mbps, which can vary depending on how busy the network is.
5G NR: Promises a baseline of 100 Mbps, making sure you get consistent quality.
Benefits:
Smooth video calls even when the place is crowded.
Better support for remote work and online learning.
Reliable connections for smart cities and IoT applications.
Latency: 10 ms (4G) vs. 1 ms (5G)
Latency is about how long it takes for data to move from point A to point B.
4G LTE: About 10 milliseconds.
5G NR: Aims for just 1 millisecond, almost like real-time communication.
Applications:
Self-driving cars need instant decisions.
Remote surgeries where every second counts.
Cloud gaming and AR/VR with barely any lag.
Mobility: 350 km/h (4G) vs. 500 km/h (5G)
Mobility performance shows how well a network can keep a connection at high speeds.
4G LTE: Up to 350 km/h, which is fine for trains and airplanes.
5G NR: Boosts this to 500 km/h, perfect for high-speed trains.
Use Cases:
Reliable connections for bullet trains.
Ensures steady service for travelers and logistics.
Connection Density: 100,000 devices/km² (4G) vs. 1 million devices/km² (5G)
Connection density tells us how many devices can hook up in a square kilometer.
4G LTE: Can handle up to 100,000 devices/km².
5G NR: Can handle up to 1 million devices/km².
Significance:
Key for massive IoT (mIoT) rollouts.
Enables smart cities with connected vehicles, sensors, and more.
Supports industrial automation with tons of machines hooked up simultaneously.
Network Energy Efficiency: 1X (4G) vs. 100X (5G)
Energy efficiency is all about how well a network delivers data for every unit of energy used.
4G LTE: The baseline standard.
5G NR: 100 times more energy efficient.
Impact:
Cuts down operational costs for network providers.
Makes way for green networking to lessen carbon footprints.
Increases battery life for IoT devices in remote areas.
Spectrum Efficiency: 1X (4G) vs. 3X (5G)
Spectrum efficiency measures how much data can be sent through a certain bandwidth.
4G LTE: The reference point (1X).
5G NR: Reaches 3X spectrum efficiency.
Importance:
Makes the most out of limited spectrum resources.
Enhances user experience, even in busy city areas.
Allows better sharing of spectrum across different services.
Area Traffic Capacity: 0.1 Mbps/m² (4G) vs. 10 Mbps/m² (5G)
Area traffic capacity refers to the total data throughput available per square meter.
4G LTE: 0.1 Mbps/m².
5G NR: 10 Mbps/m², which is a 100x increase.
Relevance:
Vital for stadiums, concerts, and big events.
Ensures solid connectivity in high-density urban areas.
Boosts productivity in industrial and enterprise settings.
Tabular Summary: 5G vs 4G Performance Goals
Metric | 4G LTE | 5G NR
Peak Data Rate | 1 Gbps | 20 Gbps
User Experienced Data Rate | 10 Mbps | 100 Mbps
Latency | 10 ms | 1 ms
Mobility | 350 km/h | 500 km/h
Connection Density | 100,000 devices/km² | 1 million devices/km²
Network Energy Efficiency | 1X | 100X
Spectrum Efficiency | 1X | 3X
Area Traffic Capacity | 0.1 Mbps/m² | 10 Mbps/m²
Streamlined Blog Structure (with keyword integration)
Kick off with a comparison of 5G and 4G performance * Make sure to introduce the main keyword right at the start.
Comparing 5G and 4G speeds (Peak Data Rate and User Experience Rate) * Include variations like “5G peak data rate” and “user-experienced data rate in 5G” naturally.
Latency advantages of 5G over 4G * Use keywords such as “ultra-low latency in 5G” and “5G for real-time applications”.
Mobility and connectivity differences between 5G and LTE * Include keywords like “5G mobility support” and “connection density in 5G networks”.
Energy efficiency and spectrum enhancements in 5G * Keywords here include “5G spectrum efficiency” and “green telecom networks”.
5G traffic capacity and its practical benefits * Use keywords like “5G vs 4G traffic capacity” and “dense network environments”.
Conclusion – Overview of 5G performance objectives * Emphasize: “5G vs 4G comparison” and “5G performance metrics”.
Conclusion
Looking at how 5G compares to 4G across these key areas shows that 5G is more than just a bump in speed. With data rates that are 20 times faster, latencies reduced by 10 times, the ability to connect 100 times more devices, and energy efficiency that's 100 times better, 5G is built to enable future innovations in IoT, self-driving cars, smart cities, telemedicine, and beyond.
For telecom pros, these metrics are crucial for planning deployments. And for tech lovers, they reveal the vast possibilities of 5G in changing how we live digitally.
In short, 5G isn't just an evolution—it’s a revolution.
