CU/DU Virtualization and Open RAN Interfaces: Enabling Cloud-Native 5G Networks

CU, DU Virtualization and Open RAN Interfaces: Cloud-Native RAN for Next Generation 5G
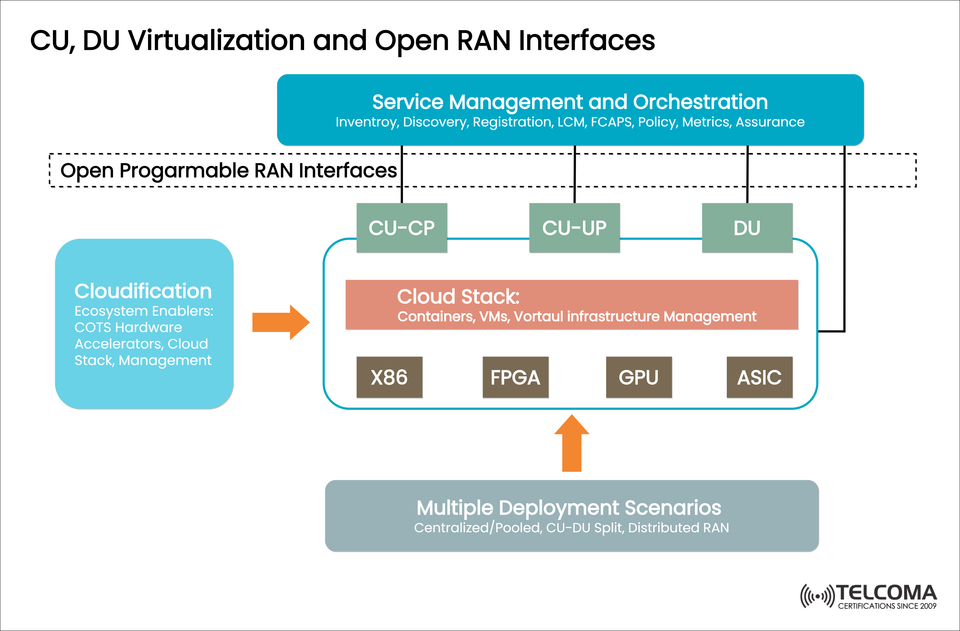
As the telecom industry moves to open, cloud-native architectures, CU/DU virtualization and Open RAN interfaces are critical building blocks for scalable, flexible 5G networks. This blog post describes the logical model and components seen in the diagram, and discusses how cloudification, orchestration, and virtualization enable 5G deployments.
This document is targeted towards telecom-oriented audiences and network architects that want to understand how disaggregated and virtualized RAN architectures can be instantiated using open software and COTS/commercial hardware.
🌐 What is CU/DU virtualization?
In traditional RAN architectures, the control and user data plane functions are tightly integrated together and bound to real, physical hardware. RAN virtualization disaggregates these functions into;
CU-CP (Centralized Unit – Control Plane): Provides control signaling and session management;
CU-UP (Centralized Unit – User Plane): Manages any user data transmission;
DU (Distributed Unit): Acts on the real-time, lower-layer radio protocols.
The upper three components can now run as Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) or containers that can run on Cornmerical Off-the-Shelf (COTS) hardware, and allow scaling at deployment time and execution time.
☁️ Cloudification: The Enabler for Modern RAN
What is cloudification?
Cloudification involves migrating the network functions to be on a cloud-native platform by utilizing:
What is Cloudification?
Cloudification is the process of migrating network functions to cloud-native platforms, which can be based upon:
COTS (Commercial Off-The-Shelf) hardware, such as x86 servers.
Virtualization tools (VMs and containers).
Cloud stacks which provide orchestration and infrastructure.
Key Aspects regarding Cloudified RAN:
Aspect Function
Cloud Stack Hosts containers, VMs, and manages virtual infrastructure
X86 / FPGA / GPU / ASIC Provides hardware flexibility to enhance performance, provide acceleration and minimize costs
Containers & VMs Allow provisioning of layered, portable, and scalable network functions
Service Orchestration Allows the automation of provisioning, scaling and lifecycle management
🔗 Open Programmable RAN Interfaces
Open RAN interfaces are standardized, vendor-neutral interfaces that enable interoperability and modular RAN deployments. They enable:
Disaggregation of CU and DU
Multi-vendor integration of network elements
Central or Distributed control and data planes
These interfaces enable a multi-vendor best-of-breed approach, free from vendor lock-in and ultimately will be paramount to the success of O-RAN..
