Evolving the 5G Network: From Traditional RAN to vRAN and MEC Integration
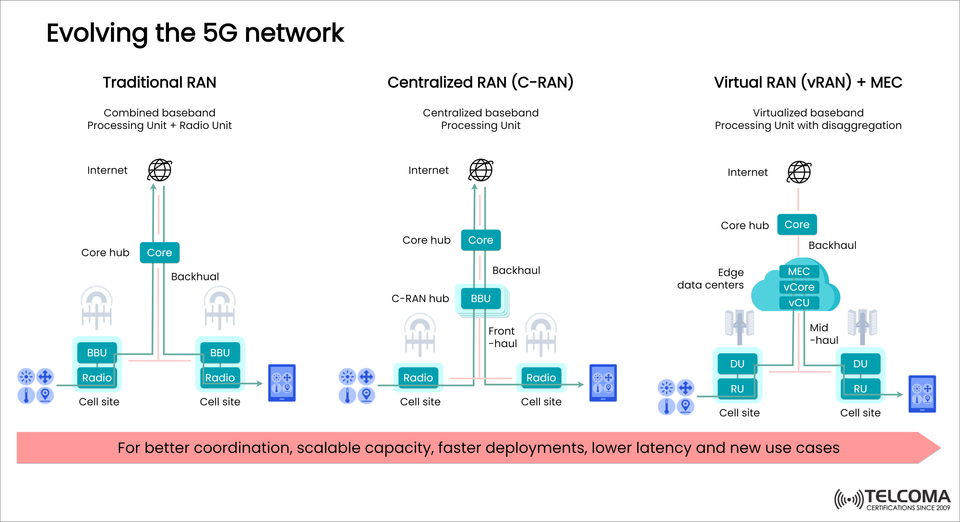

Advancing the 5G Network: Traditional RAN vs C-RAN vs vRAN + MEC
The 5G era calls for a dramatic shift in the mobile network architecture from Traditional RAN, to C-RAN, and then to vRAN with MEC.
This continues to evolve and ultimately the infrastructure will allow much greater real-time coordination, scalable capacity, and improved overall user experience.
The figure provided illustrates this evolution and far-reaching architectural migration to a more distributed edge architecture.
📶 Traditional RAN: The Old World Architecture
Key Characteristics:
Each base station has a BBU (Baseband Unit) and Radio Unit (RU).
All processing occurs at the cell site.
A backhaul connection goes from each BBU to the Core Network.
Limitations:
Cost of infrastructure and maintenance is very high.
Very limited coordination across sites.
Scalability and agility are very limited.
🏢 Centralized RAN (C-RAN): Improved Efficiency
Key Characteristics:
BBUs are centrally located in a C-RAN hub and RUs are separate.
Fronthaul links are used to connect the central BBU to various RUs located at cell sites.
More efficient pooling of resources, and load balancing for RUs.
Benefits:
CapEx and OpEx are reduced due to centralized processing.
Can facilitate upgrades and optimize the network more easily.
Can provide better inter-cell coordination and overall inter-cell performance across sites.
☁️ Virtual RAN (vRAN) + MEC: The Future-Ready Architecture
Key Features:
Baseband functions are on virtualized (vCU and vDU).
Disaggregated architecture running on cloud infrastructure.
Integrated wth MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) at edge data centers.
Benefits:
Ultra-low latency and real-time processing at the edge.
Dynamic resource allocation leveraging software-defined controls.
Ready for AI/ML applications, autonomous systems, and immersive services (AR/VR).
