F5G Use Cases: Driving eFBB, FFC, and GRE in Fixed Networks

F5G Use Cases: Advancing eFBB, FFC, and GRE in Fixed Networks
As telecom technology keeps progressing, Fifth Generation Fixed Networks (F5G) are becoming the backbone of future connectivity. Unlike older fixed generations that were mainly about speed, F5G brings in a three-dimensional framework:
eFBB (Enhanced Fixed Broadband) – Offers gigabit-class speeds and scalable broadband.
FFC (Full-Fiber Connection) – Expanding fiber to every corner, from homes to machines.
GRE (Guaranteed Reliable Experience) – Providing ultra-low latency and dependable performance.
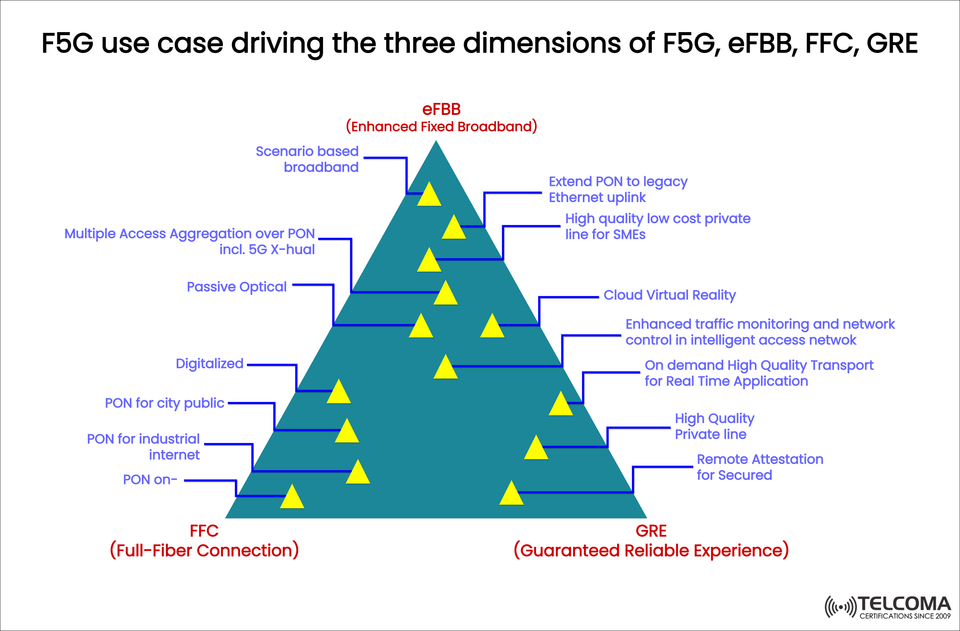
The following diagram shows how real-life use cases are boosting the adoption of these three aspects. Let’s dive deeper into each one.
eFBB: Enhanced Fixed Broadband Use Cases
Enhanced Fixed Broadband (eFBB) gives a 10x speed boost compared to F4G networks. It ensures that both users and businesses can utilize multi-gigabit services powered by 10G-PON, WiFi 6, and scalable optical transport networks.
Key Use Cases for eFBB
Scenario-Based Broadband: Customized broadband delivery for various settings—residential, enterprise, and industrial.
Multiple Access Aggregation over PON (including 5G X-haul): Using Passive Optical Networks (PON) to combine different access methods, including 5G mobile backhaul and fronthaul.
Passive Optical Extensions: Expanding PON coverage to work smoothly with Ethernet uplinks and older systems.
SME Private Lines: Providing affordable, high-quality fixed lines for small and medium-sized businesses.
Benefits of eFBB
Quicker access for homes (like streaming on multiple devices, cloud gaming, VR).
Reliable, scalable bandwidth for businesses.
Integration of fixed-mobile convergence, easing 5G rollouts.
FFC: Full-Fiber Connection Use Cases
Full-Fiber Connection (FFC) pushes fiber deeper into the network, enhancing density and enabling fiber-to-everywhere situations. Unlike previous setups (FTTH only), F5G supports FTTO, FTTR, FTTD, and FTTM.
