6G MTC Towards 2030: Drivers, Use Cases, Requirements, and Service Classes Explained
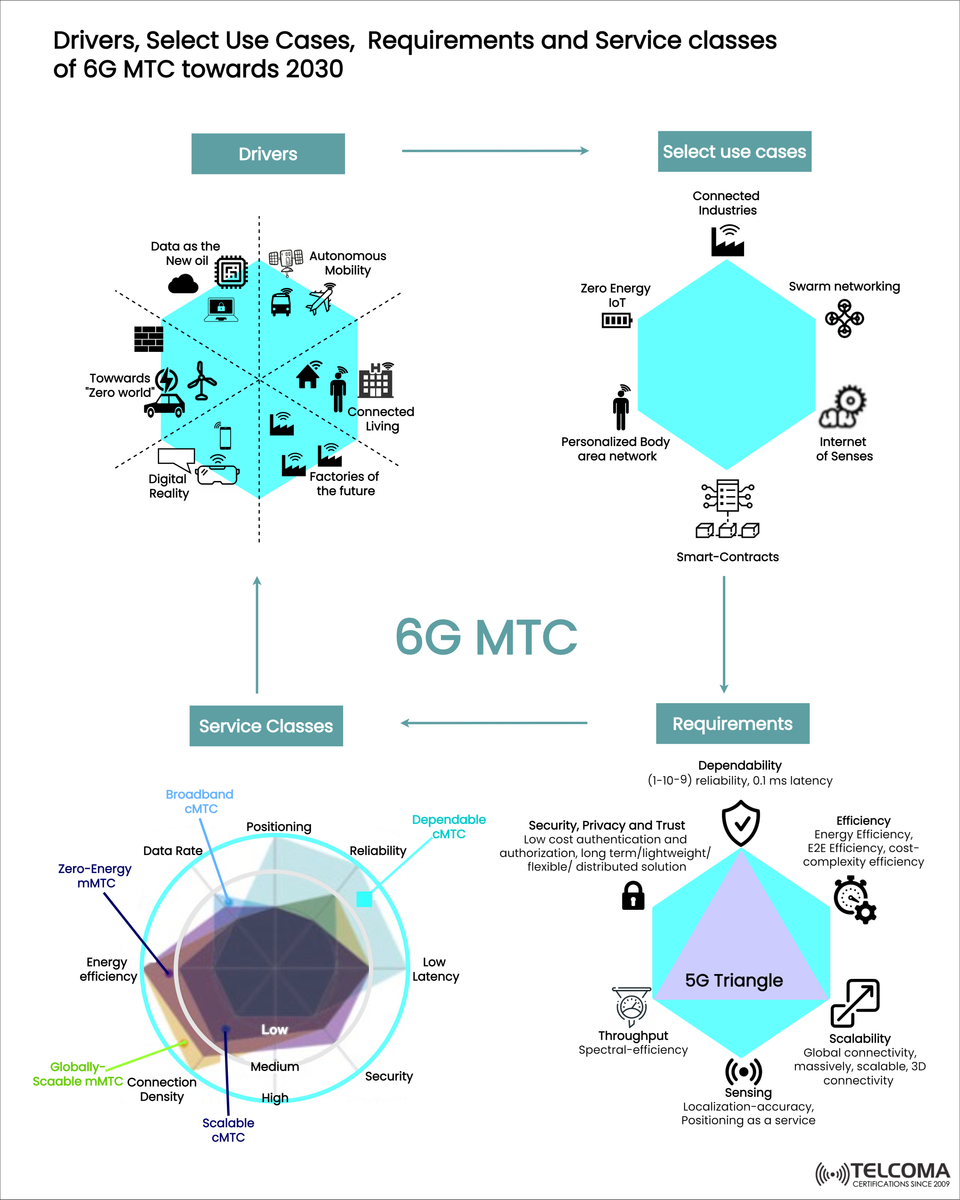

Looking Ahead to 6G MTC by 2030: Key Drivers, Use Cases, Requirements, and Service Classes
As we move past 5G and into the sixth generation of mobile networks (6G), Machine-Type Communication (MTC) is shaping up to be a critical element. This isn’t just about connecting people; it’s all about the communication between devices, machines, and smart systems—all doing their own thing autonomously.
By 2030, 6G MTC is set to create hyper-connected ecosystems that will support a variety of applications, from self-driving cars and smart factories to personalized healthcare and collaborative robotics. In this blog, we’ll explore the drivers, select use cases, requirements, and service classes that will define 6G MTC in the coming years.
Major Drivers of 6G MTC
The push toward 6G comes from a mix of social, technical, and industrial changes. The infographic outlines six key drivers:
Data as the New Oil — With data growing at an exponential rate, figuring out how to extract and use it intelligently will be crucial for 6G.
Autonomous Mobility — Think self-driving cars, drones, and smarter transport systems that need super-reliable, low-latency MTC.
Connected Living — From smart homes to healthcare devices, 6G MTC will integrate seamlessly into our daily lives.
Factories of the Future — Industry 4.0 is all about connecting machines on a massive scale, maintaining them predictively, and incorporating AI for automation.
