Functional Architecture of D2D Communication in LTE: A Deep Dive into ProSe and V2X
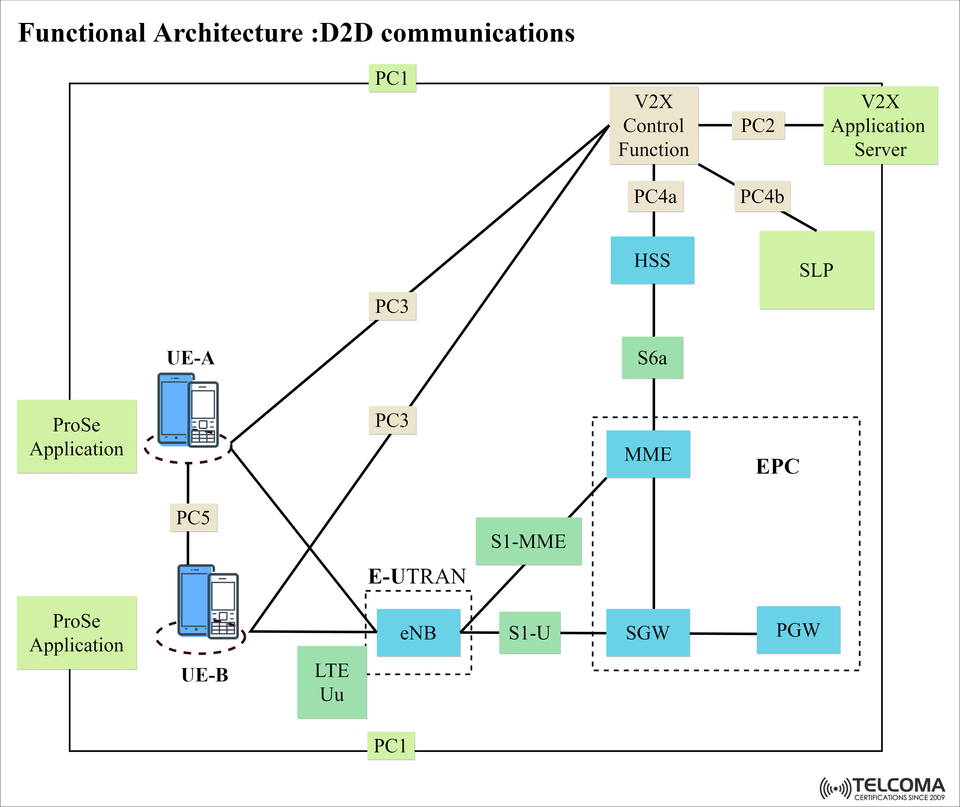

📶 Grasping the Functional Architecture of D2D (Device-to-Device) Communications in LTE
Device-to-Device (D2D) communication—known as Proximity Services (ProSe)—is a significant enabler of the 4G LTE and 5G user-driven and user-to-user environment. D2D allows user equipment (UES) to communicate directly without incurring the load associated with 'tromboning' back through the core network. The representation shown in the picture above depicts one way in which D2D interacts with Evolved Packet Core (EPC), ProSe applications, and Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) functions.
In this post we will discuss the components, interfaces, and how these systems work together.
🔍 What is D2D Communication in LTE?
D2D communication is defined as direct data exchange between two UEs (e.g., smartphones, Internet of Things devices) without following standard network paths. D2D is commonly used in the following applications:
Public safety networks
A guidance system for autonomous driving (V2X)
Gaming and multimedia sharing
Location-based services
Network offloading in congested environments
🧱 Component of D2D Architecture
Component Function
UE-A & UE-B User devices involved in direct communications.
ProSe Application UE application providing proximity services.
eNB (evolved NodeB) The radio access node supporting D2D control signaling.
MME (Mobility Management Entity) Provides control plane operations in the EPC.
SGW & PGW Manages data plane traffic
HSS (Home Subscriber Server) Stores subscriber profiles and authentication.
V2X Control Function Coordinates D2D/V2X resource allocation.
V2X Application Server Provides V2X specific application logic.
SLP (Secure Location Platform) Assists with UE localization and reporting positional information.
🔗 Key Interfaces in D2D Functional Architecture
Interface Purpose
PC1 Secures two-way connection for UE between the ProSe App and SLP for location awareness.
PC2 Secures the signaling exchange of policy between the V2X App Server and the Control Function.
PC3 Initiates and manages signaling related to the D2D discovery and communication.
