6G Goals Explained: How the Next Generation of Wireless Will Surpass 5G

6G Goals: The Roadmap to the Next Generation of Wireless Networks
The jump from 4G to 5G was a real game changer, bringing ultra-fast mobile broadband, better IoT integration, and low-latency apps. But as the world’s craving for data keeps growing and new uses pop up, the industry is already looking ahead to 6G.
6G isn’t just about faster internet. It’s about building a programmable, sustainable, and smart communications ecosystem that can back immersive technologies like holographic communications, tactile internet, and AI-driven networks.
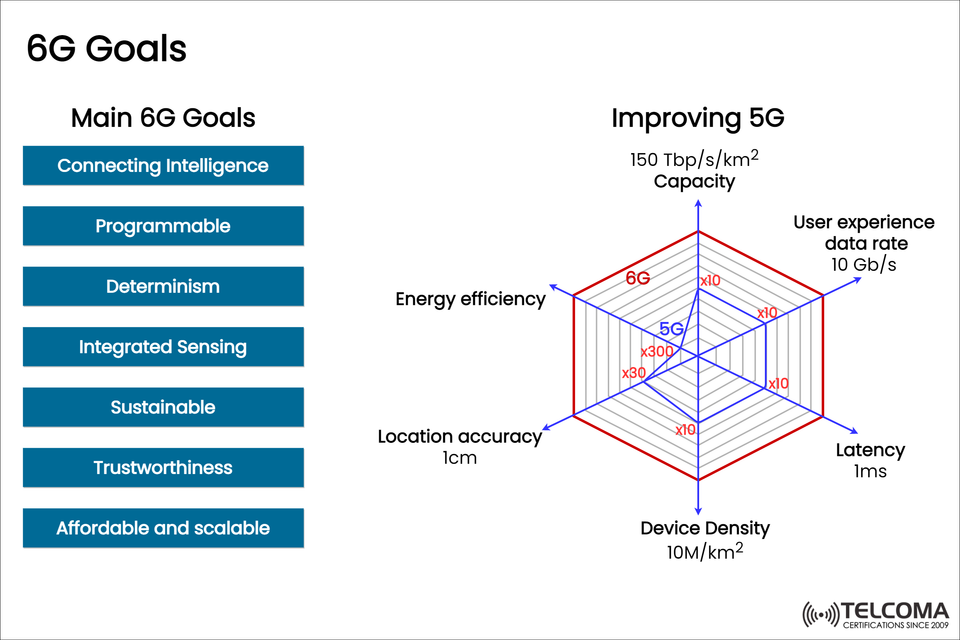
The diagram included lays out a clear path for 6G goals, showcasing its key pillars and how it steps up from 5G in terms of capacity, latency, energy efficiency, accuracy, and scalability.
The Main Goals of 6G
Unlike what we saw in earlier generations, 6G focuses on more than just throughput — it’s about overall performance. According to the chart, here are the main goals for 6G:
Connecting Intelligence: Making AI part of the network so it can optimize itself and make decisions on its own.
Programmable: These networks will be highly adaptable, able to adjust resources as needed for different services.
Determinism: This means guaranteed performance and reliable latency for essential applications.
Integrated Sensing: Merging communication capabilities with sensing for things like self-driving cars and digital twins.
Sustainable: Creating energy-efficient and eco-friendly infrastructure.
Trustworthiness: Delivering secure, transparent, and privacy-respecting connectivity.
Affordable and Scalable: Keeping deployment costs low so that these benefits are available worldwide, not just in big cities.
These goals emphasize that 6G is much more than just a faster version of 5G — it’s a whole new platform for the next wave of applications.
Improving Over 5G: The Key Metrics
The radar chart in the image compares the expected performance improvements from 5G to 6G across six key areas. Here’s a breakdown:
- Capacity: 150 Tbps/km²
5G: Offers decent capacity but struggles in very crowded situations.
6G Goal: Targeting up to 150 terabits per second per square kilometer, allowing for super-dense connectivity in smart cities, stadiums, and industrial areas.
Impact: This will support billions of devices, real-time holograms, and highly interconnected societies.
- User Experience Data Rate: 10 Gbps
5G: Delivers user data rates around 1 Gbps.
6G Goal: Aiming for a 10x increase to 10 Gbps per user, which will make things like seamless 8K/16K streaming, VR/AR, and holographic communications a reality.
