How 5G-WAN Extends the Corporate VPN with SD-WAN and MPLS Integration

🌐 How 5G-WAN expands the Corporate VPN: Bridging SD-WAN and MPLS for Modern Enterprises
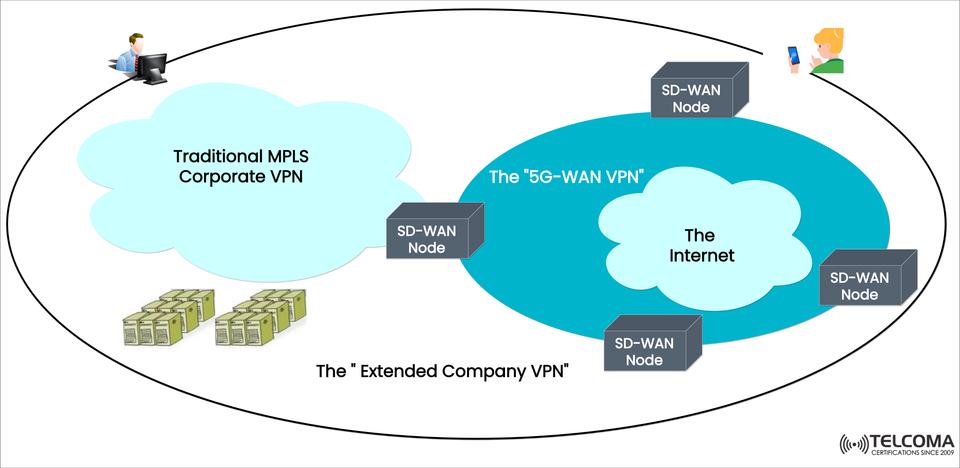
Enterprise networks are changing, and traditional MPLSet-VPNs can't keep up with the flexibility, cloud-readiness and mobility needs of modern organizations. The above diagram depicts a next-generation approach—the “Extended Company VPN”—where SD-WAN nodes on the Internet (5G-WAN VPN) and traditional MPLS authorize and secure connection to form a unified, secure and scalable corporate network.
Let’s unpack this architecture and how it adds value to tech-enabled enterprises.
🏢 The Architecture: A Hybrid VPN
The image shows three major components:
Traditional MPLS Corporate VPN:
A secure, highly reliable network connecting centralized resources, or sources of data including data centers, and headquarters.
The “5G-WAN VPN”:
SD-WAN nodes on the Internet (on 5G or broadband) that create secure cloud-aware tunnels for branch offices, remote users and mobile employees.
The Extended Company VPN:
The outer boundary, containing two VPN infrastructures of MPLS and SD-WAN; while keeping secure communication open between remote and core enterprise resources.
🚀 What is a 5G-WAN VPN?
A 5G-WAN VPN is a type of SD-WAN that employs 5G cellular connectivity, or broadband internet, as its transport. A 5G-WAN VPN uses SD-WAN nodes to create encrypted tunnels to provide the performance and security similar to that of MPLS.
Benefits:
✅ Low latency over high-speed 5G links
✅ Flexible deployment: remote workers, vehicles, pop-up sites, etc.
✅ App-aware routing and failover
✅ Less reliance on fixed circuits
🔗 Always consider SD-WAN as a way of integrating MPLS - this is important
Integrating SD-WAN with MPLS allows for hybrid network topologies where:
Cloud and mobile traffic is routed through SD-WAN, over the internet
Critical internal systems operate over MPLS for QoS and compliance
SD-WAN Nodes act as gateways that can dynamically send packets, over SD WAN, to the cloud or to the corporate core
This dual routing structure supports both cloud-first and security-first approaches.
📊 Side-by-side Comparison:
Traditional VPN v Extended VPN
Feature Traditional MPLS VPN Extended Company VPN
Transport Private MPLS MPLS + Internet (5G/BB)
Access On-prem Hybrid; mobile, branch, cloud
Scalability Limited Highly scalable
Latency Consistent Consistent, Optimized through SD-WAN policies
Security Centralized Secure + Distributed
Cost High Lower through internet offload
📡 Real-World Use Cases
Take a look at these instances when this model truly excels:
Retail Chains: Connecting pop-up stores over 5G via SD-WAN
Remote Workforce: Secure cloud application access without using MPLS backhaul
Multi-Cloud Environments: Intelligent traffic routing to AWS, Azure, etc.
Industrial IoT Implementations: Securely ship data from IoT edge devices to headquarters.
🛠️ Key Technologies Under the Hood
SD-WAN Nodes: Handles all routing, encryption, QoS, and failover.
Virtual Network Overlays: Creates logical tunnels across hybrid links.
Zero-Touch Provisioning: Allows fast installation of new nodes.
Centralized Orchestration: Allows operators to operate from a cloud dashboard layer to manage the entire network fabric.
🧠 Conclusion:
Step Forward into the Extended Company VPN
The amalgamation of 5G-WAN VPNs using SD-WAN into the Traditional MPLS Corporate VPN represents a large step forward in Enterprise Networking. In this Extended Company VPN approach, we offer:
Single Observatory
IQ Routing
Better User Experience
Flexible Remote Access
This is a resilient solution that integrates Legacy and Digital. For telecom professionals and network architects, combining the SD-WAN and VPN hybrid model into your enterprise is no longer a choice, but a must for a resilient, scalable, and cloud-capable enterprise.
🧩 Best Practices for Deploying an Extended Company VPN
To optimize the advantages of connecting SD-WAN to MPLS via a 5G-WAN VPN, telecom architects and enterprise IT teams should consider best practices:
✅ Segment Traffic Wisely
Use application-aware SD-WAN policies to prioritize the following types of traffic:
VoIP and real-time traffic over MPLS
SaaS and cloud apps over Internet links
Bulk data transfers during off-hours
✅ Leverage Redundancy & Failover
Deploy dual uplinks (MPLS + Internet/5G) for each SD-WAN node
Active-active tunneling with automatic failover
Real-time monitoring for performance-aware routing
✅ Utilize Centralized Orchestration Tools
Manage all SD-WAN nodes and all traffic flows via a cloud controller. Key features include:
Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP)
Policy templates built by region or by business unit
Security enforcement and compliance audits
✅ Integrate security from the beginning
Include the following to ensure security regulations are enforced:
End-to-end encryption for all SD-WAN tunnels
Built in firewall and intrusion prevention at the edge
Secure access policies for remote users and mobile devices
📘 Glossary for quick reference
Term Definition
SD-WAN Software Defined Wide Area Network; provides virtualization of WAN links for flexibility
MPLS Multiprotocol Label Switching; legacy private WAN with QoS
5G-WAN VPN SD WAN Nodes delivered over either 5G, or broadband that provide connectivity for users back to enterprise resources
Extended Company VPN Hybrid VPN which uses SD WAN over the internet and MPLS
ZTP Zero Touch Provisioning, the ability to provision remote devices with minimal human provisioning
📣 Concluding remarks
As enterprises navigate distributed workforces, cloud-native applications, and mobile-first access, their network backbone must evolve. The Extended Company VPN, as presented with the 5G-WAN VPN example and SD-WAN over the Internet, represents the deployment model for connectivity into future ready enterprises.
Since you are an enterprise CIO, network engineer, or telecom professional, this architecture provides a flexible, scalable, and secure way to digitally transform your enterprise.
