6G Architecture Explained: Designing the Next Wireless Generation Beyond 5G
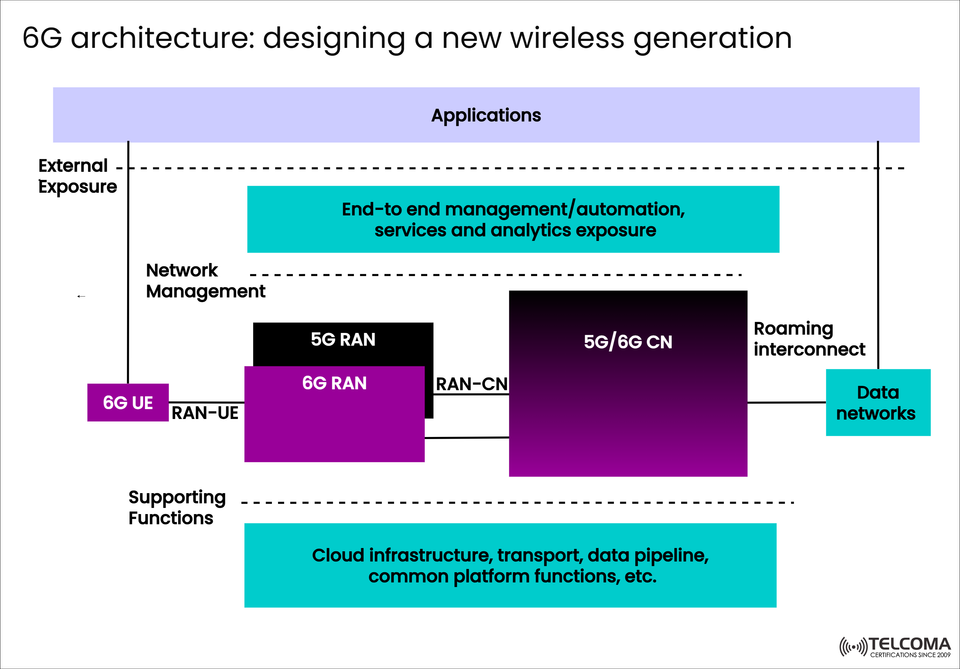

6G Architecture: Crafting the Next Era of Wireless Communication
As we move from 5G to 6G, the emphasis is shifting from just better connectivity to creating smart, self-managing networks that can predict issues and integrate smoothly between physical and digital worlds.
The image titled “6G architecture: crafting the next era of wireless communication,” visually captures this shift. It shows how 6G builds on the current 5G setup by incorporating automation throughout, AI management, cloud systems, and a unified RAN-CN interaction—all aimed at developing a self-optimizing, service-oriented ecosystem.
Moving from 5G to 6G: A Shift in Network Design Paradigms
From Connectivity to Intelligence
While 5G emphasized high bandwidth, low latency, and extensive IoT capabilities, 6G takes it further by embedding intelligence, automation, and contextual awareness throughout the network.
Think of the 6G architecture not as a sudden change, but more like a layered improvement to 5G, where the two generations can work side by side. The diagram shows 5G RAN and 6G RAN working together through a shared 5G/6G Core Network (CN)—this keeps everything compatible while paving the way for next-gen services.
Key Elements of the 6G Architecture
The 6G network is structured around five main functional layers as shown in the image:
Applications Layer
External Exposure and Network Management
RAN Layer (5G RAN + 6G RAN)
Core Network Layer (5G/6G CN)
Supporting Cloud Infrastructure
Each layer plays a crucial role in delivering end-to-end intelligence, ultra-low latency, and global service orchestration.
6G User Equipment (6G UE)
At the heart of this architecture is the 6G UE (User Equipment)—the gateway to the network. These devices are expected to:
Handle multi-band communication, from sub-6 GHz all the way to terahertz (THz) frequencies.
Allow for AI-driven signal optimization right at the device level.
Combine sensing, computing, and communication functions, becoming part of the larger “connected intelligence” ecosystem.
Unlike traditional devices, 6G UEs will function as active nodes in the network, carrying out data processing, environmental sensing, and real-time context sharing.
6G RAN: Redefining Access Connectivity
The Radio Access Network (RAN) layer is where 6G brings its most notable innovations. The diagram illustrates the coexistence of 5G RAN and 6G RAN, connected to the 5G/6G Core Network (CN) via the RAN-CN interface.
