Centralized EPC vs Distributed 5G MEC UPF: Key Architectural Shift Explained
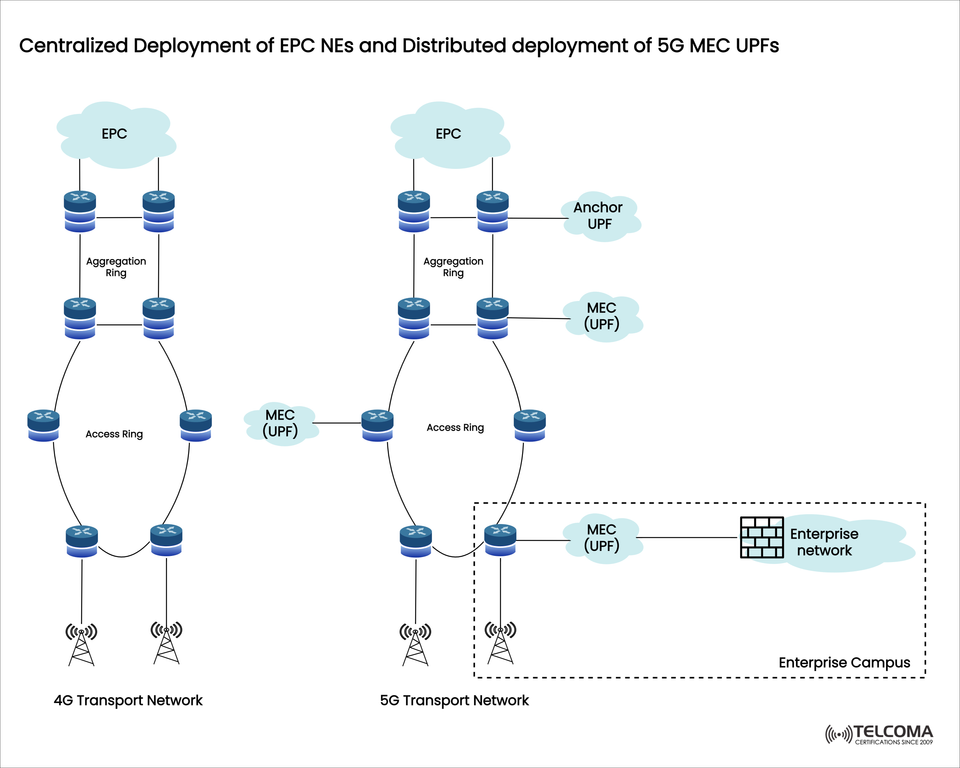

Centralized EPC Versus Distributed 5G MEC UPF:
An Architectural Shift Mobile networks are evolving from 4G to 5G, and the transport and core networks that support them have also undergone an architectural shift. One of the most significant architectural changes is fundamentally moving from a centralized EPC deployment in 4G to a distributed deployment of MEC UPFs in 5G.
This blog post describes this change in detail, together with noting improvements in latency, performance, and enterprise applications.
📡 4G Transport Network: Centrally Deployed EPC
In a 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution) network, users access the network through multiple base stations. The Evolved Packet Core (EPC) is centrally deployed at the regional or national datacenter. Transport carrier traffic flows from the Access Ring, through an Aggregation Ring before reaching the EPC.
Key Characteristics:
📍 Centralized network elements processed in the core
⌛ More latency associated with the centralized packet routing process
📶 Appropriate use case for traditional mobile broadband use cases
🚫 Limited support for ultra-low latency applications
Diagram Requirements:
Access Ring → base stations (eNodeBs) providing user access
Aggregation Ring → aggregation of traffic toward the EPC
EPC → process user plane traffic in a centralized location
🚀 5G Transport Network: Distributed MEC UPF Architecture
In 5G, distributed UPF elements known as Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) UPFs are deployed at the edge of the network. MEC UPFs will reside in much closer in proximity to the user and in some instances, be co-located next to the user.
📊 Side-by-Side Comparison
Feature 4G EPC (Centralized) 5G MEC UPF (Distributed)
Location of Core Functionality Central Data Center Edge / Access Ring / Enterprise
Latency Higher Ultra-low
Data Processing Model Centralized Localized at edge
Enterprise Use Case Support Limited Strong with on-prem MEC
Network Flexibility Low High
Backhaul Dependency High Reduced
🏭 Enterprise Use Case Highlight
In the 5G model, an enterprise campus network can host its own MEC UPF, enabling:
Data localization (no backhaul data need occur)
Real-time analytics and control (in edge).
More security and compliance (closer to enterprise edge).
This is particularly advantageous for:
Smart factories
Healthcare institutions.
Financial data centers.
Critical IoT operations—e.g., safety, security, reliability.
✅ Conclusion
The transition from centralized EPC in 4G to distributed MEC UPFs in 5G is much more than a technical upgrade in status, rather, it is a complete rethinking of the notion of where and how data is processed. By moving the network function closer to the user, 5G architectures greatly improve latency, scalability, and enterprise application enablement.
As, before the telcos and enterprises explored, MEC will become the backbone of modern agile 5G networks.
📌 Suggested Tags for WordPress (SEO Friendly)
rust
Copy
Edit
5G MEC architecture, distributed UPF deployment, centralized EPC vs distributed MEC, 5G transport
📌 Slide 1: Title Slide
4G EPC to 5G MEC UPF
A visual comparison between centralized and distributed mobile core deployments.