PC4a/PC4b Provides connectivity from the V2X Control Function to both the HSS and SLP respectively.
PC5 Direct link between UE-A and UE-B for D2D.
S1-MME/S1-U Defined LTE interfaces for control traffic and user plane traffic.
S6a Related to MME and HSS for subscriber information.
LTE-Uu Standard one for radio interface, UE and eNB.
🚗 V2X and D2D: A Synergistic Integration
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) uses D2D communication to support real-time data ‘sharing’ between vehicles (V2V), with the infrastructure (V2I), and with pedestrians (V2P). This architecture supports:
Low-latency notifications (e.g. collisions warnings).
Efficient use of bandwidth by utilizing direct D2D paths.
Increased safety and automation of transport network.
The Role of ProSe in Public Safety and Other Use Cases
ProSe allows for communication without having a core network available (e.g., disaster zones). Capabilities of ProSe include:
- UE-to-UE discovery for first responders
- Relay communication for extending coverage.
- QoS embedded functionality for mission critical apps.
Benefits of D2D Communication in LTE
- Low Latency Communication to D2D relative to a direct link (PC5)
- Core network offload (bandwidth savings)
- Location-based services and discovery
- Improved public safety communication.
- Smart V2X coordination via control functions.
Challenges and Considerations for D2D Communication
- Interference issues - unlicensed spectrum.
- Security of intermediate communications.
- Policy control and authorization for ProSe services.
- Complex coordination with EPC, V2X, and app reasonable file types.
Real-World Applications of D2D Communication
Device-to-Device communication is not merely a theoretical exercise—it is already being used or piloted in real-world applications:
- Emergency & Public Safety Communications
Enables first responders to communicate when there is no base station in disaster zones (e.g., earthquake, fire, etc.). - 🚗 Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS)
Vehicles transmit real-time notifications (e.g., traffic, hazards).Enables autonomous vehicles to interact through ultra-reliable, low-latency communications (URLLC). - 🎮 Edge Applications and Content Sharing
Direct peer-to-peer (or P2P) content transfer limits traffic. May also be used for local games, video streaming, or VR/AR environments where low latency is essential. - 📡 Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Provides local communications between industrial machines and/or robots in a factory. Supports smart grid communications in energy networks. - 📈 Looking Ahead: D2D for both 5G and D2D
While D2D use is part of LTE Advanced, the application of D2D becomes even more critical with 5G and as follows:
LTE (4G) 5G NR
D2D - ProSe D2D - Sidelink, NR SL
Centers primarily on public safety. Opens opportunities beyond public safety to vehicle to anything (V2X), drone communications, and even industrial IoT (IIoT).
Pure EPC Mac-Ran based architecture. 5G Core (5GC) allows for much more slicing and controls.
Having only a limited amount of discovery methods. Having considerably advanced discovery and path optimization methods based on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
In 5G, D2D becomes included in the concept of sidelink communications which are supported natively in 3GPP via Release 16 or newer; this connection will have even lower latency, much better reliability, and capability for network slicing.
🧪 Testbed and Deployment Considerations
Planning for D2D deployment in either LTE or pre-5g networks is filled with various considerations, especially the following:
🚗 Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS)
Vehicles transmit real-time notifications (e.g., traffic, hazards).
Enables autonomous vehicles to interact through ultra-reliable, low-latency communications (URLLC).
🎮 Edge Applications and Content Sharing
Direct peer-to-peer (or P2P) content transfer limits traffic.
May also be used for local games, video streaming, or VR/AR environments where low latency is essential.
📡 Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Provides local communications between industrial machines and/or robots in a factory.
Supports smart grid communications in energy networks.
📈 Looking Ahead: D2D for both 5G and D2D
While D2D use is part of LTE Advanced, the application of D2D becomes even more critical with 5G and as follows:
LTE (4G) 5G NR
D2D - ProSe D2D - Sidelink, NR SL
Centers primarily on public safety. Opens opportunities beyond public safety to vehicle to anything (V2X), drone communications, and even industrial IoT (IIoT).
Pure EPC Mac-Ran based architecture. 5G Core (5GC) allows for much more slicing and controls.
Having only a limited amount of discovery methods. Having considerably advanced discovery and path optimization methods based on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
Conclusion
An understanding of the functional architecture of D2D communications in LTE reveals how tightly weaved EPC, V2X, and ProSe work together to facilitate low-latency communication that is reliable and scalable. D2D for public safety, autonomous driving, and core optimizing presents an opportunity for huge growth to build towards the future 5G world.
