Fusion Architecture in Telecom: Real-Time Data Collection, Testing, and Performance Management

Introduction: The Importance of Fusion Architecture in Today's Telecom
As telecom networks shift towards cloud-native, virtualized, and software-defined architectures, the need for real-time visibility and automation is more critical than ever. Traditional, siloed testing and performance monitoring systems just can’t keep pace with the rapid speed, scale, and complexity of 5G, IoT, and beyond.
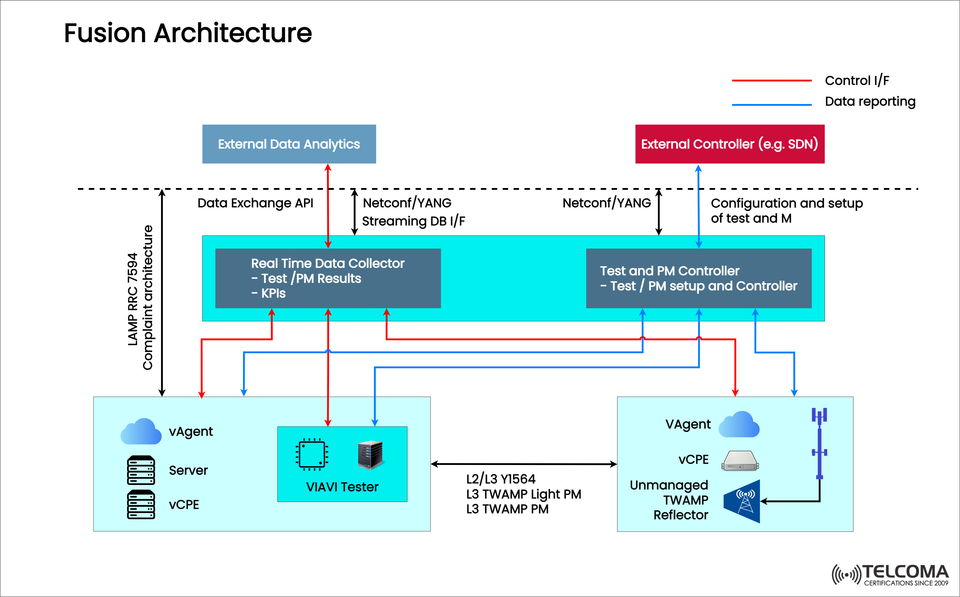
That’s where Fusion Architecture comes into play—it's a framework that blends testing, performance management (PM), automation, and analytics into a cohesive ecosystem. The diagram attached shows how elements like vAgents, controllers, and real-time data collectors collaborate, using protocols such as Netconf/YANG and TWAMP to provide actionable insights.
In this blog, we’ll dig into how Fusion Architecture operates, what its components are, and why it’s so vital for the development of the next generation of smart telecom networks.
Core Principles of Fusion Architecture
Fusion Architecture is anchored in three main principles:
Integration: Smoothly merging testing, monitoring, and analytics.
Automation: Utilizing SDN (Software Defined Networking) and real-time data gathering to minimize manual work.
Scalability: Adapting to virtualized environments (like vCPE, vAgents, and servers) and cloud-native services.
These principles empower operators to uphold high service quality while growing quickly to meet user needs.
Key Components of Fusion Architecture
- vAgent, vCPE, and Servers
vAgent: A nimble virtual agent deployed throughout the network for testing and performance monitoring.
vCPE (Virtual Customer Premises Equipment): This replaces traditional hardware with software functions that can be managed centrally.
Servers: Provide the necessary computing power for running test agents and virtual functions.
Together, these components enable flexibility and cost savings, allowing telecom providers to implement testing capabilities without needing physical probes at every location.
VIAVI Tester
Central to the architecture is the VIAVI Tester, which supports multiple testing protocols:
L2/L3 Y.1564: A methodology for activating Ethernet services.
L3 TWAMP (Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol): Measures important metrics like packet delay and loss.
TWAMP Light PM: A lighter version for performance monitoring in larger deployments.
This setup ensures operators can verify service-level agreements (SLAs) and monitor end-to-end performance across both virtualized and physical environments.
- Real-Time Data Collector
The Real-Time Data Collector plays a crucial role in turning raw test data into useful insights.
It carries out various functions, such as:
Gathering test results from agents and testers.
