6G Vision Explained: Core Pillars, Global Coverage, and the Future of Connectivity

Understanding 6G: Key Principles, Worldwide Access, and the Future of Connectivity
As we start to fully embrace 5G, researchers and telecom experts are already setting their sights on the next major advancement: 6G. This upcoming generation of wireless technology, expected to roll out around 2030, is set to transform global communications by linking not just devices and networks, but also the digital, physical, and human realms in real time.
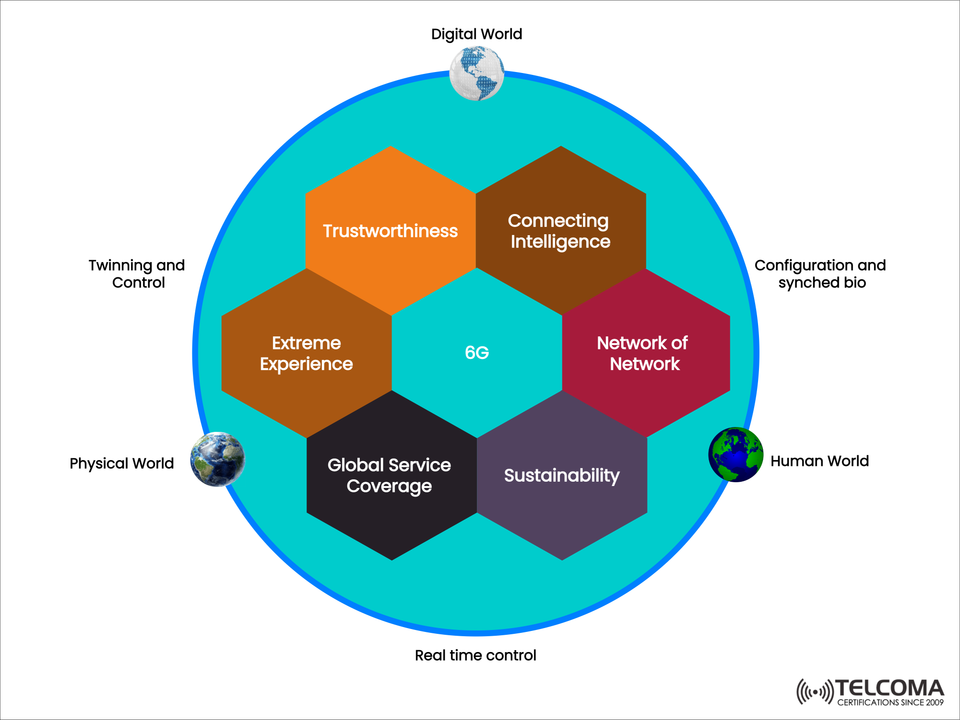
The diagram above shows the main pillars of 6G, which include:
Trustworthiness
Connecting Intelligence
Network of Networks
Extreme Experience
Global Service Coverage
Sustainability
Together, these elements will lay the groundwork for a future where communication systems deliver smooth, secure, and smart connectivity across all aspects of life.
The Importance of 6G
6G isn't just about speeding things up; it represents a major shift in how we think about connectivity. While past generations focused on bandwidth, latency, and device connections, 6G aims to weave in advanced intelligence, real-time engagement, and global accessibility.
Some of the main objectives for 6G include:
Offering immersive experiences like holographic calls and expansive AR/VR interactions around the globe.
Merging the digital realm (cloud services, AI, metaverse) with the physical realm (IoT, robotics, smart cities).
Connecting the human experience through health tracking, bio-synchronization, and tailored services.
Promoting sustainability while extending service reach worldwide.
The Six Key Pillars of 6G
The vision for 6G rests on six interconnected pillars, each crucial for the success of this ecosystem.
- Trustworthiness
As cyber threats continue to rise, it's essential that 6G provides secure, transparent, and dependable communication. Building trust will involve:
Advanced encryption and quantum-safe security measures
AI-enhanced threat detection
Clear data governance policies
Maintaining integrity across networks from start to finish
Trust will play a big role in how 6G is adopted in fields like healthcare, finance, and defense.
- Connecting Intelligence
6G will use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) at its very core. Unlike 5G, where AI is just an add-on, 6G will have integrated intelligence.