What’s New in 6G RAN:
AI-Driven RAN: Integrated AI enhances spectrum allocation, beamforming, and energy usage.
Cell-Free Massive MIMO: Ditches traditional cell limits, letting users connect to several distributed antennas at once.
Joint Communication and Sensing (JCAS): RANs act as sensors, enabling smart applications like gesture control, AR, and autonomous navigation.
Combined Terrestrial and Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN): Ensures uninterrupted connectivity via satellites, UAVs, and High Altitude Platform Systems (HAPS).
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS): Smart surfaces that dynamically adjust to enhance coverage and energy efficiency.
All these advancements create a cognitive network fabric that learns and evolves based on user behavior and environmental conditions.
5G/6G Core Network (CN): The Brain of Smart Connectivity
The 5G/6G Core Network serves as the architectural brain of next-gen communication. Designed to be cloud-native, service-based, and distributed, it seamlessly manages both 5G and 6G traffic.
Core Features of the 5G/6G CN:
Service-Based Architecture (SBA): Modular and scalable components handle functions like authentication and data management.
Multi-Access Convergence: Manages simultaneous access from 5G RAN, 6G RAN, and non-terrestrial sources.
AI-Driven Orchestration: Automates the management of network slices, functions, and resources.
Zero-Touch Operations (ZTO): Uses intention-based algorithms for self-configuration and problem resolution.
Quantum-Safe Security: Implements quantum-resistant encryption for future-proof security.
By enabling both 5G and 6G connectivity, this hybrid CN guarantees a smooth transition while keeping services available.
Key Abilities:
Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF): Collects real-time data to forecast congestion, faults, and performance issues.
AI/ML-based Automation: Facilitates closed-loop orchestration between RAN and Core.
Exposure Function (NEF): Supplies secure APIs for external developers to tap into network capabilities.
Intent-Based Management: Operators specify outcomes (“ensure 1 ms latency for AR users”), and the network automatically configures to achieve them.
This layer effectively turns the 6G network into a self-aware, self-healing digital entity, ready to adapt to changing service demands.
Supporting Functions: The Cloud-First Foundation
The Supporting Functions layer—shown at the bottom of the image—forms the infrastructure backbone of the 6G network.
Core Elements Include:
Cloud Infrastructure: Containerized setups for quick deployment and scaling of network functions.
Transport Network: High-capacity, software-defined pathways for backhaul and fronthaul.
Data Pipeline: Supports AI training, analytics, and context-aware decision-making.
Common Platform Functions: Handle security, orchestration, telemetry, and lifecycle management.
In 6G, this infrastructure is completely disaggregated and virtualized, enabling the network to adapt and grow as new services come to life.
External Exposure and Data Network Interconnect
The image also presents an External Exposure interface that connects the network with Applications and Data Networks.
External Exposure Functions:
Allow third-party developers and industry sectors (like automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing) to directly integrate with the network via APIs.
Support network-as-a-service (NaaS) business models.
Enable cross-domain orchestration with cloud, edge, and enterprise systems.
Through Roaming Interconnect, the 6G core links to global data networks, guaranteeing consistent service and policy compliance across the board.
AI, Automation, and the Vision for 6G
Artificial Intelligence isn’t just an add-on in 6G—it’s woven into every layer of the network.
AI-Driven Features Include:
Autonomous Network Management: Predictive analytics for proactive fault recovery.
Cognitive Resource Allocation: Spectrum and power are optimized on the fly.
Contextual Services: The network adjusts quality of service based on user location, device type, or application needs.
Collaborative Learning: Distributed AI nodes across edge, core, and devices share insights for quicker adaptation.
This blend of capabilities turns 6G into a self-learning, adaptive system that keeps pace with user expectations.
Closing Thoughts: Laying the Groundwork for Smart Connectivity
The 6G architecture signifies a significant leap toward networks that think, adapt, and grow.
As the diagram shows, its layered setup—bringing together 5G RAN coexistence, AI-led management, cloud-native infrastructure, and service exposure—creates the framework for a genuinely cognitive wireless ecosystem.
6G is set to do more than just connect devices; it will link intelligence, experiences, and realities. By integrating automation, AI, and sensing capabilities, 6G networks will serve as the nervous system of the digital universe, facilitating breakthroughs in holographic communication, industrial robotics, and immersive metaverse experiences.