Keeping an eye on performance management (PM) KPIs.
Sending data to external analytics platforms through APIs.
Thanks to Netconf/YANG streaming interfaces, the collector ensures fast data exchange while staying compatible with modern SDN frameworks.
- Test and PM Controller
This controller serves as the orchestrator of the entire system.
It manag es test configurations and setups.
Controls performance monitoring tasks.
Interfaces with external controllers like SDN orchestrators.
In short, it facilitates centralized command and automation for network testing and monitoring.
- External Controller (e.g., SDN)
Fusion Architecture connects closely with SDN controllers, which:
Automate configuration and resource allocation tasks.
Enable closed-loop automation, allowing issues flagged by monitoring tools to trigger corrective actions automatically.
This leads to a self-optimizing network, lowering operational costs while enhancing user experience.
- External Data Analytics
The data collected doesn’t just stay in the system—it gets sent to external analytics engines.
It uses Data Exchange APIs for smooth integration.
Supports AI/ML-driven insights for predictive maintenance and traffic optimization.
Offers operators actionable dashboards for better decision-making.
This ensures that the architecture not only keeps track of things but also drives business intelligence.
Interfaces and Protocols in Fusion Architecture
The architecture depends on standardized interfaces to ensure it’s flexible and interoperable:
Netconf/YANG: Used for configuration, control, and streaming telemetry.
Data Exchange API: Integrates with analytics platforms and OSS/BSS systems.
TWAMP (Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol): For measuring latency, jitter, and packet loss.
By pulling together these protocols, Fusion Architecture guarantees accuracy, scalability, and real-time responsiveness.
How Control and Data Flow Works
The accompanying diagram illustrates two main flows:
Control Interfaces (Red Lines): Commands sent from controllers to testers and agents.
Data Reporting (Blue Lines): KPIs and performance data returning to controllers and analytics.
This dual flow ensures both command accuracy and real-time visibility, forming the foundation of automated network assurance.
Benefits of Fusion Architecture for Telecom Professionals
End-to-End Visibility * Monitor KPIs across both virtual and physical domains. * Get real-time insights into user experiences.
Automation and Orchestration * SDN integration cuts down on manual tasks. * Automatic troubleshooting and service assurance.
Cost Efficiency * Virtual agents lessen dependency on hardware. * Centralized control leads to lower OPEX.
Service Assurance for 5G * Supports latency-sensitive applications like IoT, URLLC, and private 5G networks. * Validates network slicing SLAs.
Scalability * A cloud-native architecture allows for rapid deployments. * Easily connects with AI/ML analytics platforms.
Table: Overview of Fusion Architecture Components
Component Function Key Benefit v Agent / vCPE / Server Deployable agents for testing & monitoring Flexibility, reduced hardware dependency VIAVI TesterL2/L3 and TWAMP performance testing SLA validation, service activation Real-Time Data Collector Collects KPIs & test results Real-time insights, API-driven analytics Test & PM Controller Orchestrates testing & monitoring Centralized automation and control External Controller (SDN)Automates network configuration Closed-loop self-optimizing networks External Analytics Advanced insights from test data AI/ML-driven optimization and planning
Fusion Architecture in Action: An Example Scenario
Picture a telecom operator rolling out private 5G for an enterprise campus:
Setup: The Test and PM Controller sets up vAgents across various locations.
Testing: The VIAVI Tester checks throughput using Y.1564 and monitors packet delay with TWAMP.
Data Collection: The Real-Time Data Collector compiles results and relays them to analytics.
Automation: The SDN controller spots congestion and adjusts traffic routing automatically.
Optimization: Analytics platforms suggest changes in spectrum allocation to boost performance.
This seamless process ensures enterprise clients get guaranteed SLAs with minimal downtime.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future with Fusion Architecture
As telecom networks adopt virtualization, cloud-native designs, and automation, Fusion Architecture lays the groundwork for achieving real-time visibility, scalability, and intelligence.
By bringing together testing, performance monitoring, controllers, and analytics in one framework, operators can shift from being reactive to proactive, self-optimizing networks.
For those in the telecom industry, grasping Fusion Architecture is essential—it’s not just a tool for monitoring but a cornerstone for creating autonomous, AI-driven networks that will lead the way for 5G, IoT, and beyond.
