End-to-End 5G Service Design and Orchestration: Architecture, Components & Workflow

Explaining End-to-End 5G Service Design and Orchestration
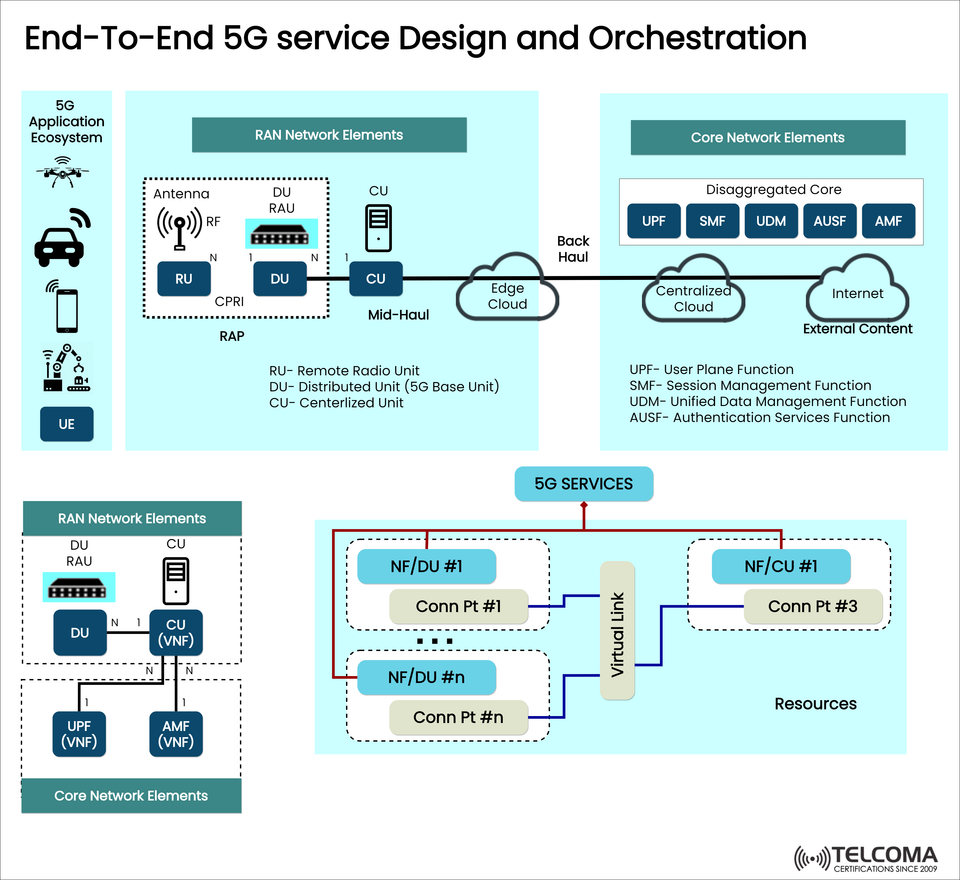
5G isn’t just about speed; it’s a whole ecosystem that combines software-defined architecture, virtualization, automation, and edge computing. The diagram up top shows how end-to-end 5G service design and orchestration help deliver ultra-reliable, low-latency, and high-bandwidth services from user devices to the core network and beyond.
This blog breaks down each part in the diagram, detailing how RAN elements, core functions, clouds, and orchestration frameworks work together to provide seamless 5G connectivity and service flexibility.
Understanding End-to-End 5G Architecture
In 5G, the service chain starts at the user equipment (UE), travels through the RAN (Radio Access Network), core network, and edge/cloud infrastructure, and ultimately reaches external content or services.
This framework supports various use cases—such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, IoT, and enhanced mobile broadband—that each have their own networking needs.
Key Components of 5G Service Design
Layer | Function | Example Components
5G Application Ecosystem | Hosts user and enterprise applications | IoT devices, drones, connected cars
RAN Network Elements | Manage radio connectivity and data transmission | RU, DU, CU
Core Network Elements | Handle data routing, authentication, and policy | UPF, SMF, UDM, AUSF, AMF
Cloud Layers | Provide computational and storage resources | Edge Cloud, Centralized Cloud
Orchestration & Services Layer | Automate configuration, scaling, and optimization | Network Functions Virtualization (NFV), MANO, Orchestrators
RAN Network Elements: The Frontline of 5G
The Radio Access Network (RAN) is where users first connect with the 5G ecosystem. It has distributed and virtualized components that separate hardware and software to boost flexibility and scalability.
- Remote Radio Unit (RU)
Manages radio frequency (RF) functions.
