Cloud-Delivered SD-WAN Architecture: How Encrypted Tunnels Connect Branch Offices and Data Centers

🏢 Cloud-Delivered SD-WAN: The Contemporary WAN Evolution
As enterprises continue to rapidly adopt cloud-first models, the traditional WAN (which is based on rigid MPLS circuits) starts to fail. Cloud-delivered SD-WAN has become the preferred architecture, due to its flexibility, scalability, and security.
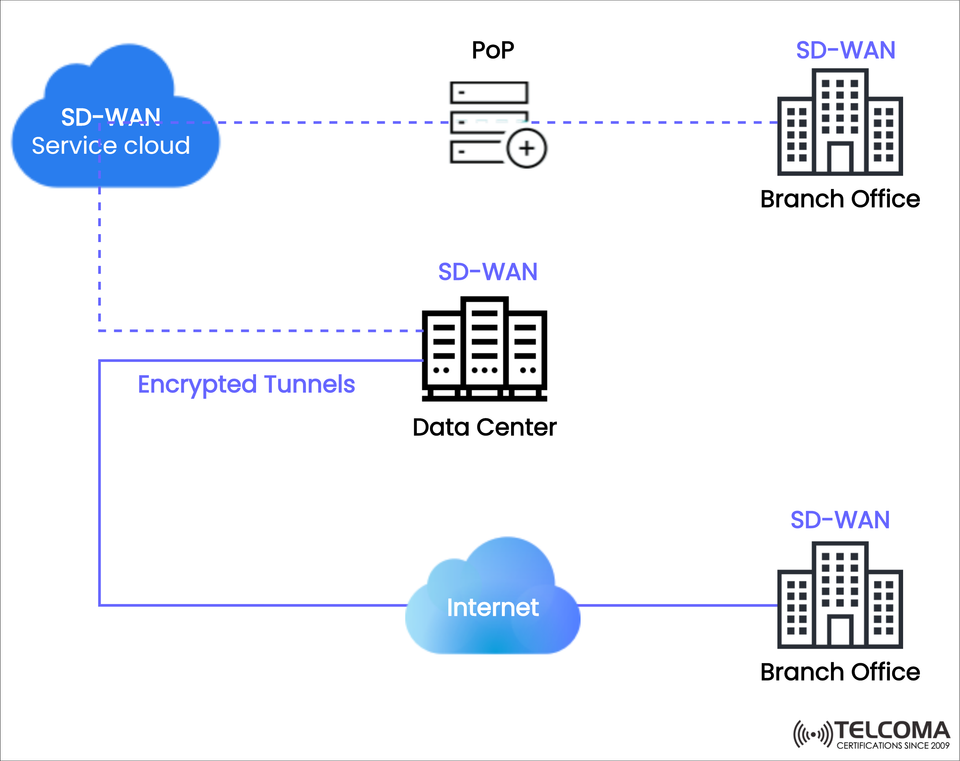
The article above shows a real-world example of how an SD-WAN overlay is designed with cloud service points, encrypted tunnels, and direct connectivity to branch offices or data centers.
🔐Key Architectural Components
- SD-WAN Service Cloud
Functions as a central orchestration layer, aggregate and manage all traffic for SD-WAN.
Traffic optimization, policy enforcement, and monitoring in a single solution.
Cloud-native delivery model that does not rely on hardware appliances. - Point of Presence (PoP)
Edge locations that are hosted by an SD-WAN vendor.
Geographically distributed across a region to reduce latency to each PoP.
Connect branch traffic to cloud/SaaS apps closer to the user to minimize delays. - Branch Offices using SD-WAN Edge
Branch routers are used to set up an encrypted tunnel directly to the SD-WAN cloud or PoPs.
Allows users direct-to-internet 'break outs' with centralized SD-WAN control.
Reduces branch traffic alone from backhauling data across place. - Connection to a Data Center
Connection via encrypted tunnels to SD-WAN overlay.
Provides footprint to legacy applications that have not yet migrated to the cloud.
Allows for hybrid workloads in private infrastructure. - Internet Transport
Commodity broadband (DSL, cable, LTE, fiber) turns into a secure transport medium
SD-WAN provides segmentation of traffic, QoS, and encryption
🔄 Encrypted Tunnel Flow (Diagram above)
From To Tunnel Type Functionality
Branch Office Internet Encrypted tunnel Direct secure access to SaaS/cloud
Branch Office PoP -> SD-WAN Cloud Encrypted overlay Orchestrated routing & security policies
SD-WAN Cloud Data Center Encrypted tunnel Access to legacy workloads
💡Why Enterprises Adopt Cloud-Delivered SD-WAN
✅ Benefits to Cloud-Delivered SD-WAN
Faster Deployment: No need to provision MPLS lines.
