CI/CD Model for Telco Cloud: DevOps Automation in Modern Telecom Networks
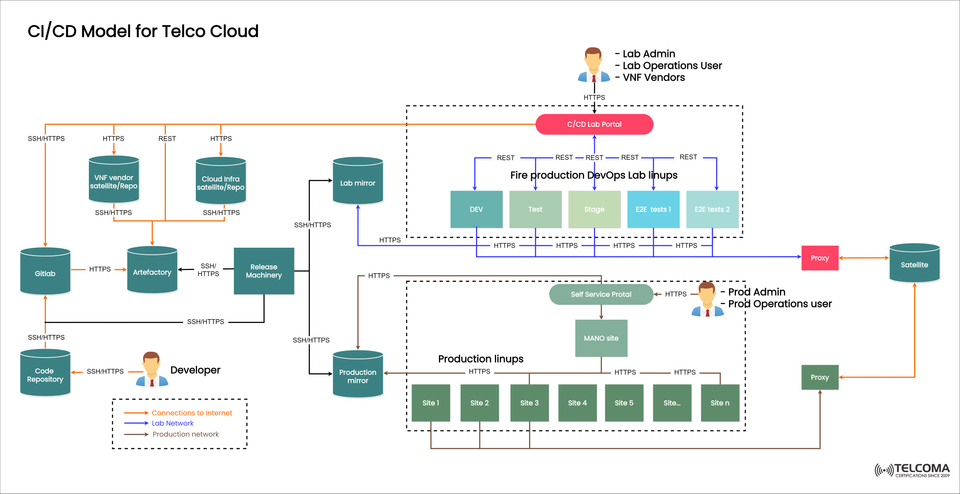

🚀 Overview of CI/CD in the Telco Cloud Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) is an important paradigm in today's telecom infrastructure. The evolution to networks that operate in cloud-native environments (or transformations) will affect how telecom operators will need to change from monolithic rollouts to agile, automated delivery pipelines.
The image we provided shows a complete CI/CD Model for Telco Cloud, and shows how the developer, staging, and production environments are connected, in a secure and scalable way.
🧱 Principal Components of Telco CI/CD Architecture The architecture in the image is DevOps-focused with clear separation between development (lab) and production spaces. Below is a description of each of the major components:
👨💻 Developer Zone
Code Repository - A place where developers save, control, and manage source code.
GitLab - Functions as the version control and CI trigger.
Artefactory - A repository of VNF packages, binaries, and dependencies.
Release Machinery - Delivers the updates to the lab and production environments.
🧪 Lab CI/CD Environment
Lab Mirror - A replication layer from external repositories.
CI/CD Lab Portal - The space that lab admins, VNF vendors, and operations will use.
Dev/Test/Stage/E2E Lineups - Slices of multiple testing locations to validate network functions (VNFs) and configuration.
Lab Network (Blue Lines) - Isolated from production to avoid cross-contamination.
🚀 Overview of CI/CD in the Telco Cloud Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) is an important paradigm in today's telecom infrastructure. The evolution to networks that operate in cloud-native environments (or transformations) will affect how telecom operators will need to change from monolithic rollouts to agile, automated delivery pipelines.
The image we provided shows a complete CI/CD Model for Telco Cloud, and shows how the developer, staging, and production environments are connected, in a secure and scalable way.
🧱 Principal Components of Telco CI/CD Architecture The architecture in the image is DevOps-focused with clear separation between development (lab) and production spaces. Below is a description of each of the major components:
👨💻 Developer Zone
Code Repository - A place where developers save, control, and manage source code.
GitLab - Functions as the version control and CI trigger.
Artefactory - A repository of VNF packages, binaries, and dependencies.
Release Machinery - Delivers the updates to the lab and production environments.
🧪 Lab CI/CD Environment
Lab Mirror - A replication layer from external repositories.
CI/CD Lab Portal - The space that lab admins, VNF vendors, and operations will use.
