End-to-End Disaggregated System: Mobile Core and Split-RAN Architecture

Introduction: Why Disaggregation is Key for Mobile Networks
As telecom companies gear up for 5G and beyond, there's a growing need for networks that can scale, respond quickly, and provide flexibility. This is leading us away from traditional, hardware-heavy setups. The answer? Disaggregated systems, which break down the conventional all-in-one functions into modular, software-driven parts.
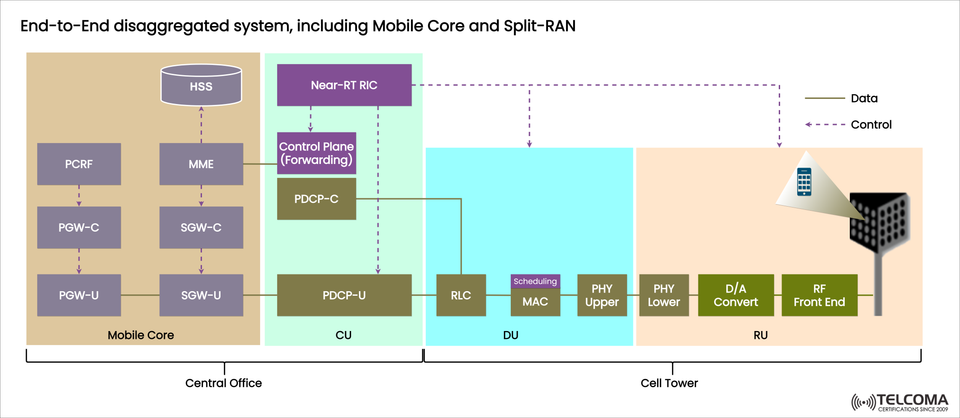
The diagram illustrates an end-to-end disaggregated system that includes:
Mobile Core (EPC/5GC functions).
Split-RAN architecture (Central Unit, Distributed Unit, Radio Unit).
A Near-RT RIC (Near Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller) for optimization.
This approach allows operators to create networks that are cloud-native, programmable, and cost-effective.
Mobile Core in Disaggregated Systems
The mobile core plays a crucial role in user authentication, ensuring mobility, and forwarding data. In a disaggregated setup, the control and user planes are divided:
PCRF (Policy and Charging Rules Function): Takes care of QoS and charging policies.
MME (Mobility Management Entity): Manages mobility and session control.
SGW-C (Serving Gateway Control Plane): Oversees user session forwarding.
SGW-U (Serving Gateway User Plane): Responsible for forwarding user data packets.
PGW-C (Packet Gateway Control Plane): Manages connections to external networks.
PGW-U (Packet Gateway User Plane): Forwards data packets to the internet or data networks.
HSS (Home Subscriber Server): Stores subscriber data for authentication and profiles.
In disaggregated cores, these functions can be run on virtual machines or containers, which enhances scalability and allows for independent updates.
Split-RAN Architecture
Traditionally, the Radio Access Network (RAN) has been centralized, but with disaggregation, we're seeing a split-RAN model that distributes functionality among three major units:
Central Unit (CU):
Contains higher-layer functions like PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol).
Divided into:
PDCP-C (Control Plane): Deals with signaling, session setup, and control.
PDCP-U (User Plane): Manages user traffic.
Connects with the Near-RT RIC for smart control and optimization.
Distributed Unit (DU):
Handles real-time functions nearer to the cell site.
Includes:
RLC (Radio Link Control) for error correction and retransmissions.
MAC (Medium Access Control) for resource scheduling.
PHY Upper/Lower for processing at the physical layer for radio communications.
Radio Unit (RU):
Positioned at the cell tower, managing radio frequency tasks.
Includes:
D/A Convert (Digital-to-Analog Conversion).
RF Front End for signal transmission to and from user devices.
This distribution sharpens the optimization of latency-sensitive tasks at the edge (DU/RU), while consolidating higher-level tasks in the CU for better efficiency and control.
Role of Near-RT RIC in RAN Intelligence
The Near Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Near-RT RIC) represents a major advancement in O-RAN setups. It enables:
Policy-driven optimization of the RAN.
Closed-loop automation for traffic management, load balancing, and handling interference.
Support for xApps that boost RAN intelligence with modular applications.
In this framework, the Near-RT RIC interacts with both CU and DU through control signaling, ensuring real-time adaptability to network conditions.
Data and Control Plane Separation
The diagram shows how Data and Control are separated:
Control Plane:
Involves functions like MME, SGW-C, PGW-C, PCRF, PDCP-C, and Near-RT RIC.
Looks after signaling, mobility, and session setups.
User Plane (Data):
Includes SGW-U, PGW-U, PDCP-U, RLC, MAC, PHY, RU.
Responsible for actual data transfer to and from user devices.
This separation (CUPS: Control and User Plane Separation) is crucial in 5G architecture, allowing for independent scaling of both signaling and traffic operations.
Advantages of End-to-End Disaggregated Systems
Disaggregation offers a range of advantages for both operators and businesses:
Flexibility: Core, CU, DU, and RU can be deployed independently.
Cloud-Native: Functions can operate in containers or VNFs for greater agility.
Scalability: User and control planes can scale independently.
Vendor Diversity: Operators can mix and match hardware and software from different vendors.
Cost Efficiency: Lower CAPEX/OPEX by leveraging standard hardware.
Low Latency: Processing happens closer to the edge (DU/RU).
Automation: Near-RT RIC facilitates intelligent, AI-driven RAN management.
Example Workflow in a Disaggregated System
User Equipment (UE) connects to the RU through RF signals.
The RU executes RF and D/A conversion and sends signals to the DU.
The DU carries out MAC scheduling, RLC, and PHY functions, passing higher-layer tasks to the CU.
The CU’s PDCP-C/U processes control signaling and user data.
Functions in the Mobile Core (MME, SGW, PGW, PCRF, HSS) authenticate users, manage sessions, and reroute traffic.
The Near-RT RIC continuously tweaks RAN parameters in near real-time.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Disaggregated Architecture
Aspect Traditional Network Disaggregated System
RAN Architecture Monolithic eNodeB/gNodeB Split into CU, DU, RU
Mobile Core Integrated EPC/5GC Control/User plane separation (CUPS)
Scalability Limited Independent scaling of control & data
Latency Optimization Centralized Edge-based processing at DU/RU
Vendor Flexibility Proprietary Multi-vendor interoperability
Intelligence & Automation Static configuration AI/ML-driven Near-RT RIC optimization
Future Outlook of Disaggregated Networks
Looking ahead, end-to-end disaggregation is set to be the foundation for 5G evolution and 6G:
6G Native AI: AI-enhanced RICs will automatically optimize network functions in real time.
Cloud-Edge Convergence: CU and core functions will move closer to MEC for ultra-low latency.
Network Slicing Expansion: Disaggregation makes managing and isolating slices easier from end to end.
Open RAN Ecosystem: Disaggregation encourages interoperability across various vendors and open standards.
Conclusion
The end-to-end disaggregated system, which features both the mobile core and split-RAN (CU, DU, RU), is transforming telecom architecture. By separating data and control planes, adopting cloud-native strategies, and including Near-RT RIC for intelligence, operators enjoy unmatched agility, scalability, and efficiency.
For telecom experts, getting a firm grasp on disaggregated systems is crucial—this is what will underpin 5G and 6G networks.
The future is all about open, modular, and intelligent networks, with disaggregation at the forefront.