🔧 Service Management and Orchestration (SMO)
At the top of the architecture there is Service Management and Orchestration, which provides:
Inventory & Discovery
Registration & LCM (Lifecycle Management)
Policy & FCAPS (Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, Security)
Assurance & Metrics
This layer unifies the various RAN components and guarantees end-to-end automation and visibility, while also simplifying the operational complexity of the RAN and improving operational efficiency and performance.
🚀 Multiple Deployment Scenarios
Because CU and DU functions can be virtualized, deployment models become much more flexible and dependent on network requirements and performance limitations.
Deployment Modes:
Centralized RAN: CU/DU in hosted in data centers or edge cloud
CU-DU Split: CU is logical in the cloud and DU on site
Distributed RAN: DU and CU are deployed pretty close to cell sites
Scenario Use Case
Centralized/Pooled CU Urban Areas with high capacity needs
Edge-Deployed DU Latency-sensitive applications
Distributed RAN Private, Low-Latency, or Rural Networks
📊 Summary of CU/DU Virtualization Benefits
✅ Scalability - all resource elements can be scaled up and down on demand & dynamically
✅ Cost-efficacy - use COTS rather than proprietary hardware
✅ Flexibility - deployment area topologies can be implemented best suited to your own needs
✅ Vendor interoperable - open interfaces allow you true mix and matching
✅ Automation - done pretty efficiently through the SMO and orchestration layers
🧠 Last Thoughts
The CU and DU virtualization (thanks to open RAN interfaces and cloud-native tech) is ushering in a change in the telecom space that allows operators to innovate, create cost efficiencies, and deploy 5G networks faster than they have ever been deployed. With the overview of building blocks shown in this diagram (cloud stacks, orchestration, and deployment models), network professionals should be more prepared to plan for future requirements of a RAN architecture.
🧩 Deployment Strategies: Adapting RAN for Your Needs
When planning CU/DU virtualization and Open RAN deployment strategies, balancing performance, geography, and cost will determine the appropriate decision. Operator should consider the following:
🔹 Centralized CU with Edge DU
Optimally suited for high-density urban setups where;
CU functions are based in centralized cloud data centers
DU functions are placed closer to the radio sites to minimize latency.
🔹 Fully Centralized RAN (C-RAN)
CU and DU functions are both hosted in physically centralized space.
Best suited for good fronthaul capacity environments.
🔹 Distributed RAN
CU and DU functions are deployed at or near the edge or cell sites.
Typical in rural areas for high reliability, or in private 5G networks.
💻 Hardware Acceleration and Platforms
Modern RAN workloads are compute-bound, and virtualized methodologies must balance flexibility with performance. There are several hardware components to consider:
Hardware Use Case
X86 General compute with unlimited support for VMs/containers
FPGA Custom, optimized acceleration for the MAC/PHY layer
GPU Well-suited for signal processing and AI-based RRM
ASIC High performance and low power for fixed workloads
Cloud stack orchestrates these platforms, ensuring VNFs are mapped to hardware depending on real-time requirements and SLAs.
🧩 Deployment Strategies: Tailored RAN to Your Needs
When determining CU/DU virtualization and Open RAN deployment strategies, it is important to balance performance, geography, and cost, and your choices will ultimately be informed by this balance. Operators should think about the following:
🔹 Centralized CU with Edge DU
The centralized CU with edge DU option provides an optimal strategy for urban high-density locations because, as the name implies;
- CU is located in a centralized cloud data center,
- DU located as close to the radio as possible when latency is a major consideration.
🔹 Fully Centralized RAN (C-RAN)
All CU and DU functions are strictly housed in a physically centralized space. This deployment strategy would provide the best opportunity for areas with good fronthaul capability.
🔹 Distributed RAN
CU and DU function being deployed at or up to the edge or cell site. This strategy is typical for rural areas when high reliability is desired (eg. high ambient seasonal weather), or for private 5G networks.
💻 Hardware acceleration and platforms
The most recent RAN workloads are compute bound, and virtualization has to balance flexibility with performance. The hardware has several possibilities:
Hardware Use Case
X86 General compute with a virtually unlimited amount of VM/containers to support
FPGA Custom optimized acceleration for the MAC/PHY layer
GPU Well suited for signal processing and AI based RRM
ASIC Allows for high performance and low power for fixed workloads
The cloud stack orchestrates them all at a normative layer so that VNFs are mapped to the hardware depending on real time operational need and SLA Requirements.