📌 Slide 2: The Evolution Path
4G EPC: Centralized Core → High Latency
5G MEC: Distributed UPF → Edge Processing
Transition enabled by SDN/NFV & MEC Principles
📌 Slide 3: 4G Transport Architecture
Diagram: EPC connected via aggregation ring
Notes:
User traffic travels back to centralized EPC
Longer round trip paths
Single point of failure = lower resilience
📌 Slide 4: 5G Transport Architecture
Diagram: MEC UPFs at Access Ring & Enterprise
Notes:
UPF's located closer to users
Allows for local breakout and enterprise routing
Distributed, scalable, low-latency
📌 Slide 5: Why Distributed MEC UPFs?
✅ Ultra-low latency for real-time applications
✅ Off-loading traffic off core/backhaul
✅ Local data sovereignty & security
✅ Scalability in dense deployments
📌 Slide 6: Enterprise Use Case Focus
Smart Manufacturing 🏭
Autonomous Vehicles 🚗
AR/VR in Retail 🛍️
Private 5G Networks 🛡️
Illustration: Enterprise campus with on-prem MEC UPF
📌 Slide 7: Summary Table (Visual Style)
Metric 4G EPC (Centralized) 5G MEC UPF (Distributed)
Latency 20–100 ms <10 ms
UPF Location Core Data Center Near Edge / On-prem
Enterprise Support Limited Advanced, secure
Backhaul Load High Significantly Reduced
📌 Slide 8: Final Takeaway
5G MEC = Local Intelligence, Global Agility
📘 PDF Cheat Sheet:
“4G vs 5G Core Deployment Quick Reference”
Single Page Overview Format
Title: Core Network Evolution: from EPC to MEC-UPF
📍 Use Cases:
- Mobile operators looking to update to 5G
- Enterprises deploying private 5G
- Consultants & architects for network design
Key Concepts:
Centralized EPC (4G):
- EPC = user and control plane centralized
- End-to-end latency is higher
- Not suited for low-latency / edge apps
Distributed MEC-UPF (5G):
- User Plane Functions of the core pushed to the edge of the network
- Allows for local breakout for edge services
- Improved performance, reliability and control.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | 4G EPC | 5G MEC UPF |
|---|---|---|
| Core Design | Centralized | Distributed |
| Latency Profile | Moderate–High | Low–Ultra-low |
| Enterprise Integration | Limited | Deep, on prem enabled |
| Traffic Handling | Centralized | Supports local breakout |
| App Suitability | MBB | URLCC, mIoT, Private 5G |
✅ Downloadable Assets Available:
Would you like any of the following to complement this post?
✔️ Infographic (PNG / PDF)
✔️ LinkedIn Carousel (8-slide)
✔️ Cheat Sheet (PDF)
✔️ Editable Slide Deck (PowerPoint or Google Slides)
✔️ HTML for blog upload (w/ SEO tags)
🧠 Expert Insights & Best Practices
✅ When to Select MEC UPF vs Centralized EPC
| Deployment Context | Preferred Model | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Dense urban 5G rollouts | Distributed MEC UPF | local breakout will reduce backhaul congestion |
| Smart factories / IIoT | MEC UPF (on-premise) | enables ultra-low latency + data |
📘 PDF Cheat Sheet: "4G vs 5G Core Deployment Quick Reference"
Single Page Overview Layout
Title: Core Network Development: from EPC to MEC-UPF
📍 Use Cases:
- Mobile operators wanting to upgrade to 5G
- Enterprises rolling out private 5G.
- Consultants & architects for network planning.
Key Worldviews:
Centralized EPC (4G):
- EPC = user and control plane centralized
- End-to-end latency is higher
- Not optimized for low-latency / edge apps
Distributed MEC-UPF (5G):
- User Plane Functions of the core are pushed to the edge of the network
- Local breakout for edge services, enabled
- Offers higher levels of performance, reliability and control.
Comparison Chart:
| Feature | 4G EPC | 5G MEC UPF |
|---|---|---|
| Core Model | Centralized | Distributed |
| Latency Profile | Moderate-High | Low-Ultra-low |
| Enterprise Adoption | Limited | Deep, on prem enabled |
| Traffic Flow Model | Centralized | Supports local breakout |
| Suitable Apps | MBB | URLCC, mIoT, Private 5G |
✅ Available Downloadable Assets:
Would you like any of the following to go along with this post?
✔️ Infographic (PNG / PDF)
✔️ LinkedIn Carousel (8-slide)
✔️ Cheat Sheet (PDF)
✔️ Editable Slide Deck (PowerPoint or Google Slides)
✔️ HTML for blog upload (w/ SEO tags)
🎯 Targeted Engagement Strategies
To increase engagement and value for your telecom-focused audience of CTOs, communications engineers, and 5G solution architects, try these techniques:
📣 1. Ask Targeted Questions
At the end of the blog or in promotions on social media you could include:
❓ “How are you architecting for MEC - cloud or on-premise in your organization?”
❓ “Are you still using a centralized EPC? What is the holdup on your MEC rollout?”
❓ “What is the biggest challenge with UPF placement in your 5G networks?"
📊 2. Include a Quick Poll (LinkedIn / blog widget)
“Where do you anticipate seeing most of your 5G UPFs deployed by 2026?”
⭕ Central Core
⭕ Regional Aggregation Sites
⭕ Enterprise Edge (on-prem)
⭕ Cloud-Native MEC Platform
📹 3. Reimagine As Visual or Video -
✔ Carousel Slides (for LinkedIn / Instagram)
Slide 1 Title
Slide 2 EPC in 4G = Centralized
Slide 3 MEC UPF in 5G = Distributed
Slide 4 Latency Comparison
Slide 5 Enterprise Use Case
Slide 6 Summary Table
Slide 7 Final Take Away
Slide 8 Call-to-Action or Poll