Connects to antennas and converts digital signals to analog for transmission.
Linked to the DU through CPRI (Common Public Radio Interface) or eCPRI.
- Distributed Unit (DU)
Handles real-time tasks like scheduling, coding, and radio link control.
Positioned closer to the edge to reduce latency.
Communicates with the RU via Fronthaul connections and with the CU through Midhaul.
- Centralized Unit (CU)
Manages higher-layer protocols (PDCP, SDAP).
Takes care of separating the control and user planes.
Connects with the core network over Backhaul links.
Together, the RU, DU, and CU create the RAN Access Point (RAP) that enables smooth data flow from the user to the network core.
Core Network Elements: The 5G Brain
The 5G Core (5GC) is fully cloud-native and disaggregated, allowing its functions to scale independently. It supports a service-based architecture (SBA), which makes networks modular and programmable.
Disaggregated Core Components
UPF (User Plane Function): Takes care of data forwarding and packet routing to connect user traffic with external networks.
SMF (Session Management Function): Manages session setup, IP allocation, and policy enforcement.
UDM (Unified Data Management): Stores user subscription and profile information.
AUSF (Authentication Server Function): Manages authentication for secure access to the network.
AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function): Handles mobility management, registration, and connection setup.
This separation helps with network slicing, service agility, and multi-access edge computing (MEC)—crucial for modern 5G applications.
Cloud Layers: Edge and Centralized Clouds
- Edge Cloud
Near the RAN to host functions that are sensitive to latency.
Cuts down on data transport time and supports real-time applications like AR/VR and autonomous driving.
- Centralized Cloud
Located in data centers, hosting control plane and management tasks.
Offers scalability and coordination across several edge clouds.
The link between edge and centralized clouds ensures services are efficiently distributed—edge for speed, core for scalability.
End-to-End Service Orchestration in 5G
The orchestration layer ties all components together—from network resources to virtualized functions—to guarantee top-notch performance, scalability, and automation.
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and 5G Services
In a virtualized 5G network:
Network Functions (NFs) like DU, CU, UPF, and AMF are implemented as Virtual Network Functions (VNFs).
Each VNF runs on cloud infrastructure handled by orchestration frameworks like MANO (Management and Orchestration).
The diagram demonstrates how NF/DU #1 to NF/DU #n and NF/CU #1 represent the virtualized instances of distributed and centralized units. These VNFs connect through Virtual Links that ensure smooth communication and data transfer.
How 5G Service Orchestration Works
Service Design: * Identify 5G services (like eMBB, URLLC, mMTC). * Set performance parameters and network slices.
Resource Allocation: * Virtual resources (compute, storage, network) are dynamically assigned. * VNFs are activated based on the service requirements.
Automation and Scaling: * Orchestration platforms keep an eye on KPIs. * Resources are adjusted automatically.
Service Assurance: * Real-time analytics confirm SLA compliance. * AI-driven systems help predict and avoid performance issues.
This overall orchestration allows operators to effectively roll out and manage services across the RAN, core, and cloud.
Benefits of End-to-End 5G Orchestration
- Flexibility and Agility
Dynamic scaling and modular functions enable networks to react quickly to shifts in demand.
- Reduced Latency
Edge computing and separating DU/CU functions get critical tasks closer to users.
- Cost Efficiency
Virtualization cuts down on hardware dependency, which lowers CAPEX and OPEX.
- Network Slicing
Dedicated network segments make sure performance is optimized for specific applications (like IoT vs. high-speed video).
- Automation and Self-Healing
AI-enhanced orchestration supports predictive maintenance and faster recovery from faults.
Use Cases Made Possible by End-to-End 5G Design
Use Case | Network Requirement | Enabled By
Smart Manufacturing | Ultra-reliable low latency | Edge Cloud + Network Slicing
Autonomous Vehicles | Real-time processing | DU near edge + UPF at MEC
Smart Cities | Massive IoT connectivity | Core network disaggregation
AR/VR Gaming | High bandwidth, low delay | CU at edge + virtualized resources
Conclusion: Laying the Groundwork for 5G Innovation
End-to-end 5G service design and orchestration sit at the core of the 5G revolution. By virtualizing network functions, spreading out computing resources, and using intelligent orchestration, telecom operators can provide flexible, efficient, high-performance services at scale.
Every layer, from RAN to Core to Cloud, works together to create a connected ecosystem—one that drives innovations like smart cities, autonomous systems, and the digital enterprises of the future.
5G orchestration goes beyond just managing connectivity; it’s about integrating intelligence into the network itself.