Key Use Cases for FFC
PON for City Public Networks: Fiber-based connections driving smart city structures—traffic management, public WiFi, and safety monitoring.
PON for Industrial Internet: Facilitating Industry 4.0 automation with ultra-reliable fiber connectivity to machines and sensors.
Digitalized Access: Bringing fiber to every corner for low-loss, high-reliability connections.
Benefits of FFC
10x greater fiber density compared to F4G.
Consistent, end-to-end connectivity for mission-critical services.
Preparing networks for IoT, smart grids, and industrial automation.
GRE: Guaranteed Reliable Experience Use Cases
Guaranteed Reliable Experience (GRE) makes sure of predictable latency, high reliability, and steady performance, cutting down delays from about ~10 ms (F4G) to as low as 1 ms.
Key Use Cases for GRE
Cloud Virtual Reality (VR): Enables real-time immersive VR without motion sickness due to latency.
Enhanced Traffic Monitoring and Network Control: Smart monitoring that adjusts traffic flow for mission-critical services.
On-Demand High-Quality Transport for Real-Time Applications: For financial trading, telemedicine, or remote operations that need ultra-stable networks.
High-Quality Private Lines: Dedicated connections with guaranteed performance for businesses.
Remote Attestation for Security: Verifying devices and networks in real-time to maintain trusted connectivity.
Benefits of GRE
Ultra-low latency for VR, AR, and cloud gaming.
Secure, stable, and guaranteed connections for enterprises.
Facilitator of remote surgery, smart manufacturing, and autonomous systems.
How F5G Dimensions Work Together
The strength of F5G isn’t just in each separate dimension, but in how eFBB, FFC, and GRE link up to enable advanced applications:
eFBB delivers the bandwidth (10 Gbps-class).
FFC ensures fiber reach and density to every spot.
GRE provides reliability and low latency for real-time applications.
Together, they support next-gen services like:
Cloud VR/AR gaming
Smart cities with IoT integration
Industrial automation with FTMM (Fiber to the Machine)
Hybrid cloud enterprises
Secure, real-time healthcare applications
F5G vs. F4G: What’s New?
DimensionF4G (Ultra-Fast Broadband)F5G (Gigabit Fixed Network)Broadband~1 Gbps (GPON + WiFi 5)~10 Gbps (10G-PON + Wi Fi 6)Fiber Reach FTTH only FTTH, FTTO, FTTR, FTTD, FTTMLatency~10 ms~1 msServices4K video streaming Cloud VR, industrial IoT, smart cities Security Best-effort delivery Remote attestation, secure lines
This comparison shows that F5G is more than just speed—it’s about bringing fiber everywhere and ensuring reliability at scale.
Why F5G Use Cases Matter
These use cases highlight that F5G is not just a simple upgrade, but a transformational evolution in fixed networks.
For Telecom Operators: New revenue opportunities in enterprise connectivity, cloud services, and industrial solutions.
For Enterprises: Secure, dedicated, and dependable lines for digital transformation.
For Consumers: Smooth immersive experiences, ranging from cloud gaming to metaverse applications.
For Smart Cities: Infrastructure that backs sensors, energy grids, and smart transport systems.
A Comprehensive Look at F5G: Development, Technical Features, and Applications
The fixed broadband landscape has seen a tremendous shift over the last thirty years. We've gone from the slow PSTN connections of the late 80s to today’s lightning-fast fiber connections, transforming the experiences for individuals, businesses, and entire sectors.
Now, with Fifth Generation Fixed Networks (F5G) coming onto the scene, telecom providers and tech innovators are stepping into a new age where gigabit speeds, full-fiber coverage, and ultra-reliable low-latency performance come together to fuel the digital economy.