Distributed AI: Smarter processing done closer to users (MEC – Multi-Access Edge Computing).
Network optimization: Networks that can self-heal and optimize on their own.
Context-aware services: Personalizing connections based on user behavior and environments.
Collaborative intelligence: Devices, sensors, and networks collaborating seamlessly.
- Network of Networks
6G aims to bring together various types of networks into a single, cohesive system. This includes:
Ground-based 5G/6G networks
Non-ground networks (like satellites and HAPS - High Altitude Platforms)
IoT networks and industrial setups
Specialized networks for things like public safety and private business needs
This combination will ensure constant connectivity, even in remote or underdeveloped areas.
- Extreme Experience
One of the most thrilling promises of 6G is the potential for extreme user experiences. Imagine:
Holographic calls with almost no delay
Total immersion in AR/VR and extended reality (XR) applications
Digital replicas of cities, factories, or even human bodies for real-time interactions
A tactile internet where remote touch and control feel instant
These experiences will require ultra-low latency, top-notch reliability, and huge bandwidth—key aspects of 6G.
- Global Service Coverage
Unlike 5G, which is mostly limited to well-developed areas, 6G aims for true global coverage. This will be done by combining ground-based and non-ground networks.
Satellite networks to serve rural and isolated areas
Fluid mobility across ground, air, and sea networks
Broad access to broadband for education, healthcare, and commerce needs
This level of connectivity promotes digital inclusivity, helping to close the digital gap.
- Sustainability
With growing concerns about climate change and increasing energy demands, sustainability is a key focus in the design of 6G. The aim is to:
Build energy-efficient networks that reduce carbon emissions
Incorporate renewable energy into infrastructure
Utilize Green AI to decrease processing power needs
Design both hardware and software for longer life cycles
A sustainable approach to 6G will balance innovation with environmental responsibility.
The Worlds Connected by 6G
The diagram also illustrates how 6G bridges three different worlds:
Digital World: Cloud computing, AI, metaverse, and blockchain.
Physical World: IoT devices, robotics, smart cities, and automation in industries.
Human World: Health monitoring, biometric syncing, and tailored digital experiences.
With real-time control, duplication, and bio-synchronization, 6G will integrate these worlds into one cohesive ecosystem.
Key Features of the 6G Vision
Here’s a quick overview of what makes 6G groundbreaking:
Feature Description Real-time control Allows instant interactions between people, machines, and digital representations. Twinning and Control Physical systems mirrored in the digital world for immediate oversight. Configuration & Synched Bio Personalized health-related services connected to human biology. Extreme Experience Immersive technology like holography, AR/VR, and tactile internet. Global Service Coverage Comprehensive connectivity blending ground and non-ground networks. Sustainability Eco-friendly networks prioritizing energy efficiency.
Challenges Facing 6G
While the goals are ambitious, several challenges must be tackled:
Creating energy-efficient hardware for ultra-high frequencies (THz spectrum).
Ensuring security and trust in highly connected environments.
Managing spectrum allocation to achieve global coverage.
Developing cost-effective infrastructure for remote locations.
Aligning international standards for smooth interoperability.
Potential Applications of 6G
The 6G ecosystem will empower a range of industries:
Healthcare: Remote surgeries, real-time patient monitoring, digital organ twins.
Manufacturing: Industry 5.0 with human-robot teamwork and predictive maintenance.
Smart Cities: Self-driving transport and AI-powered city planning.
Entertainment: Engaging gaming experiences, holographic concerts, worldwide AR/VR events.
Education: Remote classrooms with AR/VR immersion, equal access for all.
Wrapping Up
6G is more than just an upgrade—it’s a revolution in how we connect. By combining trust, intelligent connections, network unity, immersive experiences, global access, and environmental consciousness, 6G will reshape how people, machines, and digital systems interact.
It aims to merge the digital, physical, and human aspects in real time, making communication not only faster but also smarter, safer, and more inclusive.
For those in the telecom industry, this means gearing up for a new age of AI-driven, globally connected, eco-friendly networks. For tech enthusiasts, it offers a peek into a future where the lines between digital and physical realities blur.
The countdown to 6G is already on.
