Enhancing RAN Efficiency with Resource Pooling: From Conventional DU to Cloud RAN

Enhancing RAN Efficiency: Resource Pooling with Cloud RAN Virtualization
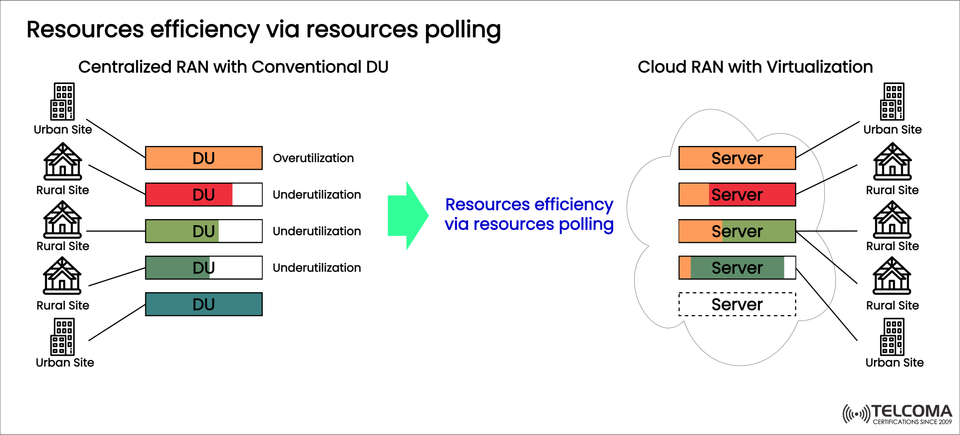
In the increasingly dynamic telecom environment of today, efficiency in Radio Access Network (RAN) is critical to meet varying traffic flows in differing urban and rural environments. The figure highlighted shows a meaningful change in architecture from Centralized RAN with Dedicated Distributed Units (DUs) to Cloud RAN (C-RAN) with resource virtualization reflecting the potential improvement in utilization and performance through resource pooling.
The Problem: Resource Imbalance with Traditional RAN
Conventional Centralized RAN architecture has a Dedicated DUs (i.e. radio units located at every individual site: urban, rural, etc.) the deployment is out at different separate sites. While this is conceptually simple, the implications, for example, are where:
In the context of higher density traffic flows, there is Over-utilization within high traffic areas such as urban
Yet at the same time we have Underutilization within low traffic rural sites, and or
There is Waste - with respect to server hardware and power costs, and
Lack of relevant scalability or flexibility; therefore
Observed Issues from the Figure:
Urban DU is overloaded (orange).
Multiple rural DUs are underutilized (green or red).
Each DU is isolated, i.e. the ability to utilize all available resources is hindered.
The Solution: Cloud RAN within resource virtualization
Cloud RAN (C-RAN) allows for the use of virtualized centralized architecture where DUs are virtualized and run as software defined resources, i.e. that are hosted on shared servers within a cloud environment.
For Cloud RAN the Resource Pooling:
Feature Cloud RAN Advantage
Dynamic Resource Allocation Allocates compute and memory exactly where it is needed
Resource Pooling
Resource Pooling in Action: What this image shows
We're going to start on the right hand of the image above. As can see in the illustration:
Tons of centralization happening with a shared pool of servers handling all site traffic.
Sites with high load can leverage compute resources from underutilized servers.
There is one server available and on standby (dashed line) to give dynamic scaling.
This approach will yield:
Load balancing
Resource efficiency
Better user experience
Cloud RAN vs. Traditional DU: A Comparison Table
Feature Traditional DU RAN Cloud RAN (vRAN)
Architecture Type Static & site based Dynamic & centralized
Resource Allocation Fixed per site Pooled across sites
Efficiency Low while in low-demand areas High using elasticity
Scalability Hardware based Flexible and scalable
Maintenance On site Centralized/cloud managed.
Use Cases That Benefit from Cloud RAN
Urban Environments: When a large density of sites experience high processed traffic during peak hours.
Rural Areas: Where additional hardware liabilities can be leverage with a spare capacity without wasting hardware.
Disaster Recovery: In times of a disaster that affects some remote processing while you move to quickly re-purpose compute capacity from the unaffected segment.
Energy Saving operators: When reducing energy consumption is important, leveraging intelligent resource orchestration
Deployment Considerations for Cloud RAN with Resource Pooling
Although Cloud RAN provides a significant degree of efficiency, there are a few enablers which will need to be resolved in order to have an efficient Cloud RAN.
✅ High-Capacity Fronthaul Network
Cloud RAN separates the Radio Unit (RU) from the centralized DU (virtualized).
Requires a low latence, high-bandwidth fronthaul (e.g., CPRI/eCPRI over Pu fiber).
Particularly critical in rural-to-central pool connections.
✅ Virtualized platform
Requires a robust virtualized infrastructure, using NFV (Network Functions Virtualization).
Common choices include OpenStack, Kubernetes, or telco-grade cloud stacks.
✅ Orchestration Tools
Dynamic resource allocation requires intelligent orchestrators.
Example platforms include ONAP, ETSI MANO, or vendor-based controllers
✅ Hardware Abstraction
Decouples network functions from physical servers using VIMs (Virtualized Infrastructure Managers).
Cloud RAN Deployment Examples
- Rakuten Mobile (Japan)
First fully virtualized RAN using cloud-native design.
Centralized all DU functions in the cloud data centers.
Obtained reductions in CapEx/Opex through resource pooling.
- Verizon and AT&T (USA)
Transitioning to centralized vRAN architecture to deploy 5G.
Using Intel platforms to run vDU/vCU functions centrally.
How Cloud RAN Supports 5G:
Enables massive MIMO and beamforming through centralized compute.
Dynamically configurable for slicing and private 5G.
Native support for AI/ML resource prediction and optimization engines.
Preparing for 6G:
Distributed intelligence + centralized pooling = hybrid AI.
Cloud-native RAN supports terahertz spectrum coordination.
Supports zero-touch autonomous networks with real-time analytics.
Summary: Why resource pooling is the future.
Primary Advantage Operator Impact
Elastic compute sharing Prevents over/under utilization
Centralized management makes operations and scaling easier
Less infrastructure Lower deployment and maintenance costs
Greater energy efficiency Reduction in servers needed when low load
Cloud agility Easy to rollout an upgrade, scale, or failover
Conclusion
The progression from legacy DU RAN to Cloud RAN with resource pooling is more than a sophisticated evolution, but a necessity for operators building next generation wireless networks. The efficiencies, flexibility, and scaling opportunities in Cloud RAN prepare the RAN for tomorrow's traffic whether from smart cities or AR/VR autonomous networks.
Operators that make this movement today are not only driving down their costs, but better position their networks for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the primary difference between traditional DUs and Cloud RAN?
A: Traditional DUs are hardware-dependent units that are deployed at each site, leading to inflexibility and often less-efficient resource utilization. Cloud RAN "runs" with virtualized, centralized servers that enable it to dynamically share resources among sites, introducing better utilization and scalability.
Q2: Do we need 5G to benefit from Cloud RAN?
A: No. Cloud RAN works seamlessly with 5G; however, it is also capable of benefitting LTE and pre-5G networks by providing centralized control, virtualization, and resource pooling. Cloud RAN is more naturally aligned with the architecture of 5G.
Q3: Is Cloud RAN the same as Open RAN?
A: Not exactly. The term Cloud RAN generally refers to the virtualization and pooling of RAN functions typically within a vendor-specific environment. On the other hand, Open RAN generally refers to a level of interoperability between components from multiple vendors. Cloud RAN can be Open RAN if it leverages the defined open interfaces.
