Exploring 4G to 5G Deployment Options: NSA vs SA Strategies Explained

4G to 5G Deployment Options - Migration Paths for NSA & SA
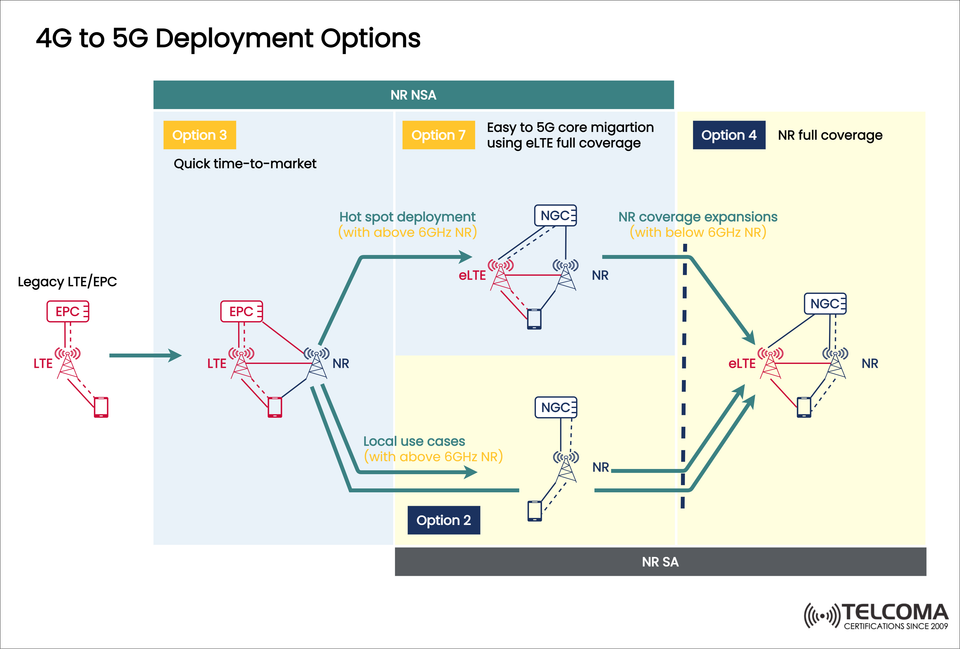
The journey from 4G LTE to 5G is not as simple as it sounds. This path will require several architectural shifts to arrive at your ultimate goal. The image above serves as a useful reference for how various options have been developed for various deployments – each taking full advantage of the various operator strategic goals, infrastructure available, and spectrum.
For telecommunications professionals, network engineers, and technology strategists, this architectural reference illustrates all possible 5G migration paths and can aid in planning for efficient 5G deployment and your investment.
🧱 Deployment Architecture Overview
The transition path follows two deployment architectures for 5G:
NSA (Non-Standalone) – leverages existing 4G EPC with LTE infrastructure and adds NR (New Radio) capability.
SA (Standalone) – is a full 5G architecture deploying a 5G Core (NGC) and NR, independent of LTE.
Each option (Option 2, 3, 4, 7) can reflect different priorities in determining enterprise 5G speed-to-market, localized use cases, and support future scalability.
🔄 Deployment Options Summary
Option Architecture Description Use Case
Option 3 NSA Add NR to existing LTE/EPC for quick time-to-market Urban NR hot spots
Option 7 NSA + eLTE + NGC Move to 5GC while using LTE as control anchor Full eLTE coverage, core upgrade path
Option 2 SA Straightforward 5G SA deployment with NR & 5GC Local/enterprise deployment above 6GHz
Option 4 SA For full 5G deployment of wide NR coverage & 5GC National 5G rollout
📡 Key Technologies and Terms
LTE (Long-Term Evolution): 4G access technology from earlier years.
EPC (Evolved Packet Core): 4G core network.
NR (New Radio): 5G radio interface.
NGC (Next-Gen Core): 5G core architecture with service-based interfaces.
eLTE (Enhanced LTE): Enhanced LTE used as anchor in 5G NSA deployments.
🔍 Visual Summary of Deployment Flows
Legacy to NSA (Option 3): Operators can quickly enable a 5G NR deployment by taking advantage of the existing EPC with an LTE anchor. It provides a fast way to deploy 5G networks.
