5G vs 4G vs Wi-Fi 6 vs NB-IoT: Comparing Wireless Technologies

5G vs 4G vs Wi-Fi 6 vs NB-IoT: A Deep Dive into Wireless Technologies
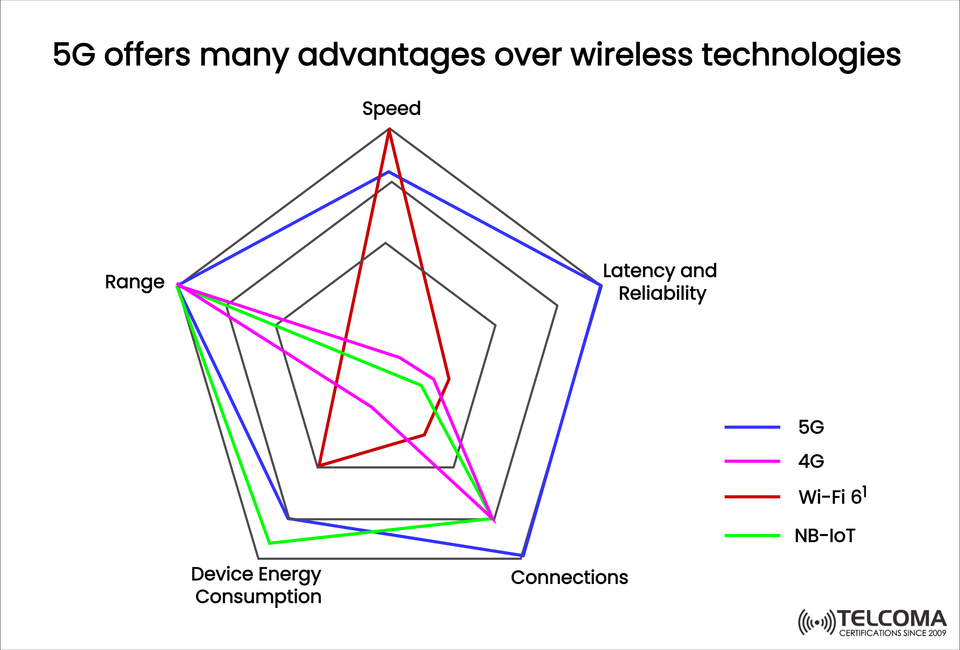
The world of telecommunications is changing fast, with different wireless technologies existing side by side to cater to various connectivity needs. The chart we've uploaded compares 5G, 4G, Wi-Fi 6, and NB-IoT across five important factors:
Speed
Latency & Reliability
Connections
Device Energy Consumption
Range
For tech buffs and telecom experts, getting a handle on these trade-offs is key for network strategies, app development, and planning for future infrastructure.
Let’s dive into each technology and see how they stack up.
Speed: 5G Takes the Lead, Wi-Fi 6 Shines Locally
5G: Offers peak downlink speeds of up to 20 Gbps, paving the way for 8K streaming, cloud gaming, AR/VR, and sophisticated enterprise apps.
Wi-Fi 6: Competes closely, reaching speeds of up to 9.6 Gbps, but is limited to local area coverage.
4G LTE: Tops out around 1 Gbps (when using LTE Advanced Pro), which is fine for HD streaming but not ideal for immersive experiences.
NB-IoT: Designed for IoT sensors, it offers low throughput (from tens of kbps to about 250 kbps).
Verdict: For broad, ultra-fast connectivity, 5G is the standout, while Wi-Fi 6 excels in local high-speed environments like offices or homes.
Latency and Reliability: A Game Changer
5G: Hits latency as low as 1 ms, which is crucial for self-driving cars, critical services, and remote surgeries. Its reliability comes from URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications).
Wi-Fi 6: Offers improved latency of around 10 ms, good for gaming and local real-time tasks, but falls short of 5G’s reliability in critical scenarios.
4G: Has a latency of 30–50 ms, fairly good for browsing and streaming, but not suitable for newer real-time IoT needs.