📊 Comparison Table: A Rapid Overview of RAN Evolution
Feature Traditional RAN C-RAN vRAN + MEC
Processing Location At cell site (BBU/RU) Centralized BBU hub Virtualized at edge/cloud
Architecture Type Monolithic Centralized Disaggregated + Virtualized
Latency Medium Medium to low Ultra-low
Scalability Limited Moderate High (cloud-native)
Use Case Support Standard 4G/5G Enhanced 5G Advanced (IoT, XR, URLLC)
Cost Efficiency Low Moderate High
Intelligence Minimal Somewhat centralized AI-ready at the edge
🔍 Why vRAN and MEC are Key to 5G and Future
Transitioning to a virtualized and edge data center architecture is not only about offloading hardware. It also allows for new services including:
Smart factories with ultra reliability low latency (URLLC).
Autonomous vehicles that leverage edge AI.
Advance AR/VR gaming and experiences put into the metaverse.
Enterprise and campus private 5G networks.
With the flexibility and intelligence provided, it will only be possible to do these things with vRAN and MEC architecture.
✅ Conclusion: The Future of RAN is Virtual and Edge-optimized
The evolution from traditional RANs to fully virtualized, cloud-native architectures represents a profound change in how we design, deploy and scale telecom networks. It is important that everyone in the telecom ecosystem—including and especially network architects—attend to these transformations as we prepare to architect the next generation of infrastructure powered by intelligence, agility and resiliency.
As we navigate towards 6G, virtualization, automation and edge will be the building blocks for hyper-connected, ultra-responsive networks.
🌐 vRAN + MEC Real-World Use Cases
The advent of vRAN + MEC enables transformational use cases across virtually all industries:
- Industry 4.0 / Smart Manufacturing
Real-time analytics and automation leveraging sensors, machine vision and robotics.
Remote control of machines and equipment over low-latency 5G.
MEC will develop local processing capabilities, which will enable all of the above things to happen with minimal delay.
- Smart Cities
Real-time traffic lights, public safety systems, surveillance.
Distributing edge computing helps to efficiently process massive quantities of sensor data generated from IoT.
Edge computing with vRAN essentially allows urban connectivity to scale like never before, without weighing down the central core.
- Healthcare
Remote surgeries and diagnostics using real-time data.
Mobile health units that will use 5G and localized MEC servers.
Highly secure, reliable and tailored network slices will be created for the specific purpose of medical procedures.
Gaming & XR (Extended Reality)
Real-time, cloud gaming and little, if any, lag when using edge-rendered content.
Autonomous Vehicles
vRAN and MEC enable vehicle to everything (v2x) communications.
Allows predictive traffic flow and collision avoidance.
🧠 Intelligent Network Management: AI Meets RAN
The evolution to vRAN also allows for the incorporation of AI and ML to manage networks:
Dynamic load balancing based on real-time traffic flows.
Predictive maintenance of infrastructure using telemetry data.
Fault detection and healing within a virtual environment.
These capabilities are critical for zero touch operations (ZTO) and intent-based networking, refer to the progression to autonomous networks.
🔧 Implementation Challenges & Considerations
While there are enormous benefits of vRAN + MEC, deploying at scale requires:
A robust fiber infrastructure for fronthaul/midhaul links.
Investment in cloud-native platforms and orchestration tools.
Interoperability standards to avoid vendor lock-in (O-RAN Alliance role).
Workforce skilled in virtualization, DevOps and edge computing.
📈 What's Next? RAN Evolution Towards 6G
As we continue to mature in 5G, the evolution continues downward toward 6G with:
AI-native networks that adapt autonomously.
Integrated space-air-ground communications systems.
Further movement towards edge computing and network slicing.
Seamless convergence of the digital and physical worlds via XR and digital twins.
📝 Takeaways
Changing our articulation of architecture from Traditional RAN to vRAN + MEC isn't just a technical shift—it's a strategic shift that will support the evolution of mobile connectivity. With a scalable, agile, and intelligent architecture that allows telecom networks to be on the front foot for the next evolution of digital disruption.
As mobile connectivity undergoes this evolution and becomes more prevalent, telecom professionals, infrastructure providers, and network engineers must prepare for Cloud, Automation, and Edge intelligence to remain competitive in a fast-paced industry.