In this guide, we’re diving into:
The progression of fixed network generations (F1G–F5G)
The technical foundations of F5G (eFBB, FFC, GRE)
The real-world applications driving growth and creativity
- Progression of Fixed Network Generations
The table below outlines how fixed network generations have evolved:
Generation Downstream per User Upstream per User Key ServicesArchitectureTimelineF1G<2 Mbps<2 Mbps Voice (PSTN/ISDN), Dial-up InternetCOLE1988–1993 (Launched ~1990)F2G2–30 Mbps~0.5 Mbps High-Speed Internet, SD VideoCO DSLAM1999 (ADSL), 2003 (ADSL2+)F3G30–100 Mbps15–100 Mbps HD Video FTTC/FTTB, VDSL22006F4G100 Mbps–1 Gbps50–500 Mbps UHD 4K Video FTTH/FTT dp (GPON, G.fast)2010–2016F5G1–10 Gbps1–10 Gbps Cloud VR, Smart Cities, IoT FTTH, FTTR (10GPON)2017–2018
Key Insights from the Evolution
F1G–F2G centered around basic connectivity for voice and the early internet.
F3G introduced HD video and broadband as a crucial utility for daily life.
F4G accelerated fiber-to-home installations for UHD content and streaming.
F5G makes fiber ubiquitous and offers enterprise-level reliability for future-focused tech like VR, industrial IoT, and smart urban areas.
- Technical Features of F5G
F5G isn’t simply about faster speeds; it’s anchored on three main pillars that define what it can do:
a) eFBB – Enhanced Fixed Broadband
Definition: Broadband that’s 10 times faster than F4G, driven by 10G PON, WiFi 6, and 200G/400G OTN aggregation.
Performance: About ~10 Gbps download speeds.
Applications:
Streaming on multiple devices (4K/8K)
Cloud gaming
High-speed broadband for businesses
b) FFC – Full-Fiber Connection
Definition: Fiber reaching every endpoint—homes, offices, desks, and machines.
Performance: 10 times the fiber density and extremely stable, low-loss connections.
Applications:
Fiber-to-the-room (FTTR) for smart home setups
Fiber-to-the-machine (FTTM) for Industry 4.0
Infrastructure for smart cities
c) GRE – Guaranteed Reliable Experience
Definition: A ten-fold reduction in latency (dropping from around 10 ms in F4G to about 1 ms in F5G) with stable, predictable connections.
Performance: Enables real-time responses.
Applications:
Cloud-based VR/AR
Remote healthcare (like tele-surgery)
Autonomous systems
Secure private lines
- Applications Fueling F5G Growth
The three pillars—eFBB, FFC, and GRE—come alive through various practical applications.
a) eFBB Applications
Broadband deployment based on specific scenarios (residential, enterprise, industrial).
Aggregation of multiple access points using PON, including 5G x-haul.
Affordable, high-quality private lines for small and medium enterprises.
Passive optical network expansions integrated with legacy Ethernet.
b) FFC Applications
Smart city networks driven by PON-based fiber infrastructures.
Connectivity for Industrial IoT via fiber-to-machines.
Fully digitized infrastructure ensuring fiber is accessible everywhere.
Fiber connections for public utilities (transportation, energy networks).
c) GRE Applications
Cloud Virtual Reality with sub-1 ms latency.
Advanced traffic monitoring and smart network management.
Instantaneous transport for financial services and telemedicine.
Secure connections featuring remote validation.
Top-notch private lines for enterprises with guaranteed performance.
Conclusion
The use cases illustrating F5G’s three dimensions—eFBB, FFC, and GRE—paint a picture of the future of connectivity.
eFBB delivers 10 Gbps broadband with scalable aggregation.
FFC spreads fiber across the board—homes, offices, machines, and cities.
GRE guarantees reliability with 1 ms latency for real-time applications.
For telecom professionals, this opens up new possibilities in service differentiation, enterprise solutions, and infrastructure upgrades. For tech enthusiasts, F5G represents the unseen force powering next-generation experiences like VR, industrial IoT, and smart cities.
As the digital economy keeps growing, F5G is setting the stage for a secure, immersive, and ultra-reliable connected world.