Digital Reality — Extended reality (XR), digital twins, and immersive experiences rely on reliable, high-speed MTC.
Towards a “Zero World” — A focus on zero emissions, zero energy, and sustainable IoT systems is pushing green innovation in telecommunications.
These drivers show why we need MTC that’s super-reliable, energy-efficient, and scalable, which will help pave the way for 6G adoption across different sectors.
Notable Use Cases of 6G MTC
6G MTC is set to unleash next-gen applications that far exceed what 5G can currently do. Here are some highlighted use cases:
Connected Industries — Automation throughout smart factories and logistics, backed by reliable communication.
Zero Energy IoT — Battery-free IoT devices that use energy harvesting, which helps cut down on maintenance costs.
Swarm Networking — Drones, robots, and autonomous agents working together in a coordinated manner.
Internet of Senses — Sending touch, taste, and smell digitally for more immersive communication experiences.
Smart Contracts — Communication between devices using blockchain to automatically enforce agreements.
Personalized Body Area Networks (BANs) — Wearable and implantable devices that provide real-time health monitoring and insights.
These applications show that 6G MTC isn’t just about speed—it’s about creating smarter, more reliable, and sustainable communication systems.
Requirements for 6G MTC
For 6G MTC to really take off, it has to meet some tough technical and operational standards. The infographic breaks this down using the 5G Triangle framework, which has been expanded for 6G:
Dependability — Reliability must have 10^-9 failure probability, with latency needing to be as low as 0.1 ms for time-sensitive applications.
Efficiency — Energy-efficient IoT devices and overall efficiency to lower costs and minimize environmental impacts.
Scalability — Connections must be massively scalable, enabling 3D connectivity across aerial, land, and marine networks.
Security, Privacy, and Trust — Need for lightweight, decentralized authentication and strong data privacy for sensitive MTC applications.
Throughput & Spectral Efficiency — Optimizing spectrum usage in crowded IoT settings.
Sensing and Localization — Offering Positioning-as-a-Service for autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
These requirements illustrate how 6G MTC combines reliability, efficiency, scalability, and trust—creating the foundation for future-critical communications.
Service Classes of 6G MTC
To cater to the diverse set of applications, 6G MTC is split into service classes tailored for specific needs:
- Broadband cMTC
Focus: High data rates.
Applications: Digital reality, immersive media, and industrial video analytics.
- Dependable cMTC
Focus: Extreme reliability and low latency.
Applications: Self-driving cars, healthcare, emergency services.
- Scalable cMTC
Focus: Massive device connections.
Applications: Smart cities, nationwide IoT solutions.
- Zero-Energy mMTC
Focus: Ultra-low power or energy-harvesting IoT.
Applications: Environmental monitoring, wearable tech.
- Globally-Scalable mMTC
Focus: Worldwide connectivity and seamless interoperability.
Applications: Supply chain management, logistics, and global asset tracking.
Visualizing Trade-offs
The service classes differ across several factors like latency, reliability, security, connection density, and energy efficiency. For example:
Broadband cMTC aims for maximum throughput but might compromise on energy efficiency.
Dependable cMTC focuses on reliability and low latency, which can make it more resource-heavy.
Zero-Energy mMTC is all about sustainability but comes with trade-offs in data capacity and latency.
This layered approach makes sure that 6G can handle everything from energy-efficient wearables to mission-critical autonomous vehicles at the same time.
Comparing Service Classes
Here’s a straightforward comparison:
Service Class | Focus | Typical Applications
Broadband cMTC | High data rates | XR, Digital twins, AR/VR
Dependable cMTC | Reliability, low latency | Autonomous driving, medical robotics
Scalable cMTC | Massive device density | Smart cities, Industry 4.0 IoT
Zero-Energy mMTC | Energy efficiency | Wearables, environmental sensors
Globally-Scalable mMTC | Worldwide connectivity | Supply chain, logistics
This classification ensures that 6G MTC aligns network resources with various application needs.
Implications for Telecom Professionals
As telecom networks gear up for 6G, experts need to get ready for:
Changes in Network Design — Building architectures to support extreme reliability and near-zero latency.
AI/ML Integration — Using AI to optimize for unpredictable traffic patterns and swarm behaviors.
Security by Design — Implementing lightweight cryptographic methods to secure billions of devices.
Sustainability Initiatives — Focusing on energy efficiency and zero-energy IoT rollouts.
Global Collaboration — Standardizing service classes globally to ensure everyone can play nice together.
Conclusion
The move toward 6G MTC by 2030 is set to transform the landscape of communication. With influences from autonomous mobility, digital reality, connected living, and sustainability, 6G MTC will enable next-gen applications like swarm networking, the Internet of Senses, and zero-energy IoT.
Meeting the stringent requirements for dependability, efficiency, scalability, and security will be essential. With a range of service classes—from broadband to zero-energy—6G MTC will cater to every application, whether it’s crucial for life or just a large-scale IoT deployment.
For telecom professionals, this means gearing up not just for faster networks, but also for a smarter, more trustworthy, and sustainable communication framework that supports industries, societies, and our daily lives well into 2030 and beyond.
