Functional Framework for RAN Intelligence: Enabling AI-Driven 5G Networks

Functional Framework for RAN Intelligence: Making AI-Driven 5G Networks a Reality
As 5G networks advance to accommodate ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), and massive IoT (mMTC), the need for automation, flexibility, and smart technology in the Radio Access Network (RAN) is higher than ever. Traditional management systems based on fixed rules just can’t keep pace with the challenges of today’s wireless environments.
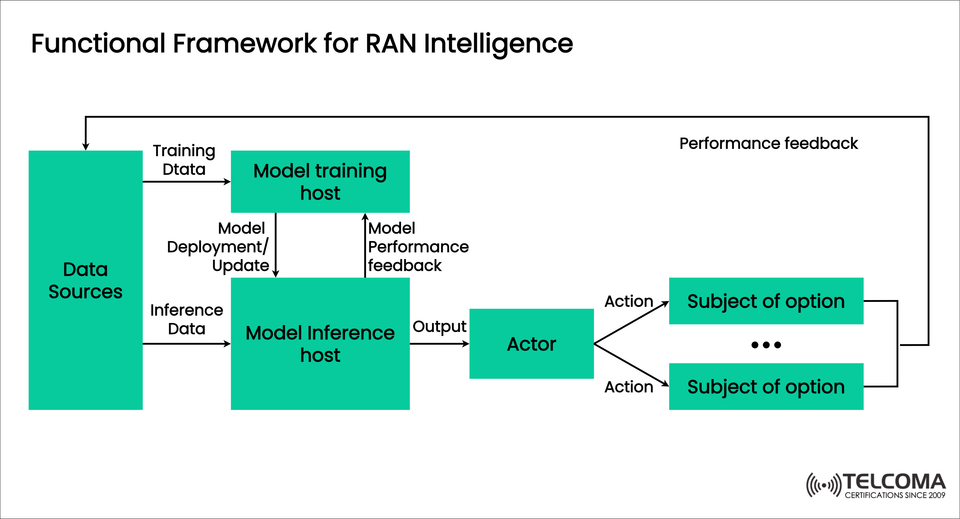
This is where RAN intelligence frameworks step in. By incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), RAN systems can automatically enhance performance, cut down on latency, and make better use of spectrum. The image above shows the functional framework for RAN intelligence, outlining how data, model training, inference, and decision-making all work together.
Why RAN Intelligence is Crucial for 5G
RAN acts as the gateway to mobile networks, connecting user devices with the core network. In 5G, it has to manage:
High numbers of devices in city areas.
Changing network demands from autonomous vehicles, AR/VR, and IoT.
Applications that need real-time, low-latency responses.
Intelligent RAN (iRAN) frameworks introduce automation and adaptability through AI models, which facilitate:
Dynamic management of resources.
Optimizing energy consumption.
Boosting user Quality of Experience (QoE).
Self-healing and self-organizing features.
Elements of the Functional Framework for RAN Intelligence
The framework, as shown in the diagram, consists of interconnected blocks that operate in a continuous cycle. Let’s break it down step by step.
- Data Sources
Gather raw network data, including: * User traffic patterns. * Conditions of the radio channel. * QoE and QoS metrics. * Network events and alerts.
Supply training data for AI models and inference data for real-time decision-making.
- Model Training Host
Accepts training data from data sources.
Employs AI/ML techniques (like supervised learning and reinforcement learning) to develop predictive models.
Delivers trained models for use in live networks.
Monitors and refreshes models based on performance feedback from the system.
Key Role: Keeps the models up to date as network dynamics change.
- Model Inference Host
Functions in real-time.
Processes inference data from RAN.
Applies trained models to produce outputs, which include: * Optimal scheduling choices. * Load balancing measures. * Strategies for interference reduction.
Key Role: Turns AI intelligence into practical insights quickly.
- Actor
Receives outputs from the inference host.
Converts decisions into actions that directly influence RAN elements.
Actions can include: * Redistributing spectrum resources. * Modifying transmit power. * Routing traffic to underused cells.
- Subject of Option
Represents the network entities affected by the actions driven by AI.
This could involve: * Base stations (gNBs). * User Equipment (UEs). * Network slices.
Each subject carries out the assigned action, helping to optimize the network.
- Feedback Loops
Performance Feedback: Sent from subjects back to data sources.
Model Performance Feedback: Shared with the model training host to assess accuracy.
Key Role: Guarantees continuous learning and closed-loop automation.
Operational Workflow of the Framework – End-to-End Process
Data Gathering: RAN KPIs and user metrics flow into the system.
Training: AI models are trained offline with historical data.
Deployment: Trained models are implemented into inference hosts.
Real-Time Inference: Models evaluate live data for decision-making.
Action Execution: Actors execute decisions affecting RAN entities.
Feedback Loop: Outcomes are tracked and sent back to training to foster ongoing improvement.
This results in a self-optimizing network (SON) 2.0, fueled by AI.
Advantages of the RAN Intelligence Framework
Automation: Minimizes the need for manual tweaks in network optimization.
Instant Responsiveness: Quickly addresses shifting 5G traffic demands.
Efficiency: Enhances spectrum and energy use.
Flexibility: Adapts to emerging services like AR/VR, connected vehicles, and industrial IoT.
Resilience: Equips networks to self-repair from failures and anomalies.
Challenges in Rolling Out RAN Intelligence
While the upsides are obvious, there are several hurdles:
Data Privacy & Security: Protecting sensitive user information is key.
Scalability: Managing huge data volumes in ultra-dense 5G environments.
Model Accuracy: Models need to adjust swiftly to unexpected network changes.
Integration Complexity: Making sure AI frameworks blend well with older RAN systems.
Real-World Uses of RAN Intelligence
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS): AI determines the best way to use spectrum between LTE and 5G.
Energy Savings: Predictive algorithms can power down idle base stations.
Mobility Optimization: Enhances handovers to minimize call drops.
Anomaly Detection: Spots unusual traffic patterns to avert fraud or attacks.
Comparison Table: Traditional RAN vs. Intelligent RAN
Feature Traditional RAN Intelligent RAN (AI-driven)Optimization Rule-based, static Dynamic, learning-based Responsiveness Manual, delayed Automated, real-time Scalability Limited Supports massive IoT, URLLC Fault Management Reactive Proactive & predictive Energy Efficiency Minimal AI-optimized savings
The Future of RAN Intelligence
The RAN intelligence framework is essential for:
6G readiness with built-in AI capabilities.
Network slicing orchestration tailored for specific industry needs.
Zero-touch networks that operate with complete autonomy.
As AI models get more advanced, RANs will transform into fully cognitive systems that can learn, adjust, and optimize themselves without needing human input.
Final Thoughts
The functional framework for RAN intelligence signifies a major change in how networks are managed. By blending data-driven insights, machine learning, and closed-loop feedback, it turns RAN into an adaptive, efficient, and self-sufficient system.
For professionals in the telecom sector, this framework lays the groundwork for self-optimizing 5G networks, and for tech aficionados, it demonstrates the tangible effects of AI beyond just consumer tech.
As networks become more intricate, RAN intelligence will serve as the backbone of next-gen connectivity, ensuring smooth user experiences and effective operations in the 5G world and beyond.
