Disaggregated RAN Architecture in 5G: Understanding 3GPP Logical Split of CU and DU

📘 Introduction: The Shift Towards Disaggregated RAN
With the deployment of 5G, the radio access network (RAN) has experienced an architectural overhaul. The old uniform RAN has transformed into a Disaggregated RAN (or Open RAN) architecture that complies with 3GPP specifications. The disaggregated approach separates functions between the Centralized Unit (CU) and the Distributed Unit (DU) which enhances network agility, scalability, and cost savings.
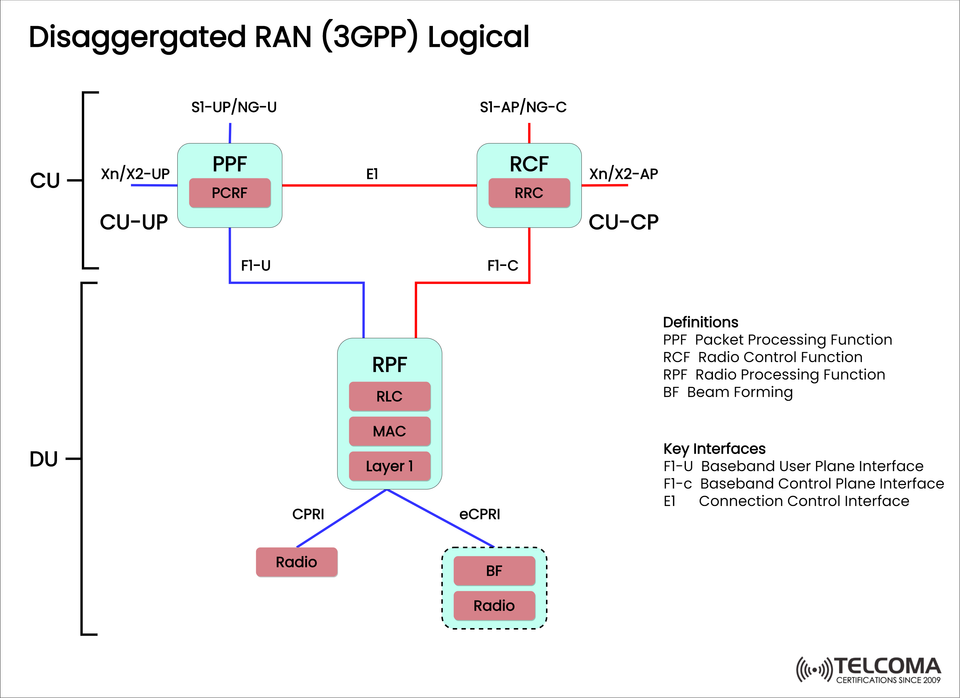
The diagram imported earlier, identifies the logical architecture of a Disaggregated RAN, focusing on:
Packet and Radio Control Functional splits
User and Control Plane separation
Standard interface definitions (E1, F1-U, F1-C, etc.)
🧠 The 3GPP Logical Architecture of Disaggregated RAN
📌 Disaggregated RAN Components:
Component Full Name Function
PPF Packet Processing Function User Plane Functions, and forwarding user traffic.
RCF Radio Control Function Controlled Plane signalling (RRC).
RPF Radio Processing Function Implementing the RLC, MAC, and PHY Layer 1
BF Beam Forming Spatial Signal Processing (optional function).
📍 CU-CP vs CU-UP.
CU-CP (Control Plane). Handled signaling responsibilities in support of mobility, security, and bearer setup via the RCF function.
CU-UP (User Plane). Used to transport actual data via the PPF.
🔗 Landscape of Interfaces in the architecture
Interface Function
E1 Between CU-CP and CU-UP (connection control)
F1-U Between CU-UP and DU (user plane interface)
F1-C Between CU-CP and DU (control plane interface)
CPRI/eCPRI Link to DU to physical radio units
Logically separating these functions can allow vendor-neutral, cloud-native deployments and will allow easier maintenance and upgrades of the architecture.
🏗 Architecture overview (from Image)
Control Plane Path:
RCF (RRC) ↔ RPF via F1-C
RCF ↔ PPF via E1
User Plane Path:
PPF (PCRF) ↔ RPF via F1-U
RPF ↔ Radio via CPRI/eCPRI
Radio Interface Layer:
RPF will host RLC, MAC and Layer 1 functions
Downlink to radio units or beamforming modules.