Better Performance: Application aware routing and local internet breakouts.
Better Security: Encrypted tunnels and centralized policy control.
Scalability: Easily Add New Branches and/or Cloud Services.
Improved Cost Structure: Use lower cost broadband with MPLS type reliability.
📌 Use Cases
Multi-branch retail stores looking for cloud SaaS access.
Hybrid enterprises have a mix of data center and cloud workloads.
Remote workforces using the internet with policy-based secure connectivity.
SaaS Optimization (e.g., Office 365, Salesforce) near PoP.
🔍 Related SEO Keywords
Cloud-delivered SD-WAN
SD-WAN PoP architecture
Secure SD-WAN tunneling
Branch Office Connectivity
Encrypted WAN overlay
Data Center SD-WAN integration
SD-WAN over the Internet
Edge-to-cloud networking
📘 Conclusion
The cloud-delivered SD-WAN technology is a base architecture for providing secure, scalable, efficient WAN connectivity as enterprise networks continue to evolve. The combination of an encrypted tunnel, cloud PoPs, and branch edge devices provide applications with optimal performance, centralized security, and a high-quality user experience.
🛠️ Real-World Deployment Strategies for Cloud-Delivered SD-WAN
To achieve a successful SD-WAN deployment involves more than just the deployment of edge devices.
Below the following are strategies used by telecom engineers and IT architects:
- Phased Rollout Strategy
Pilot Sites: Deploy SD-WAN at a few branch locations to test performance and validate security.
Monitor and tune: Use SD-WAN analytics to analyze traffic patterns, latency, and packet loss.
Scale gradually: Once successful, adopt SD-WAN in other sites, and take advantage of the templated approach configuration process. - Hybrid WAN Transition
Retain existing MPLS links during transition phase for critical traffic (VoIP, ERP, etc.)
Simultaneously, add internet links (broadband/LTE) utilizing internet links for non-critical or traffic bound to the cloud.
Gradually move to an internet-first or internet-only performance model, as the reliability of internet connectivity is developed. - Cloud Connections Readiness
List the SaaS and IaaS applications being used across the enterprise (e.g., AWS, Azure, Office 365, etc.).
Direct branch cloud access options are provided through cloud gateways or the SD-WAN PoPs (point-of-presence).
Incorporate QoS and priority traffic mechanisms.
🧩 Suggested SD-WAN Build Considerations.
Building SD-WAN with performance and availability in mind is done with thought, purpose and planning:
📌 Network Build Tips
If possible, make sure to build sites with dual WAN links - this is for availability and redundancy.
Allowing for policy-based routing (PBR) can assist you in segmenting network traffic.
Use your breakout DNS you optimize your DNS resolution - efficiency improves.
End points with encryption + firewalls are important to add at edge.
📌 Security Reminders
End-to-end encryption (IPSec or TLS tunnels) is important.
Consider zero-trust access models with identity-based policies.
Regular patching, updating, and performing software upgrades on the SD-WAN edge devices is important.
📌 Performance Tips
Take advantage of real-time application visibility, SLAs that exist (application-level or other-level).
Take advantage of WAN path conditioning (e.g., packet duplication, FEC, packet jitter buffers, etc.).
By monitoring link health metrics, you can dynamically reroute traffic over the best possible path.
🌐 Autonomate SD-WAN Into Broader Enterprise Architecture.
Having a modern network strategy does not end with SD-WAN, it includes SD-WAN integrated with:
Technology Integration Point Benefit
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) SD-WAN bundled with security (CASB, ZTNA, SWG) Unified security + networking
Multi-cloud access Direct peering with public cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) Low-latency access to all your cloud
LAN/WLAN orchestration Policies can easily extend from WAN layer to access controls layer End-to-end consistency
Network automation (NetDevOps, DevOps, etc.) API-driven policy, configuration, and monitoring makes the modern enterprise agile and repeatable.
🧠 Conclusion
Cloud-delivered SD-WAN is not just a refresh to the network but a paradigm shift in the way enterprises design connectivity for performance, scale, and security.
By,
Using encrypted tunnels to securely connect branches to cloud or data center
Using global PoPs as access to low-latency SaaS
Orchestrating everything centrally from an SD-WAN service cloud
...enterprises can make sure that users, applications, and data stay connected - securely and effectively - wherever they are located.
