Broad Classification of Machine Learning: Supervised, Unsupervised & Reinforcement Learning

📚 Major Types of Machine Learning with Their Basic Properties
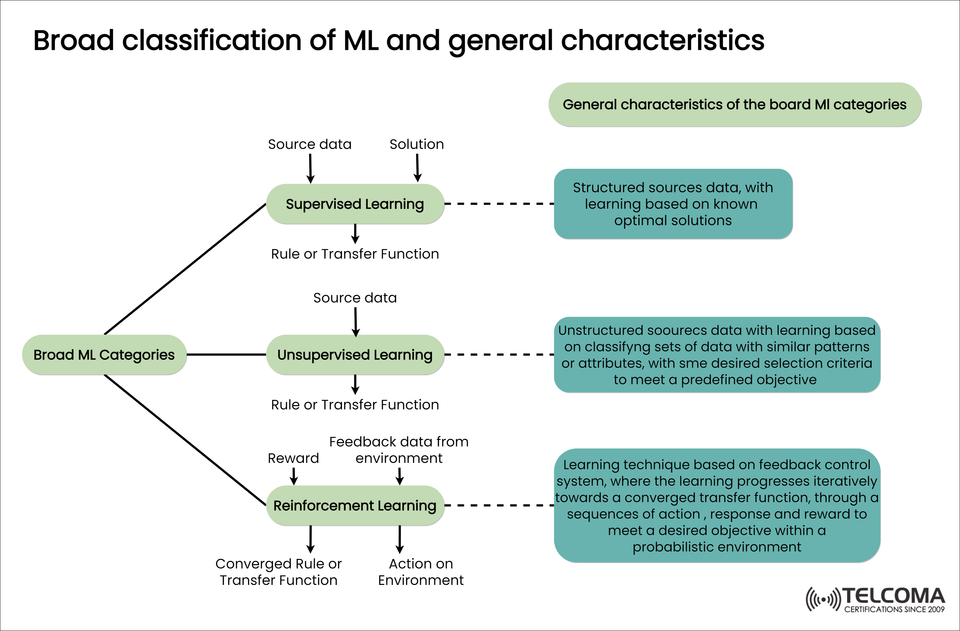
Machine Learning (ML) is the enabling technology for intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and network optimization in contemporary telecom systems. The three foundational types - Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement Learning - serve unique purposes based on data structure, goal, and approach to learning. This blog post describes each of these types of ML with their general properties and applications for the practitioners of telecom and AI.
🔵 Supervised Learning: Learning from label, data driven
Definition:
Supervised learning uses labeled data where the algorithm learns with data mapped to its known output. The objective of supervised learning is to learn a mapping (transfer function) from the input to the output data.
Key Properties:
Requires structured and labeled datasets
Learns with known optimal values
Applicable for classification and regression
Telecom Use Cases:
Spam detection in messaging systems
Customer customer churn prediction
Signal classification
QoS (Quality of Service) metrics
🟢 Unsupervised Learning: Discovering patterns without labels
Definition:
Unsupervised learning considers unstructured or unlabeled data to discover patterns, groupings, or other features in the data or sets of data without specific instructions.
Key Properties:
Works with unstructured data
Focus on grouping data or reducing the dimensionality of data
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clustering
Uses clustering and association techniques
Telecom Use Cases:
Subscriber segmentation or grouping
Network anomaly detection
Fraud detection
Dynamic spectrum availability or allocation
🟠 Reinforcement Learning: Learning through Reward and Feedback
Definition:
Reinforcement learning (RL) takes the form of behavioral learning. An agent interacts with its environment, takes actions, receives feedback (rewards or penalties), and produces a learned optimal policy, over time.
