Broadcast Target Wake Time (TWT) Operation in Wi-Fi 6: Efficient Power Saving and Scheduling

A Comprehensive Look at Broadcast Target Wake Time (TWT) Operation in Wi-Fi 6
In a world full of connected devices and high-density wireless environments, power efficiency and airtime coordination go hand in hand. One of the key features of Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is Target Wake Time (TWT)—a feature that schedules when devices wake to send or receive data, while allowing devices to sleep the rest of the time.
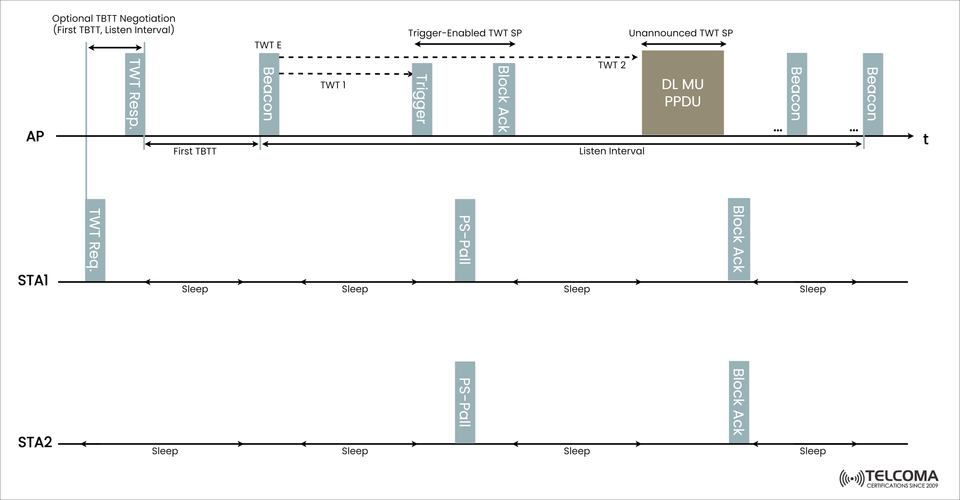
In the image above, we see an example of Broadcast TWT operation, where multiple client devices (STAs) are all scheduled based upon a shared wake time from a central Access Point (AP). This blog will explain how this mechanism works, why it matters, and it can help telecom and network professionals.
What Is Broadcast TWT?
Broadcast Target Wake Time (TWT) is a scheduling mechanism in which the AP defines a common wake-up schedule (called TWT Service Periods) for multiple devices so that they can:
- Save power by allowing STAs to sleep when inactive.
- Access to be coordinated in order to avoid collision / reduce contention.
While individual TWT (negotiated per device) presents a challenge of overhead, broadcast TWT has a less overhead because it allows a one-to-many (1:N) scheduling mechanism.
📊 Understanding the Broadcast TWT Operation Diagram
Let's review what is in the image:
AP (Access Point) creates and controls the broadcast TWT schedule.
STA1 and STA2 (client stations) wake up (often only briefly) as per the schedule and go back to sleep.
Time moves left to right.
Key Elements:
Name Description
TWT Req./Resp. Optional negotiation to set initial TWT parameters.
Beacon (TWT E) Beacon frames have a TWT Element — announcing the TWT schedule.
Trigger It starts/makes uplink transmission opportunity.
DL MU PPDU Downlink Multi-User Physical Layer Protocol Data Unit — A PPDU frame intended for multiple STAs at the same time.
PS-Poll Power Save Poll — the device is ready to receive data.
Block Ack Acknowledgment of received data.
⚙️ Types of TWT Service Periods in the Diagram
Trigger-Enabled TWT SP:
AP sends a trigger frame indicating which STAs may transmit.
Provides uplink multi-user transmission.
Unannounced TWT SP:
No trigger frame is sent, and the AP sends data (e.g., DL MU PPDU).
It is used for only downlink transmission, providing the additional benefit of reducing overhead.
🛠 Benefits of Broadcast TWT in Wi-Fi 6 Networks
🔋 Power Efficiency
Devices are in sleep mode for most of the time and are only waking per their scheduled TWT period.
Makes it most suitable for IoT, mobile, and battery-powered devices.
🛠 How to Optimize Broadcast TWT In Network Deployments
In practice, successfully implementing Broadcast TWT requires harmonization of the parameters like beacon interval and listen durations as well as the TWT Service Periods (SPs) themselves. Here’s a few best practices that professionals can use to maximize the advantages:
✅ Recommendations for Configuration
Tuning the Beacon Interval - This is crucial for the AP to advertise TWT information in beacon frames at predictable intervals which means that the TWT capable devices (STAs) can remain sync with the TWTs without the need to re-negotiate TWT in a timely manner.
Leveraging the TWT SP Duration - The duration of the TWT SPs should coincide with your payload size or application. For example:
Use short SPs for more frequently or low-data updates (ex. sensor networks)
Use longer SPs for bulk transfers or bursty traffic patterns (ex. synchronizing video).
Grouping STAs - Consider grouping STAs that have similar power/latency requirements together in the same TWT SP which can minimize the need to for the AP to manage multiple TWT SP schedules while enhancing RF performance.
Using the Trigger - There are even greater improvements in network implementation generally and network throughput in particular, when using Trigger capable TWT SPs to schedule uplink transmissions.
🔄 Implementation Considerations and Challenges
Broadcast TWT may provide tremendous benefits in a variety of applications, but like all network implementations there are a few considerations to be mindful of:
Challenge Proposed Mitigation
STA Desynchronization Consistent beacon reception, handling desynchronization logic properly in STAs.
Device Capability Variation Group only TWT capable STAs in TWT broadcast schedules.
Interference/Channel Access Utility Use of BSS Coloring and/or OFDMA can comply with TWT efficiency.
Legacy Device Interleaved Access Support for hybrid TWT and legacy access.
🌍 Regulatory and Interoperability Aspects
Standards Compliance:
Broadcast TWT defined in IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) and endorsed by the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Optional feature if Wi-Fi 6 certification but increasing acceptance in dense environments.
Vendor Support:
Backed by major silicon vendors (e.g., Qualcomm, Broadcom, Intel).
Works best when STA and AP vendors agree on implementation details (timing, response, etc.).
🔮 Future Considerations: TWT in Wi-Fi 7 and beyond
🔄 Enhanced Broadcast TWT
Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) will incorporate more capabilities for TWT with Multi-Link Operation (MLO):
STAs will be able to wake and transmit on multiple bands/channels in a simultaneous fashion.
Improved scheduling flexibility across multiple frequency links.
📶 Adaptive TWT Scheduling
Future APs may be utilizing AI-based algorithms that use traffic analytics to adjust TWT schedules dynamically.
Dynamically allocates predictive resources for time-sensitive use cases (e.g., AR/VR, industrial automation).
📚 Summary Table: Broadcast TWT Basics
Feature Description
TWT SP Scheduled time for STA wake and data send/receive.
Beacon with TWT Element Advertises timing info for STAs.
Trigger Frame Allows uplink access to be coordinated in TWT SPs.
DL MU PPDU Multi-user frame sent during SP to multiple STAs.
PS-Poll Used by STAs to indicate readiness to send data.
🧩 Wrap-Up
Broadcast TWT cases a new standard for managing and scheduling Wi-Fi power consumption by enabling synchronized wake times for multiple devices, allowing for the most efficient balance between power-saving measures and maintaining network performance.
In order to take full advantage of Wi-Fi 6, designing with TWT in mind is critical for telecom professionals, systems integrators, and enterprise IT leaders alike, especially in IoT-rich and high-density environments.
