5GCAR Project: Four Key 5G Use Case Classes for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles

5GCAR Project: Four Key 5G Use Case Classes for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles
The emergence of 5G-enabled intelligent transport systems (ITS) is changing how vehicles interact with their surroundings, including infrastructure and pedestrians. A leading initiative in this area is the 5GCAR project, which focuses on developing and assessing advanced Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) use cases.
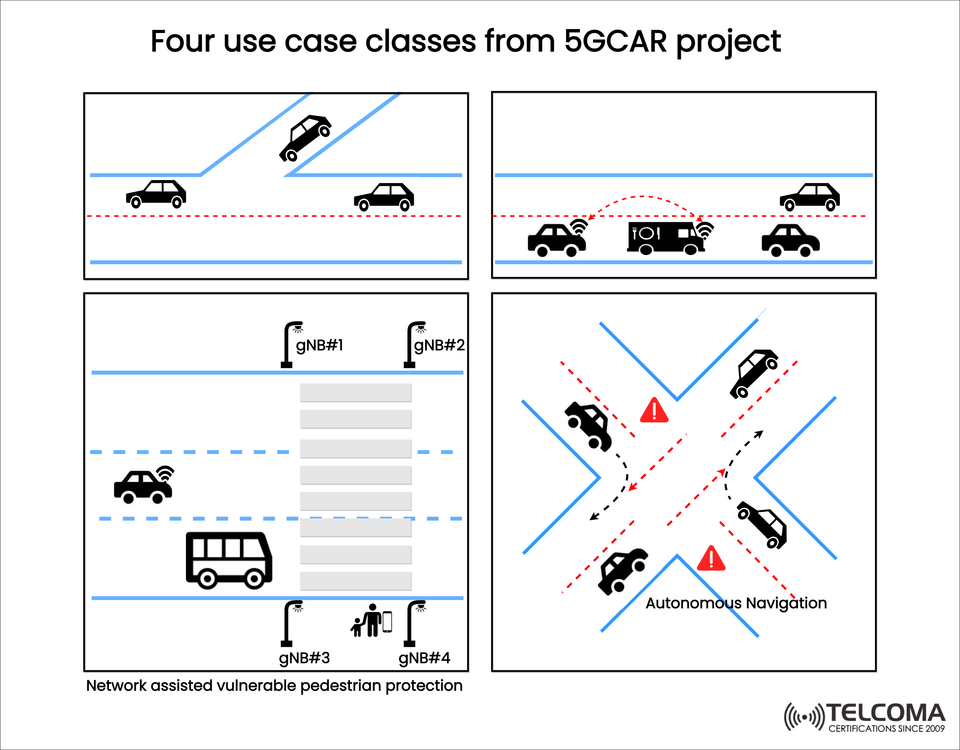
The image above showcases four use case classes from the 5GCAR project, each tackling significant safety, efficiency, and automation issues. These cases illustrate how 5G’s ultra-low latency, high reliability, and massive connectivity are crucial for future mobility.
What is the 5GCAR Project?
The 5GCAR (5G Communication Automotive Research) project is a European research effort aimed at defining and testing 5G V2X services. The aim is to create a comprehensive ecosystem that:
Promotes road safety.
Enhances traffic efficiency.
Facilitates autonomous vehicle operations.
Utilizes 5G KPIs like less than 1 ms latency, high throughput, and improved reliability.
This project sorts use cases into four main categories, each representing a unique mobility scenario.
Cooperative Maneuvering
Description:
Vehicles coordinate with one another and roadside units to perform maneuvers like lane changes, merging onto highways, or overtaking safely and efficiently.
How it Works:
Vehicles send their position, speed, and trajectory data through 5G.
This real-time communication enables cooperative decision-making.
Network support ensures messages are reliably delivered, even in heavy traffic.
Example Applications:
Merging assistance on busy highways.
Platooning coordination where vehicles follow closely behind each other.
