Directions in 5G Evolution: Release 16/17 Enhancements and Future Use Cases
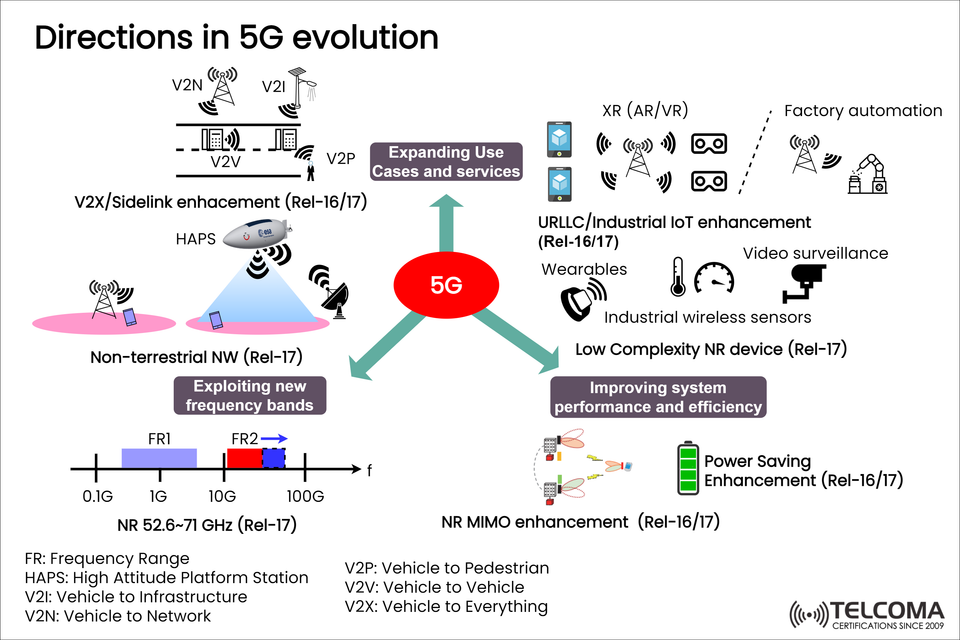

Since it first came out, 5G has really changed the game in mobile communications, providing super-fast internet, low latency, and support for tons of IoT devices. But we're not done yet. With improvements rolling out in 3GPP Release 16 and Release 17, 5G is becoming a real platform for innovation, driving growth in advanced industrial, automotive, and consumer applications.
The image above highlights some key trends in 5G evolution, such as:
New use cases and services
Tapping into additional frequency bands
Boosting system performance and efficiency
Let’s dive deeper into each of these aspects.
Expanding Use Cases and Services
The true value of 5G isn’t just about speed; it also opens doors for new verticals and applications. With Release 16 and 17, we see major enhancements for vehicle communication, industrial automation, IoT, and immersive technologies.
V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) Communication
Release 16/17 introduces sidelink enhancements that allow vehicles to communicate directly with each other and with infrastructure:
V2V (Vehicle-to-Vehicle): Makes roads safer by enabling collision avoidance and coordinated driving.
V2I (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure): Offers real-time updates from traffic signals, road sensors, and smart highways.
V2N (Vehicle-to-Network): Uses cloud-based intelligence for navigation, predictive maintenance, and managing fleets.
V2P (Vehicle-to-Pedestrian): Alerts pedestrians and vehicles to each other's presence, boosting safety.
These improvements bolster the connected mobility and autonomous driving landscape.
Industrial IoT & URLLC
Enhancements in URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) support factory automation, robotics, and mission-critical IoT applications.
Real-world uses include video surveillance, wireless sensors, and process control.
5G ensures reliable communication for safety-critical tasks by offering deterministic latency.
Extended Reality (XR: AR/VR)
5G Release 17 boosts support for AR/VR headsets and immersive experiences.
The low-latency, high-bandwidth connection makes XR practical for areas like remote training, telemedicine, and industrial maintenance.
Wearables & Consumer IoT
Everything from health monitoring devices to connected wearables see improvements in signaling and power efficiency with Release 17.
This means we can have continuous monitoring without draining the battery too quickly.
Exploiting New Frequency Bands
5G is also branching out into new spectrum ranges to handle the growing demand for data.