NB-IoT: Shows high latency (can be several seconds), which is acceptable for non-time-sensitive IoT tasks like smart meters but definitely not ideal for critical applications.
Verdict: 5G is the clear winner here, with unmatched reliability and ultra-low latency, vital for next-gen applications.
Connections: Scaling for the IoT Boom
5G: Can handle up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, essential for smart cities, connected factories, and dense urban IoT setups.
NB-IoT: Likewise aimed at massive IoT, supporting tens of thousands of devices per cell site, perfect for low-data-rate IoT.
4G: Can manage fewer simultaneous connections (~100,000 devices per km² in LTE-M), making it less scalable.
Wi-Fi 6: Supports more devices per access point compared to Wi-Fi 5, but still can’t keep up with cellular networks due to local spectrum constraints and interference.
Verdict: 5G and NB-IoT are ahead in scaling IoT connections, while 4G and Wi-Fi 6 lag behind.
Device Energy Consumption: NB-IoT Excels
NB-IoT: Optimized for ultra-low power consumption, allowing IoT devices to run for up to 10 years on a single battery.
5G: More energy-efficient than 4G thanks to network slicing and better power management, though its IoT devices still use more power than NB-IoT.
4G: Uses more energy than 5G for similar functions, which reduces efficiency for IoT applications.
Wi-Fi 6: Introduces Target Wake Time (TWT) to enhance battery life for connected devices but still doesn’t match the efficiency of NB-IoT.
Verdict: For battery-powered IoT sensors, NB-IoT takes the crown.
Range: The Coverage Game
4G: Offers wide global coverage and solid indoor penetration.
5G: Delivers great range in low- and mid-band frequencies but has issues in mmWave bands (shorter range, struggles with walls).
NB-IoT: Provides excellent deep indoor coverage and long-range rural coverage, making it ideal for remote IoT projects.
Wi-Fi 6: Limited to local indoor setups, with a shorter range compared to cellular options.
Verdict: For global coverage and IoT in remote areas, NB-IoT and 4G still play important roles. Meanwhile, 5G is quickly scaling up for the future.
Side-by-Side Comparison Table
Feature5G4G LTE Wi-Fi 6NB-IoTSpeedUp to 20 Gbps Up to 1 Gbps Up to 9.6 Gbps~250 kbpsLatency~1 ms30–50 ms~10 ms High (seconds)Connections1M devices/km²~100k devices/km²Limited (AP-based)High (tens of thousands)Energy Efficiency High (IoT-friendly)Moderate Moderate (TWT feature)Excellent (10-year battery)Range Good (mmWave limits apply)Excellent Local (short range)Excellent (rural/indoor)
Why 5G Has the Edge Over Wireless Technologies
The chart really shows it: 5G outshines most key metrics, especially in speed, latency, reliability, and scalability.
But every technology has its strengths:
Wi-Fi 6 → Ideal for local high-speed indoor networks.
NB-IoT → Best for long-lasting, low-data IoT sensors.
4G → Still relevant for coverage and backup connectivity.
So rather than replacing each other, these technologies work together to meet different needs.
Real-World Use Cases
5G: Cloud gaming, self-driving cars, AR/VR, smart factories.
4G: Global connectivity, basic IoT tasks, rural access.
Wi-Fi 6: Office spaces, smart homes, high-speed LANs.
NB-IoT: Smart meters, agricultural sensors, asset tracking.
This layered ecosystem guarantees optimized connectivity for every application.
Conclusion
The comparison of 5G, 4G, Wi-Fi 6, and NB-IoT clearly shows that 5G offers the most benefits, particularly in speed, latency, and scalability.
5G is the frontrunner in performance and future-proofing.
Wi-Fi 6 shines indoors with high speeds.
NB-IoT is unbeatable for low-power, large-scale IoT setups.
4G continues to provide crucial global coverage.
For telecom pros and tech enthusiasts, the main takeaway is that 5G isn't replacing existing wireless technologies—instead, they're all co-existing to fulfill unique roles in the connected ecosystem.
