CSI-ES Allocation in 5G NR | Channel State Information and Beam Management

The effectiveness of 5G New Radio (NR) hinges on the smart use of spectrum, effective beam management, and precise channel condition tracking. A vital component here is CSI-ES allocation, which controls the use of CSI-RS (Channel State Information Reference Signals) across both time and frequency domains.
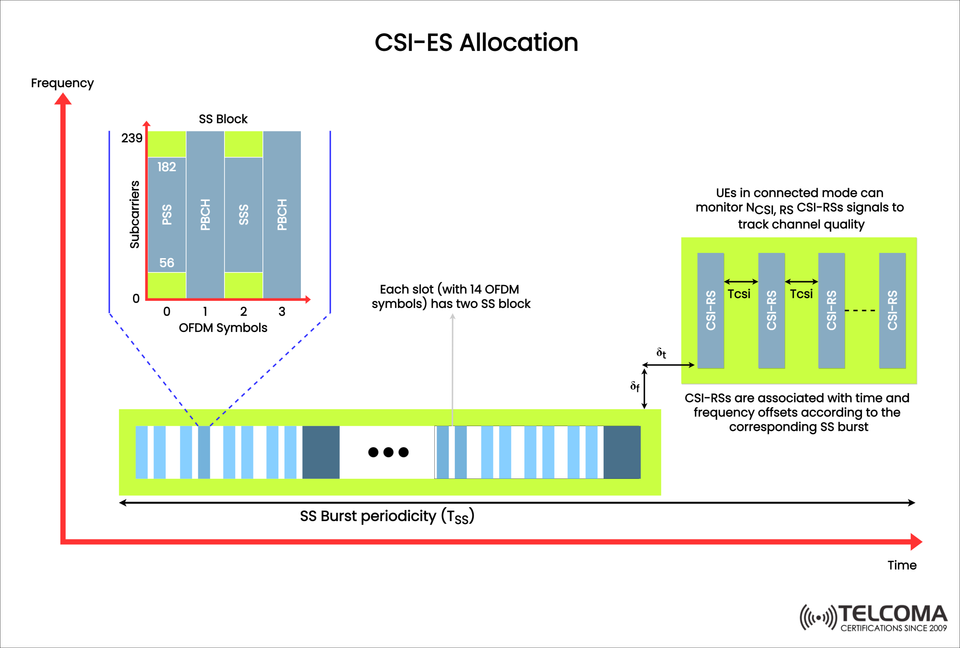
If you check out the uploaded image, you'll see:
The structure of the SS (Synchronization Signal) block.
How CSI-RS relates to time and frequency offsets.
The importance of UEs in monitoring CSI-RS to assess channel quality.
This article dives into CSI-ES allocation, its significance in 5G NR, and its role in supporting beamforming and mobility management.
What is CSI in 5G NR?
Channel State Information (CSI) is crucial feedback sent from the UE to the base station (gNB), reflecting the radio link quality and helping the network optimize:
Beamforming (for directing signals more effectively).
Resource allocation.
Adaptive modulation and coding (AMC).
To gauge channel quality, the UE relies on CSI-RS signals sent out by the gNB. The CSI-ES allocation outlines how these signals are arranged through time (slots, symbols) and frequency (subcarriers, resource blocks).
SS Block Structure in 5G
The backbone of CSI-ES allocation is the SS (Synchronization Signal) block, which allows UEs to synchronize and get initial system info.
Components of an SS Block:
PSS (Primary Synchronization Signal): Helps with symbol-level synchronization.
SSS (Secondary Synchronization Signal): Provides frame timing and cell identification.
PBCH (Physical Broadcast Channel): Shares system information (MIB).
As depicted in the image:
Each SS block covers 4 OFDM symbols in time and 240 subcarriers in frequency.
Within a slot (14 OFDM symbols), you can transmit two SS blocks.
Multiple SS blocks create an SS burst, which recurs periodically with Tss (SS burst periodicity).
CSI-RS and CSI-ES Allocation
Once the UE has synced up, CSI-RS signals allow it to keep a constant watch on the channel.
CSI-RS Functions:
Assess channel quality for beam management.
Aid handover decisions.
Facilitate link adaptation for better efficiency.