⚙ Advantages of disaggregated RAN Architecture
✅ Vendor interoperability with standardized interfaces
✅ Network Function Virtualization (NFV) capable
✅ Dynamic scaling of CU and DU resources
✅ Improved latency by placing DU resources closer to edge
✅ Centralized management for quicker upgrades and fault resilience.
🔮 The future: Open RAN and 6G
The 3GPP disaggregated RAN architecture is a foundation for Open RAN initiatives and cloud-native deployments towards 6G; additional decomposition and self-organizing networks achieved via intelligent orchestration (AI/ML) will demonstrate zero-touch networks.
🧩 Disaggregated RAN versus Traditional RAN – A Rapid Comparison
Feature Traditional RAN Disaggregated RAN (3GPP)
Architecture Monolithic Modular (CU/DU separation)
Scalability Limited High (virtualization-friendly)
Vendor Flexibility Low (vendor-locked) High (open interfaces)
Deployment Model Hardware-centric Cloud-native/NFV-compatible
Upgradability Complex, rigid Agile, container-based
Interface Standardization Proprietary or closed Standardized (E1, F1-U, F1-C)
Latency Optimization Limited edge control DU at edge, CU centralized
📡 When to Use the Disaggregated RAN Architecture
The 3GPP Disaggregated RAN is best suited to:
✅ High-density urban areas (small cells + centralized CU)
✅ Rural or remote deployments that need DU-local processing
✅ Private 5G Network for enterprises and industrial IoT
✅ Network slicing in standalone 5G architecture
✅ Multi-access edge computing (MEC) environments
🔌 Real-World Implementation of Disaggregated RAN
Equal Logic outlines the reality of the disaggregated RAN model and how this all works in practice:
Edge Data Centers having DU components (RFP), which essentially means ultra-low latency.
Cloud Platforms or centralized telco clouds hosting CU-UP and CU-CP, which enables global coordination and management of the distributed radio system.
Depending on the operational environment, beamforming (BF) is done at the DU-radial layer for massive MIMO use cases for 5G (also beyond).
The logical separation of elements enables the operator to deploy multi-vendor solutions which is the cornerstone of the Open RAN ecosystem they promote.
✅ Summary
Disaggregated RAN splits up the RAN's critical functions into CU and DU, enabling flexibility, scalability, and virtualization.
Disaggregated RAN uses standard interfaces (F1-U, F1-C, E1) to allow interoperability and multi-vendor ecosystems.
Disaggregated RAN facilitates edge computing, beamforming, and cloud-native deployment, which is essential for applications - 5G and beyond.
PPF (CU-UP) carries the user data packets, RCF (CU-CP) manages the control signaling, and RPF (DU) handles the lower-layer radio processing.
Disaggregated RAN is a building block towards Open RAN, intelligent automation and scalable cost efficiently.
📈 Strategic Advantages for Operators
🧩Vendor Agility: Mix and match CU/DU vendors to provide best class deployments.
🌍Global Scalable: Deploy centralized CUs to serve multiple DUs around the world.
⏱️ Low Latency: DUs where geographically located on the edge results in better performance for URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications).
🛠️Network Slicing and MEC: Applications or tenants benefit from disaggregated network slicing with edge processing.
📣 Final Call to Action
In order to remain competitive in the ever-evolving 5G era, telecom operators need to adopt disaggregated and virtualized RAN. Whether you are building out private 5G networks or deploying nationally you need to recognize the 3GPP logical split to release the performance, flexibility, and cost effective model of a disaggregated RAN.
📊 SEO summary
📌 SEO-Friendly Blog Title
Disaggregated RAN (3GPP) Architecture - CU-CP, CU-UP, DU & Logical Interfaces Explained
📌 Excerpt
Discover the 3GPP disaggregated RAN logical architecture with CU-CP, CU-UP and DU functions and the E1, F1-U and F1-C interfaces that provide 5G flexibility.
📌 Meta Description
Learn about 3GPP Disaggregated RAN architecture, including CU/DU split, logical functions and interfaces like F1-U, F1-C and E1 for flexible 5G deployment.
📌 SEO Keywords
Disaggregated RAN, 3GPP CU-CP CU-UP DU, F1-U interface, F1-C control, RAN architecture 5G, logical RAN split, Open RAN, radio processing function, beamforming, RCF PPF RPF.
🧾 Conclusion
The logical disaggregation of RAN functions into CU-CP, CU-UP, and DU as defined by 3GPP represents a genuinely revolutionary re-design of the network. This architecture enables multi-vendor support, cloud scalability, network slicing, and edge intelligence. For operators, it is a next-level approach to low-cost, flexible, and future-proof wireless infrastructure.