FR1 and FR2 Spectrum
FR1 (sub-6 GHz): Offers wide coverage along with reliable connectivity.
FR2 (mmWave, up to 52.6 GHz): Delivers incredibly high capacity, which is perfect for crowded city areas.
NR Frequency Bands (Release 17)
The jump into the 52.6 GHz – 71 GHz range creates fresh opportunities for super-fast data rates.
This is crucial for data-heavy applications like 8K video streaming, XR, and high-density IoT networks.
Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN)
Release 17 also includes support for non-terrestrial networks (NTN), connecting satellites and high-altitude platforms with 5G.
HAPS (High-Altitude Platform Stations): Help provide connectivity to remote areas.
LEO satellites: Expand coverage for maritime, aviation, and areas that lack broadband.
Disaster recovery: NTN can restore communication when natural disasters hit.
With NTN, 5G is taking a big step toward global coverage.
Improving System Performance and Efficiency
Besides enhancing coverage and use cases, 5G is also focusing on system-level improvements in performance, efficiency, and device optimization.
NR MIMO Enhancement (Rel-16/17)
Improvements in Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology aim for better spectral efficiency.
Enhancements boost both uplink and downlink performance, which is key in densely populated areas.
They also support advanced beamforming to maintain stable connections when on the move.
Low-Complexity NR Devices (Rel-17)
Release 17 rolls out low-cost, low-power NR devices tailored for massive IoT scenarios.
Perfect for industrial sensors, smart meters, and wearables that need long battery life without needing high data speeds.
Power Saving Enhancements (Rel-16/17)
5G introduces advanced sleep modes and smarter signaling for better power efficiency.
These features help lengthen battery life for IoT devices and wearables, leading to lower operating costs.
Summary of 5G Evolution Directions
Direction | Release Enhancements | Key Use Cases
Expanding Use Cases | V2X (Rel-16/17), URLLC, Industrial IoT, XR | Autonomous driving, factory automation, AR/VR
Exploiting New Bands | NR 52.6–71 GHz (Rel-17), NTN (satellite & HAPS) | High-speed broadband, global coverage, IoT scaling
Improving Efficiency | NR MIMO, low-complexity NR devices, power saving | IoT sensors, wearables, dense urban deployments
Challenges in 5G Evolution
Even with the exciting upgrades in 5G Release 16/17, there are still hurdles to overcome:
Spectrum allocation in the higher frequency ranges needs global coordination.
Device affordability for low-complexity NR devices is crucial for widespread adoption.
Integration with satellite networks (NTN) will require careful standardization.
As 5G grows into critical industries, security concerns are becoming more pressing.
Towards Hyper-Connectivity
With the integration of NTN (satellites and High Altitude Platform Stations), 5G is already paving the way for a global network of networks, and 6G is set to take this a step further.
6G aims to provide true global coverage by enhancing how terrestrial, aerial, and space systems work together.
Extreme Low Latency and Reliability
URLLC in 5G allows for advancements in automation, robotics, and critical IoT applications.
By the time we reach 6G, latency should drop to sub-millisecond levels, enabling things like holographic communication, tactile internet, and next-gen tele-surgery.
AI-Native Networks
Right now, 5G networks are starting to use AI for network optimization.
Looking ahead to 6G, AI and machine learning will be deeply embedded, allowing networks to be self-optimizing, self-healing, and aware of their context.
Spectrum Beyond 100 GHz
5G Release 17 is already exploring frequencies up to 71 GHz.
With 6G, we'll see an expansion into the terahertz spectrum (100 GHz – 1 THz), which will provide ultra-high data rates for things like holographic conferencing and digital twins.
Sustainability and Green Networks
There’s been a push for energy efficiency in 5G devices, reflecting the industry's dedication to saving power.
6G will put an even greater focus on carbon-neutral networks, better spectrum usage, and infrastructure powered by renewable energy.
Conclusion
The evolution of 5G through Release 16 and 17 marks a significant step toward achieving the vision of ubiquitous, reliable, and intelligent connectivity.
Expanding use cases such as V2X, industrial IoT, and XR show how 5G is reshaping various industries.
New frequency bands and non-terrestrial networks stretch the limits of global coverage and capacity.
Upgrades in system performance, like MIMO enhancements, low-complexity NR devices, and power-saving features set the stage for long-term sustainability.