CSI-ES Allocation Explained:
CSI-RS signals associate with SS bursts using time (δt) and frequency (δf) offsets.
These offsets make sure CSI-RS signals are carefully distributed across the grid.
UEs in connected mode keep an eye on NCSI (number of CSI-RS) for precise channel tracking.
In this way, CSI-ES allocation guarantees that CSI-RS signals align properly with synchronization reference points, which reduces overhead and enhances channel visibility.
CSI-ES Allocation in Time and Frequency
You can visualize the CSI-RS allocation in two main domains:
- Time Domain Allocation
CSI-RS signals are inserted at regular intervals within OFDM symbols.
The periodicity (Tcsi) indicates how often a CSI-RS is sent out.
UEs monitor channel quality changes over time, which is especially important for mobility scenarios.
- Frequency Domain Allocation
CSI-RS signals are assigned to specific subcarriers.
δf makes sure CSI-RS doesn’t overlap with data or control channels.
Frequency diversity boosts resilience against fading.
This strategic positioning ensures that UEs can effectively decode CSI-RS signals, no matter where they are in the cell.
Benefits of CSI-ES Allocation
Accurate Beam Management * CSI-ES allows UEs to gauge channel quality per beam. * Networks can shift beams dynamically for better reliability.
Improved Mobility Support * It eases handovers by providing ongoing CSI feedback. * Reduces service interruptions when users move around.
Efficient Spectrum Usage * CSI-RS are spread out without unnecessary redundancies. * Lowers overhead compared to older LTE reference signals.
Supports Massive MIMO * Various CSI-RS configurations help scale with large antenna arrays. * Boosts multi-user beamforming efficiency.
Energy Efficiency for UEs * Well-structured CSI-ES allocation means UEs focus on relevant CSI-RS, which saves battery life.
Example: CSI-ES in Action
Picture a UE in connected mode as it moves across a cell:
The gNB sends out SS blocks for synchronization.
Based on SS bursts, the gNB schedules CSI-RS with δt and δf offsets.
The UE tracks CSI-RS periodically and sends back channel state updates.
The network adjusts beam direction, triggers handovers, and modifies modulation schemes dynamically.
Without CSI-ES allocation, the UE would likely encounter dropped beams, more interference, and reduced throughput.
CSI-RS Types in 5G
5G NR outlines various types of CSI-RS for different applications:
Tracking CSI-RS: For ongoing beam tracking.
Interference Measurement CSI-RS (IM-RS): Helps UEs gauge interference levels.
Aperiodic CSI-RS: Triggered as needed for specific readings.
Semi-persistent CSI-RS: Regular but less frequent signals, which help conserve resources.
CSI-ES allocation ensures all sorts of these signals are strategically placed within the resource grid.
Challenges in CSI-ES Allocation
Overhead Management: Too much CSI-RS can squander spectrum resources.
Beam Tracking in High Mobility: Keeping alignment with fast-moving users can be tricky.
Interference: Poorly aligned CSI-RS allocations can interfere with nearby beams.
Complexity: It demands advanced scheduling and coordination at the gNB.
Even with these challenges, CSI-ES allocation is essential for optimizing 5G performance.
Applications of CSI-ES Allocation
5G Mobile Broadband: Ensures consistently high throughput.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC): Accurate channel tracking for crucial applications.
Massive IoT: Efficient use of reference signals in crowded setups.
Beamforming and Massive MIMO: Key for dynamic beam switching.
6G Research: Concepts around CSI-ES will advance for next-gen smart networks.
Conclusion
The CSI-ES allocation framework in 5G NR marks a significant step forward in managing channel quality and beamforming. Unlike LTE, where reference signals were typically more rigid and resource-heavy, 5G brings in a flexible, structured time-frequency approach for placing CSI-RS.
By syncing CSI-RS with SS bursts and controlling them through δt and δf offsets, networks gain:
Precise beam management.
Effective spectrum use.
Reliable mobility support.
Enhanced user experience in various mobility scenarios.
For telecom experts, grasping CSI-ES allocation is vital for mastering 5G NR design, deployment, and optimization. It’s the behind-the-scenes support that keeps every 5G device connected efficiently and with minimal interference.