- Latency: 1 ms (or lower)
5G: Typically around ~10 ms latency, with URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) working toward 1 ms.
6G Goal: Aiming for universal, deterministic 1 ms latency, opening doors for tactile internet, remote surgeries, and real-time control of industrial processes.
- Device Density: 10M/km²
5G: Supports about 1 million devices per square kilometer.
6G Goal: A 10x increase, targeting 10 million devices/km².
Use Case: Think smart factories, IoT ecosystems, and networks for self-driving vehicles.
- Location Accuracy: 1 cm
5G: Typically offers meter-level accuracy.
6G Goal: Improving this to 1 cm accuracy.
Impact: This is essential for indoor navigation, drone operation, AR overlays, and smart healthcare monitoring.
- Energy Efficiency
5G: Made strides compared to 4G, but still faces challenges due to heavy data traffic.
6G Goal: Striving for at least 30x–300x better energy efficiency, ensuring networks can expand without a massive spike in energy use.
Why These Goals Matter
Each of these 6G metrics aligns perfectly with changing digital needs:
Immersive Media: Technologies like holograms, the metaverse, and tactile internet need a lot of bandwidth and ultra-low latency.
Smart Industry: Reliable latency and centimeter-level accuracy are vital for real-time automation.
Sustainability: With billions of devices expected, energy efficiency will be a must.
Security & Trust: As these networks become the backbone of economies, trustworthiness will be crucial to prevent data misuse.
In a nutshell, 6G will enable future societies to be hyper-connected, intelligent, and sustainable.
Comparison Table: 5G vs 6G Goals
Metric | 5G | 6G Goal | Improvement Factor
Capacity | ~10 Tbps/km² | 150 Tbps/km² | x15
User Data Rate | ~1 Gbps | 10 Gbps | x10
Latency | ~10 ms (1 ms for URLLC) | 1 ms universal (deterministic) | x10 improvement
Device Density | ~1M devices/km² | 10M devices/km² | x10
Location Accuracy | Meter-level | 1 cm | 100x+
Energy Efficiency | Incremental gains | 30x–300x | Major breakthrough
Beyond Connectivity: The Broader 6G Vision
6G isn’t just a telecom upgrade; it’s a platform that transforms digital society.
- Intelligent Networks
6G will embed AI and machine learning at its core. Networks will predict demand, heal themselves, and dynamically allocate resources.
- Integrated Sensing and Communication
By merging sensing with connectivity, networks will act like radar systems, accurately mapping environments. This supports autonomous vehicles, drones, and AR.
- Global Affordability and Scalability
6G aims to be accessible worldwide, not just in densely populated areas. Affordable deployments will bring advanced connectivity to rural and underserved communities.
- Sustainable Connectivity
Energy use has been a big issue with 5G. 6G will introduce green design principles, renewable-powered base stations, and smarter hardware.
Challenges to Achieving 6G Goals
Though these goals are ambitious, they come with several challenges:
Spectrum Availability: 6G may need to tap into terahertz (THz) bands, which will require new hardware and models for signal propagation.
Infrastructure Costs: Making sure everything is scalable and affordable while introducing these advanced technologies.
Energy Constraints: Achieving a 300x improvement in efficiency is no easy task.
Global Standardization: Aligning global efforts for interoperability is crucial.
Security: As networks become smarter and more connected, they become bigger targets for cyberattacks.
Tackling these challenges will need collaboration among governments, educational institutions, and industry leaders.
Future Outlook: Towards 2030 and Beyond
We can expect 6G to start rolling out around 2030, but research and early testing are already going on.
Leading telecom companies, universities, and standardization groups are exploring:
Terahertz communications for ultra-high throughput
AI-native networks that can predictively optimize performance
Digital twins to help simulate and monitor real-world processes
Sustainable designs aimed at carbon-neutral networks
When 6G arrives, it'll be more than just a connectivity upgrade — it’ll be the foundation for digital societies, allowing seamless interactions between people, machines, and the physical world.
Conclusion
6G lays out a bold vision for what the future of connectivity could look like. By aiming for 10x improvements in data rates, latency, and capacity, along with centimeter-level accuracy and huge energy efficiency gains, it hopes to tackle the limitations of 5G while enabling entirely new applications.
For telecom experts and tech lovers, the journey to 6G is about more than just faster systems; it’s about building smart, sustainable, and trustworthy networks that will support the digital society of 2030 and beyond.