Key Characteristics:
Based on Trial-and-Error Learning
Uses Feedback from the Environment
Learns a Policy that Maximize Long-Term Rewards
Telecom Use Cases:
Self Optimizing Network (SON)
Autonomous Resource Allocation
Energy Efficient Base Station Control
Real-Time Traffic Routing
🧾 Summary Table: Comparison of ML Categories
ML Type Data Type Learning Objective Key Techniques Telecom Application
Supervised Learning Structured Predict labels using actual outcomes Regression, Classification Churn Prediction, QoS Monitoring
Unsupervised Learning Unstructured Discover unknown patterns or groupings Clustering, PCA Network Anomalies, Fraud Detection
Reinforcement Learning Structured/Real-Time Learn optimal policy using trial and error Q-learning, Deep RL SON, resource management
✅ Why This in Matters in Telecom
Machine learning is integral operational intelligence to drive data-hungry and real-time adaptive telecom networks. The classification of ML into three categories will allow for specific applications to be designed:
Supervised learning to design prediction models.
Unsupervised Learning to generate netork insights.
Reinforcement Learning to design adaptive controls.
An understanding of these categories allows telecom professionals to help design smart and evolving autonomous networks that continuously develop as users adapt.
🔚 Conclusion
The general framework of machine learning in: Supervised, Unsupervised and Reinforcement learning serves as the basis for cementing AI strategy in telecom. We have touched on the importance of each type in enhancing intelligent network performance ( things you wish were automated) when it comes to realising telecoms offerings and related services. It does not really matter if you are developing predictive analytical modelling or deploying autonomous systems, knowing these types of ML ensures you have a future autonomous and intelligent approach to driving your telecom innovation.
🧠 Extra Reflections for Telecom Practitioners
💡 Role of ML in 5G and beyond
Machine learning, and reinforcement learning in particular, will play an essential role in realising self-organising networks (SON) for 5G and 6G deployments. SONs are able to perform auto-optimisation for handovers, auto-optimize their beamforming and automatically manage and allocate spectrum resources; this will be critical for ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
🌐 Edge Computing, and ML
ML Algorithms, through federated learning (as discussed in past blog post) will be useful to Edge AI platform with data locality, latency and privacy.
Supervised learning will help in real time traffic classification and unsupervised learning will support anomaly detection at the edge node.
📣 Concluding Thoughts
The transformation in telecom is not just about automation but brother intelligent automation. This is where the role of these wider categories of ML contribute to strategic decision able execution. Whether you are building predictive models for...
📊 Compare ML Categories in Telecom Use Cases
| ML Category | Input Data | Learning/Inference Approach | Example in Telecom - Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Labeled (structured) data | Trains on known input-output pairs | Predicting network congestion based on historical KPIs | Accurate predictions, and fast train |
| Unsupervised Learning | Unlabeled (unstructured) data | Learns about hidden patterns and clusters with no labels | User behavior segmentation, anomaly detection | Discovery of unknown |
| Reinforcement Learning | Real-time feedback from the environment | Learns through trial and error and reward functions | Dynamic spectrum allocation, power control | Adaptive decision-making in real-time |
🧠 Real-World Examples in Telecom
Now let's look at some real-world examples of these types of ML within telecom infrastructures:
🔹 Supervised Learning in Telecom
Use Case: Call drop predictions using labelled network performance data
Tools: SVM, Decision Tree, Neural Networks
Deployment: At the core of the network, or on centralized cloud platforms
🔹 Unsupervised Learning in Telecom
Use Case: Fraud detection in billing data
Tools: K-Means Clustering, PCA
Deployment: In billing systems, CRM applications, analytics engines
🔹 Reinforcement Learning in Telecom
Use Case: Self-Organizing Network (SON) purge optimization for handover in 5G
Tools: Q-learning, Deep-Q Networks (DQN)
Deployment: Intelligent controllers at the RAN, edge AI deployment
🔚 Conclusion
Machine learning is not a future vision; it's a necessity in today’s telecom industry. Knowing the general categories of ML gives telecom engineers, AI architects, and operations teams the tools to develop smarter, self-healing, and adaptive networks.
As network architecture becomes more open and virtualized, use of the correct ML algorithm in the correct layer of the architecture (RAN, edge, core) will either give a competitive advantage to CSPs and network manufacturers or it will not.