NSA to SA through eLTE (Option 7): eLTE provides better 5GC migration by keeping the LTE anchor which enables dual connectivity providing better user experience during the transition.
Local SA Deployment (Option 2): Typically used for enterprise applications with localized NR coverage (6GHz and up).
Full SA Deployment (Option 4): Future-proof, full NR coverage using NGC with the capability of providing 5G services nationwide.
📈 Strategic Deployment Benefits
Option 3: Low-cost, fast rollout, with limited future pacing needed.
Option 7: Balanced path to upgrade from LTE to 5GC.
Option 2: For private networks or industrial areas.
Option 4: For a full national plan to 5G.
🧭 Selecting the Right Option
Required speed Recommended Option
Fast rollout to urban areas Option 3
Migration path to core Option 7
Industry/private vertical use cases Option 2
Full 5G for the nation Option 4
The journey to 5G is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Whether operators select a rapid NSA edition to deployments or follow the full SA strategic commitment, each of the options have their own unique business and technical objectives. Proper operational planning covering EPC, NGC, NR and LTE evolution can lead to success on a 5G path that is also reactive to future directions.
By understanding the nuances of these deployment options, telecommunications industry stakeholders can find the right mix of investment, launch speed, and long-term sustainable value.
Tags (Search Engine Optimization):
4G to 5G migration migration strategy, NSA versus SA 5G, EPC to NGC transition, Option 2 Option 3 Option 7 Option 4 5G, eLTE migration path, telecom 5G rollout strategy.
🔗 Suggested Internal Links (for SEO + Engagement)
In order to improve the reader journey and domain authority, you can include links to related content on your site, such as:
5G Core Network Architecture Explained
Stand Alone vs Non-Standalone 5G
eLTE; The Transition to 5G
What is New Radio (NR)?
Why Enterprises must consider Private 5G Deployment
You can have these links boost your time-on-site rate and signal your domain expertise in the 5G space.
🖼️ Image Alt Text (Accessibility + SEO)
Alt text suggestion for uploaded image:
“Diagram showing the 4G to 5G deployment options; the NSA Option 3, Option 7 . . ., as well as SA Options 2 and 4, as well as NGC and NR network coverage.”
💡 Key Takeaways
NSA (Non-Standalone) deployments have Options 3 and Option 7, and have the advantage of speed to deploy, and an existing 4G infrastructure that can be leveraged.
SA (Standalone) deployments have Option 2 and Option 4, which gave end users full 5G capability, independence from LTE and have incremental and more transformative opportunities to scale and build advanced service.
Enhanced LTE (eLTE) is a transitional strategy and was a useful tool in the upgrade from 4G to core network upgrade, as well as transition to NR.
The right deployment strategy is dependent upon the availability of your spectrum, the located markets demands, and your long game.
🧾 Schema Markup (TechArticle for SEO)
You can include this JSON-LD schema in the page header or using an SEO plugin (like RankMath or Yoast):
json
Copy
Edit
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "TechArticle",
"headline": "4G to 5G Deployment Options - NSA (Non-Standalone) vs SA (Standalone) Strategies Explained",
"description": "Learn more about 4G to 5G deployment options including NSA and SA architectures, eLTE, EPC, NGC, and NR coverage, and how to find the best migration strategy for your network.",
"image": "URL_TO_IMAGE",
"author": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Telcoma"
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Telcoma",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://telcomaglobal.com/logo.png"
}
},
"datePublished": "2025-07-12",
"keywords": "4G to 5G migration, 5G NSA SA deployment, Option 3 Option 7 Option 2 Option 4, eLTE, NGC core upgrade"
}
(Please replace "URL_TO_IMAGE" with the actual hosted image URL)
🏁 Conclusion
Deployment from 4G to 5G is not a one-off task; it is a progressive evolution. Operators will need to understand their local market, level of infrastructure readiness, and business model flexibility to make well-informed decisions. This reference model provides telecom professionals with sufficient information to make an educated decision about the best way to go down an upgrade path; whether they want speed (NSA) or evolving the network into a full 5G architecture (SA).
With the proper operational planning, and combination of EPC, NR and NGC core integration, carrier operators will be able to transition their existing networks and deliver innovative services which harness the potential of 5G user experiences.
