5G vs 6G: A Comparison of Verticals, Capabilities, and Future Potential

5G vs 6G: Comparing the Verticals, Capabilities, and Future Potential
As the telecom landscape evolves, it’s becoming essential for both tech fans and industry experts to differentiate between 5G and 6G. We've already seen 5G shake up connectivity with features like enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC), and Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC), but the upcoming generation is set to take things even further.
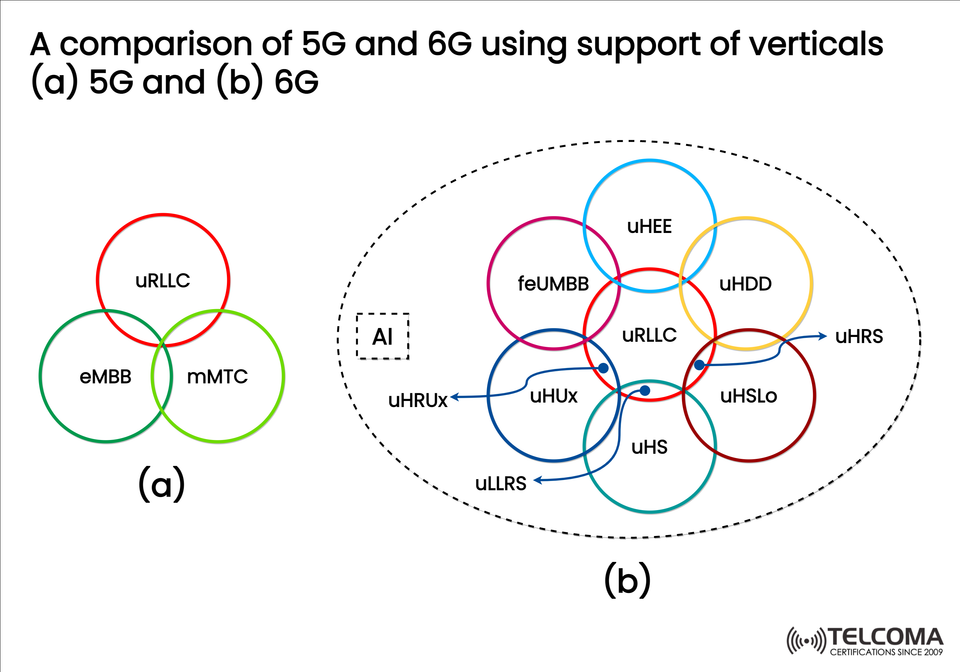
Check out the uploaded diagram for a visual breakdown:
5G (a): Centers on three core areas: eMBB, URLLC, and mMTC.
6G (b): Broadens the scope with various AI-driven sectors, including holographic communication, human-focused services, and ultra-reliable low-latency systems.
In this article, we’ll dive into these sectors and examine how 6G builds on the groundwork laid by 5G to unveil fresh opportunities.
The Three Pillars of 5G
5G stands on three critical service categories, often referred to as the 5G triangles.
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband): * Focus: High data rates and large capacity. * Applications: Streaming in 4K/8K, VR/AR, cloud gaming. * Significance: Forms the backbone of high-speed consumer data.
URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication): * Focus: Essential services needing sub-millisecond latency. * Applications: Self-driving cars, remote surgeries, automation in industry. * Significance: Guarantees dependability and quick responses in high-stakes settings.
mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication): * Focus: Connecting billions of IoT devices. * Applications: Smart cities, agricultural sensors, tracking for logistics. * Significance: Facilitates extensive IoT deployments while being energy efficient.
These components have been crucial during 5G rollouts across different sectors, but their limits in scalability, adaptability, and intelligence signal a need for growth.
Transitioning to 6G Verticals
6G isn’t merely enhancing the original three pillars of 5G; it broadens the framework with new verticals. The diagram depicts various intersecting domains that are reshaping future use cases.
