AI-Native Networks in Telecom: The Future of Intelligent, Autonomous Communication Systems

Introduction
The telecommunications industry is changing faster than ever. As we transition from 5G to 6G and beyond, networks are becoming more complex, data-heavy, and dynamic. Managing these systems manually is simply no longer practical. So, what’s the answer?
We need a shift toward AI-native telecom networks — essentially, systems designed with artificial intelligence at their core.
Unlike traditional AI-assisted tools, AI-native networks are inherently autonomous, adaptive, and self-optimizing, continually learning from their surroundings to make real-time decisions and improvements.
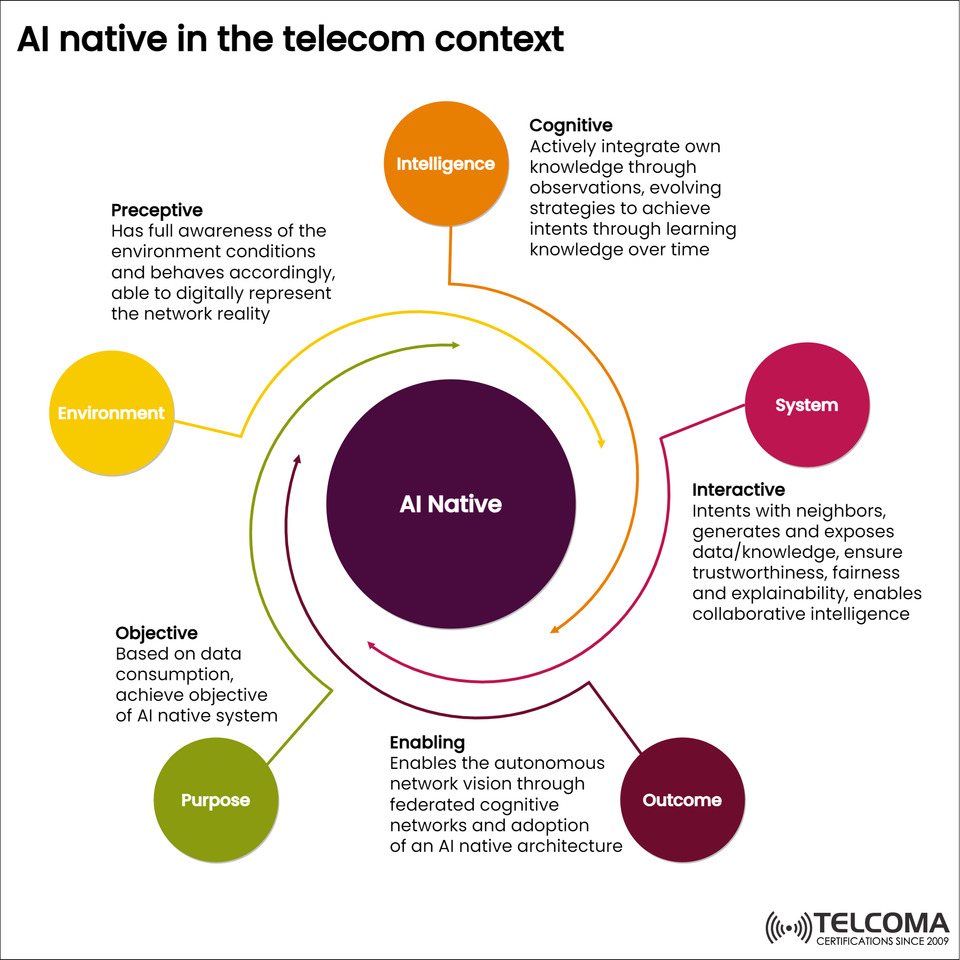
In the diagram titled “AI Native in the Telecom Context,” created by Tel
coma, this concept is broken down into five interconnected pillars — Intelligence, Environment, Purpose, System, and Outcome. Let’s dive deeper into each of these pillars and see how AI-native design is reshaping the telecom landscape.
What Does "AI-Native" Mean in Telecom?
An AI-native telecom network isn’t just a network that uses AI tools; it’s built around AI from the start. This means every part — from how data is collected to how the network is managed — relies on machine learning, cognitive analytics, and real-time adaptation.
To put it simply:
AI is the backbone, not an add-on.
The network learns, reasons, and evolves on its own.
It reacts proactively to incidents rather than waiting for human commands.
This AI-first mindset allows for zero-touch operations, intelligent automation, and sustainable optimization — all critical for a hyperconnected future in telecom.
Core Elements of AI-Native Networks
Tel coma’s visual highlights five crucial areas that define an AI-native system:
Intelligence — The Cognitive Core of AI-Native Systems
AI-native systems are cognitive, meaning they actively learn and evolve over time.
Key points:
Learning by observation: The network constantly monitors traffic, resource use, and any anomalies.
Evolving strategies: It fine-tunes routing, bandwidth usage, and energy consumption using reinforcement learning.
Knowledge retention: These systems keep a record of learned experiences, boosting accuracy in future predictions.