Dev/Test/Stage/E2E Lineups - Slices of multiple testing locations to validate network functions (VNFs) and configuration.
Lab Network (Blue Lines) - Isolated from production to avoid cross-contamination.
🧠 Key Advantages of CI/CD for Telco Cloud
✅ Faster Time-to-Market: Automated validation and deployment of VNFs and cloud infra components.
🔐 Security Compliance: Isolated lab and production network with HTTPS/SSH-based access.
📦 Standardization: Centralized repositories allow for consistency across environments.
🧪 Repeatable Testing: End-to-end test environments can catch issues before they reach production.
🧰 DevOps Friendly: Integrates developer-facing tooling (GitLab, Artifactory) for rapid iterations.
📊 Telecom Specific Considerations in This Model
Feature Benefit to Telecom Operations
VNF vendor satellite integration Real-time VNF updates from trusted, external vendors
MANO Integration Standards-based lifecycle management for network functions
Multi-Site Rollout Provides a scalable rollout capability to the edge, core, and regional data centers
Self-Service Portals Provides non-Dev user management of deployments and updates
🔚 Summary
A streamlined CI/CD model has moved from a positive enabler to a requirement as telecom operators move towards cloud-native and disaggregated architectures. With the CI/CD Model for Telco Cloud you can expect:
Scalable and secure deployments of VNFs
Collaboration between developer, vendor, and operations teams
Reliable deployment of telecom services across multi-site infrastructures.
🏗 Practical Applications of CI/CD in Telco Cloud Environments
When we talk about establishing CI/CD pipelines in the telecom cloud, it is not speculative— there are real examples of this at work, enabling significant real-world deployments on behalf of Tier-1 operators. Here are some cases:
- Virtual Network Function (VNF) onboarding
With a CI/CD pipeline, we can test and deploy new VNF versions provided by vendors, in a suppotless fashion. That means:
Minimum manual intervention
Evidence of a standardized validation meeting your E2E tests from the diagram.
Reduction vendor lock-in through interoperability validation
- Core and Edge Updates
Modern 5G networks need to deploy code frequently for:
Network slicing features
User Plane Functions (UPF)
Session Management functions (SMF)
CI/CD pipelines could mean:
Staged rollouts - testing and staging environments
Canary deployments in specific production sites (Site-1 to Site-N)
Automated rollback if failure
- Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) enables scaling of networks
Through GitOps style integration, cloud infra configuration ( e.g. Kubernetes, OpenStack, VMware) can be versioned and deployed using:
🔒 Security & Isolation Considerations
Security is paramount for Telco CI/CD frameworks due to sensitive configurations and live traffic associated with these workflows. This type of architecture encompasses:
Production divide Lab Segregation: two distinct sets of networks, for production and non-production, that prevent artefacts being tested in non-production from impacting real-time service.
Controlled Access Points: proxies that govern the outer-facing communications with vendors.
Encrypted Links: all links use HTTPS/SSH protocols to limit possible attack points.
🔄 Recommendations for Telco DevOps Teams:
To adopt the CI/CD substantially like this example, Telco teams should:
🔍 Use Pilot Projects: test out deploying with non-critical VNFs, or test networks.
🧪 Automate Testing Early: include E2E and regression tests in GitLab pipelines
📊 Monitor/Measure: use KPIs such as Deployment Frequency, Change Failure Rate, Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR).
📚 Standardized documentation: keep IaC, testing specifications, and deployment guides in its version control repository.
🧵 Feedback Loops: allow production failures or feedback to self-improve or evolve tests or configurations upstream.
📘 Glossary of Terms
Term Description
CI/CD Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment
VNF Virtual Network Function
MANO Management and Orchestration (ETSI standard for NFV)
E2E Tests End-to-End Testing validating end to end functionality
GitLab DevOps tool for source control and CI automations like pipelines
Artefactory Repository manager for binaries, docker images, artefacts and packages
Proxy Gateway that controls and monitors external access to internal