Important 6G Verticals and Their Functions
feUMBB (Fully Enhanced Ultra Mobile Broadband): * An evolution of eMBB providing Tbps-level speeds. * Supports immersive XR, holographic communication, and ultra-high-res media.
uHEE (Ultra High Energy Efficiency): * Aims for eco-friendly networking with low-energy per bit transmission. * In line with global net-zero and green telecom initiatives.
uHDD (Ultra High Data Density): * Handles massive amounts of simultaneous data flow. * Essential for smart factories, healthcare IoT, and communications in space.
uHS (Ultra High Security): * Features quantum-safe encryption and AI-based security monitoring. * Tailored for critical sectors like finance, defense, and healthcare.
uHSLo (Ultra High Service Localization): * Offers centimeter-level positioning accuracy. * Key for applications in autonomous drones, robotics, and smart transport.
uHRS (Ultra High Reliability Services): * Increases reliability metrics beyond what 5G’s URLLC offers. * Vital for emergency responses, aviation, and industrial robotics.
uHUx (Ultra Human-Centric eXperience): * Focuses on human-sensory integration, encompassing touch, smell, and real-time holographic presence. * Moves beyond screen interactions to create multisensory internet experiences.
uHRUx (Ultra High Rate Ubiquitous eXperience): * Guarantees seamless, high-speed connectivity everywhere — from remote villages to space communication.
uLLRS (Ultra Low Latency Reliable Services): * Enhances URLLC by achieving sub-millisecond, deterministic latency. * Critical for the future tactile internet and brain-machine interfaces.
AI's Role in 6G
The diagram highlights how AI (Artificial Intelligence) is central to 6G. Unlike its role in 5G, where AI was mostly about optimization, 6G takes it to the next level:
AI-Native Design: Networks are built with AI-driven architectures at their core.
Autonomous Operations: Networks will be self-optimizing, self-healing, and self-scaling.
Data-Aware Services: Instant adjustments for traffic, quality of service (QoS), and security threats.
User-Centric Customization: AI tailors services to users’ habits, allowing personalized holographic or tactile experiences.
AI is set to transform 6G from just a communication network into a smart ecosystem.
Key Differences: 5G vs 6G Verticals
Here’s a straightforward comparison:
Aspect 5G Verticals (a) 6G Verticals (b) Broadband eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) feUMBB (Fully Enhanced UMB with Tbps speeds) Reliability & Latency URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) uLLRS (Ultra Low Latency Reliable Services), uHRS (Ultra High Reliability Services) Mass Connectivity mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication) uHDD (Ultra High Data Density), IoT-centric layers Energy Efficiency Not a core focus uHEE (Ultra High Energy Efficiency) Security Standard encryption, limited AI uHS (Ultra High Security), quantum-safe protocols User Experience High speed + low latency uHUx (Human-Centric eXperience), uHRUx (Ubiquitous Experience) Positioning Limited to meters-level accuracy uHSLo (Service Localization at cm-level accuracy) AI Integration Supportive role AI-native, embedded across all verticals
Why 6G Verticals Matter
The introduction of new verticals in 6G isn’t just about faster speeds — it's a significant shift in focus:
Sustainability First: uHEE ensures that networks are energy-efficient.
Security Built-In: uHS offers protection against advanced threats for critical services.
Immersive Services: uHUx allows for holographic meetings and multisensory interactions.
Reliability at Scale: uLLRS and uHRS provide assurances for essential environments.
Precision Connectivity: uHSLo guarantees centimeter-level accuracy, which is crucial for autonomous systems.
These new verticals illustrate how 6G meets societal, industrial, and human-focused demands far beyond what 5G offered.
Real-World Applications of 6G Verticals
Healthcare: Remote surgeries using tactile internet and holographic consultations.
Industry 5.0: Collaboration between humans and robots in factories with ultra-reliable low-latency systems.
Smart Cities: AI-managed traffic, precise navigation, and eco-friendly infrastructure.
Immersive Media: Real-time holographic entertainment and immersive XR experiences.
Space Communications: Networks that connect satellites and land-based systems for comprehensive coverage.
Challenges Ahead
Though there's a lot of promise, rolling out these 6G verticals won’t be without its hurdles:
Spectrum Scarcity: Efficient management of terahertz and visible light spectrum will be essential.
Energy Demands: Even with uHEE, the heavy data loads and AI-driven tasks may still require high energy.
Interoperability: Standardization across borders and industries is vital.
Privacy Risks: The personalized nature of AI raises ethical concerns.
Conclusion
Looking at the 5G and 6G verticals highlights how connectivity is evolving from three fundamental pillars (eMBB, URLLC, mMTC) to a complex AI-driven ecosystem of advanced services (uLLRS, uHUx, feUMBB, and beyond).
6G isn’t just about speed — it’s smarter, more sustainable, and human-focused. For those in telecom, the big takeaway is clear: get ready for networks that don’t just connect devices but create intelligent, immersive, and ultra-reliable experiences.
By 2030, these verticals will shape the way we communicate, collaborate, and innovate — solidifying 6G as the true backbone of a connected future.