In layman’s terms, intelligence allows the network to think, reason, and adapt on the fly — acting as the brain of the AI-native ecosystem.
Environment — Awareness and Adaptation
The environmental awareness of AI-native systems enables them to detect real-world conditions and respond as needed.
How AI-Native Networks Perceive the Environment:
They are fully aware of environmental factors such as user mobility, device density, and network load.
They create a digital twin of the entire network’s reality.
They can adapt to changing conditions like interference, weather changes, or usage surges.
By understanding and mirroring both physical and virtual environments, AI-native networks can proactively optimize resources and maintain uninterrupted connectivity.
Purpose — Data-Driven Objectives
Each AI-native system is driven by a clear, data-based goal. Unlike traditional rule-driven systems, AI-native networks align their operations with intent-based outcomes, using data as their guide.
Key points:
Objectives are set by intent (like minimizing latency, maximizing throughput, or boosting user experience).
AI models analyze real-time data to achieve these goals dynamically.
Ongoing feedback keeps the system aligned with shifts in network demands.
This intent-based networking (IBN) concept helps telecom systems automatically turn broad objectives into actionable network policies.
System — Interactive and Collaborative Intelligence
An AI-native telecom system is not isolated; it’s interactive and collaborative. It communicates with nearby systems, devices, and applications to ensure trust, fairness, and transparency.
Core features:
Interactivity: The network shares and receives insights from other entities.
Trustworthiness: AI-driven decisions are clear and understandable.
Fairness: Algorithms are monitored to avoid bias in service delivery.
Collaborative intelligence: AI models across networks work together to optimize performance from end to end.
This approach turns telecom networks into ecosystems of connected intelligence, all working together to improve service quality (QoS) and reliability.
Outcome — Enabling the Autonomous Network Vision
The outcome of adopting an AI-native approach is achieving autonomous networks — ones that can self-configure, heal, optimize, and protect themselves.
Key components:
Federated cognitive networks: Multiple AI agents collaborate while respecting data privacy.
AI-native architecture: Built around AI orchestration instead of traditional management models.
Autonomous decision-making: Reduces the need for human intervention, leading to quicker reactions and lower operational costs.
In the end, AI-native systems empower telecom operators to achieve zero-touch operations — a crucial goal for the next generation of digital infrastructure.
How AI-Native Networks Differ from AI-Assisted Networks
Feature AI-Assisted Network AI-Native Network AI Integration Added as a supporting tool Built into network architecture Decision-Making Human-guided Fully autonomous and self-learning Adaptability Reactive Proactive and predictive Data Utilization Limited analytics Continuous, real-time learning Objective Alignment Static configuration Intent-driven, dynamic goals Scalability Restricted by human input Infinitely scalable through automation
The shift from AI-assisted to AI-native networks signifies a move from automation to autonomy, fundamentally transforming the operational DNA of telecommunications.
Benefits of AI-Native Networks in Telecom
Operational Efficiency * Cuts down on manual network management and reduces human errors. * Supports automated fault detection and predictive maintenance.
Enhanced User Experience * Dynamically optimizes bandwidth and latency based on user intent and traffic demands.
Resilience and Reliability * AI-driven anomaly detection keeps the network stable during heavy usage.
Cost Optimization * Better resource usage lowers OPEX and CAPEX for operators.
Sustainability * Smart energy management reduces the carbon footprint.
Security and Trust * Cognitive AI models spot intrusions and cyber threats quicker than traditional systems.
Scalability for 6G and IoT * Manages the rapid increase in devices in smart cities and industrial IoT networks.
Challenges in Adopting AI-Native Architecture
Even though the benefits are significant, moving to an AI-native telecom network isn’t without its hurdles:
Data Privacy: Federated learning must comply with data protection regulations.
Algorithm Bias: AI systems need to uphold fairness and explain ability.
Infrastructure Overhaul: Legacy systems require redesign to support native AI integration.
Skill Gap: Professionals in telecom must be trained in AI, ML, and data analytics.
Overcoming these challenges calls for industry collaboration, policy support, and continuous innovation.
Future of AI-Native Telecom Networks
The AI-native design will lay the groundwork for 6G networks and what comes next. According to trends in global telecom:
Networks will evolve into fully autonomous ecosystems driven by distributed AI.
Intent-based orchestration will take the place of manual setups.
AI-driven spectrum management will unlock higher frequency bands like terahertz communication.
AI will facilitate sustainable, secure, and adaptive connectivity across all areas — from terrestrial to satellite systems.
Embracing the AI-native paradigm isn’t just a tech upgrade; it’s a shift in how telecom networks think, learn, and evolve.
Conclusion
The idea of AI-native telecom networks marks a major advancement toward more intelligent and autonomous communication systems.
As shown in the Telcoma diagram, an AI-native ecosystem thrives on five connected pillars — intelligence, environment, purpose, system, and outcome — enabling a network that learns, reasons, and optimizes itself in real-time.
By integrating AI into the core architecture, telecom networks can achieve zero-touch automation, unmatched scalability, and human-like adaptability — paving the way for a connected, cognitive world in 6G and beyond.