5G Role:
Thanks to ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), safety-critical instructions can be sent within milliseconds to prevent collisions.
Cooperative Sensing (Sensor Sharing)
Description:
Vehicles, infrastructure, and other road users exchange sensor data (like camera, radar, and LiDAR) to form a shared perception of the environment.
How it Works:
A bus or truck that blocks a driver's view can share its camera feed with nearby cars.
Detection of pedestrians and cyclists is enhanced by combining data from various sensors.
Network-assisted communication allows perception to extend beyond the direct line of sight.
Example Applications:
Identifying vehicles obscured by obstacles.
Sharing real-time video or radar data with surrounding vehicles.
5G Role:
The high data rate of 5G (eMBB) makes exchanging large amounts of sensor data feasible, while low latency ensures timely information delivery for critical safety decisions.
Network-Assisted Vulnerable Road User Protection
Description:
5G allows vehicles to detect and protect vulnerable road users (VRUs)—like pedestrians, cyclists, or scooter riders—even in tricky situations.
How it Works:
Roadside units (gNBs) use sensors or device-to-network communication to identify VRU presence.
Pedestrians with smartphones can send safety warnings to nearby vehicles.
Cars can be alerted to slow down or stop to avoid accidents.
Example Applications:
Detecting pedestrians crossing near schools or bus stops.
Warning systems for cyclists at tricky intersections.
5G Role:
Connecting massive numbers of devices (mMTC) ensures scalability, while URLLC makes sure alerts are received without delay.
Autonomous Navigation with Network Support
Description:
Vehicles use 5G connectivity to boost their autonomous navigation capabilities, especially in complex urban settings like busy intersections.
How it Works:
Cars exchange trajectory data at intersections to avoid bumps.
Roadside infrastructure adds extra context, like traffic light statuses or warnings about accidents.
Cooperative algorithms decide the safest and most efficient routes for all vehicles.
Example Applications:
Safely crossing intersections with limited visibility.
Coordinated navigation in areas with heavy traffic.
5G Role:
With its low-latency communication and high reliability, 5G makes sure that autonomous vehicles are updated promptly and can react immediately to changes around them.
Technical Requirements Across the Four Use Cases
The success of these 5GCAR use cases hinges on 5G KPIs, such as:
Latency: Less than 1 ms for crucial safety decisions.
Reliability: Over 99.999% for dependable communication.
Data Rate: Multi-Gbps for real-time video/sensor sharing.
Connection Density: Millions of devices per km² for large-scale IoT.
Mobility Support: Up to 500 km/h for highway scenarios.
Benefits of 5GCAR Use Cases
Better Road Safety: Early alerts help prevent accidents.
Traffic Efficiency: Cooperative maneuvers ease congestion.
Enhanced User Experience: Reliable communication makes navigation smoother.
Support for Autonomous Vehicles: Safeguarding self-driving cars in complicated environments.
Challenges and Considerations
Even though there’s a lot of promise, putting these 5GCAR use cases into action comes with its own set of challenges:
Infrastructure Costs: It needs a dense network of 5G gNBs.
Interoperability: Different manufacturers’ vehicles and devices must work together seamlessly.
Data Privacy: Sharing sensor and location data has to adhere to strict privacy regulations.
Security Risks: Increased points of potential attack in V2X networks demand robust encryption and authentication.
Conclusion
The 5GCAR project lays out a roadmap for how 5G networks are set to transform connected mobility. By outlining use cases in cooperative maneuvering, cooperative sensing, pedestrian safety, and autonomous navigation, it highlights the importance of ultra-reliable, low-latency, and high-capacity communication.
For tech enthusiasts, these scenarios illustrate how 5G goes beyond smartphones, improving real-world safety and automation. For telecom professionals, they reveal the essential network design and KPI requirements that will help make connected and autonomous driving a reality.
As 5G V2X continues to roll out globally, the insights from 5GCAR will help steer the industry towards safer roads, smarter cities, and fully autonomous transport networks.
