How Blockchain Technology is Revolutionizing the Manufacturing Industry
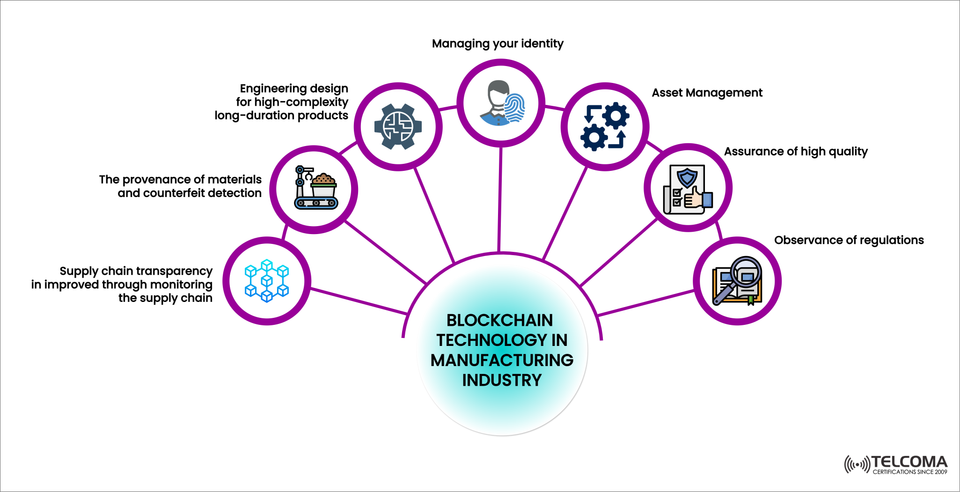

Blockchain Technology in Manufacturing
In our increasingly connected world, manufacturing is quickly turning into a data-driven environment where factors like transparency, security, and efficiency are crucial. You’ll find technologies such as IoT, AI, and cloud computing woven into smart factories, but one technology stands out for its ability to enhance trust and traceability throughout the supply chain: blockchain.
The image above illustrates key uses of blockchain in the manufacturing sector, including:
Transparency in the supply chain
Tracking the origin of materials and detecting counterfeits
Traceability in engineering design
Managing identities and assets
Upholding quality standards
Ensuring regulatory compliance
Let’s dive deeper into each of these applications and see how blockchain is influencing the future of manufacturing and telecom-enabled Industry 4.0 environments.
What is Blockchain in Manufacturing?
Blockchain is essentially a decentralized digital ledger that keeps track of transactions across different nodes securely and permanently. In the manufacturing realm, it acts as a shared, tamper-proof system that ensures data integrity, traceability, and automation throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Key Features of Blockchain in Manufacturing:
Decentralization: Eliminates the need for centralized middlemen in supply chains.
Transparency: Offers real-time visibility into product movements.
Immutability: Guarantees that records of production and quality can’t be changed.
Smart Contracts: Automates compliance and payment processes based on confirmed events.
Security: Employs cryptographic methods to validate data.
At its core, blockchain offers a single source of truth — a vital aspect in industries where data authenticity and traceability are essential for operational success and meeting regulations.
- Boosting Supply Chain Transparency
One of the standout benefits of blockchain in manufacturing is its ability to enhance supply chain transparency. The image captures this idea, showcasing how “supply chain transparency improved through monitoring” tackles one of the industry’s biggest hurdles: a lack of visibility.
How It Works:
Each transaction or product movement is logged as a block within the chain.
All parties involved — manufacturers, suppliers, logistics companies, and retailers — share access to a common ledger containing verifiable data.
IoT sensors and RFID tags provide real-time updates (like temperature, location, and timestamps) to the blockchain.
Benefits:
Enables end-to-end traceability from raw material sourcing to final delivery.
Lowers the risk of fraud and counterfeiting.
Facilitates faster dispute resolution with clear data records.
Enhances demand forecasting thanks to reliable historical data.
With 5G-enabled IoT networks, manufacturers can achieve real-time blockchain updates for data synchronization on a large scale.
- Tracking Material Provenance and Counterfeit Detection
Counterfeit materials can seriously jeopardize quality and safety, particularly in industries like aerospace, automotive, and telecom hardware manufacturing. Blockchain offers unchangeable proof of origin for every component produced.
Key Functions:
Assigns a unique digital token (like an NFT identifier) to each batch or product.
Logs every stop along the product’s journey onto the blockchain.
Allows manufacturers and customers to quickly verify authenticity.
Example Use Case:
A telecom equipment maker can check the blockchain record of each microchip in a 5G base station to ensure its authenticity, which includes the supplier details, testing protocols, and certification info.
Benefits:
Helps eliminate counterfeit threats
Guarantees ethical sourcing and sustainability
Builds trust with both end-users and partners
- Managing Engineering Design for Complex and Long-Lasting Products
When it comes to producing high-complexity and long-lasting products — like aircraft, telecom towers, or industrial robots — there are many design revisions and supplier interactions to juggle. Blockchain secures the entire engineering lifecycle, ensuring both version control and design authenticity.
Blockchain in Engineering Design:
Monitors design changes and ownership among collaborators.
Prevents unauthorized changes or theft of intellectual property (IP).
Offers a tamper-proof record for design approvals, certifications, and updates.
Result:
Manufacturers gain a traceable audit trail for product design, which is key for compliance and ongoing maintenance.
- Digital Identity and Asset Management
The image showcases “Managing your identity” and “Asset Management” — two essential uses of blockchain in the manufacturing value chain.
a. Digital Identity Management
Identity systems powered by blockchain allow manufacturers, suppliers, and even machines to have verifiable decentralized identifiers (DIDs).
Human identities are protected using biometric or cryptographic keys.
Machines and IoT devices can create digital identities for secure communication.
This is particularly vital in Industry 4.0 settings, where human-to-machine and machine-to-machine communication is prevalent.
b. Asset Management
Blockchain supports real-time tracking of assets, confirming ownership and logging maintenance histories.
Some potential applications include:
Tracking industrial tools, robots, or production lines.
Keeping records of maintenance for predictive servicing.
Automating asset handovers via smart contracts.
- Ensuring High Quality
Quality assurance is another area being reimagined by blockchain. Every quality check, inspection result, and certification can be securely logged on the blockchain for transparent accountability.
How Blockchain Enhances Quality:
Collects real-time sensor data from production equipment.
Confirms that products meet necessary standards before they’re shipped.
Stores third-party inspection records and test results securely.
This is crucial for telecom gear or semiconductor production, ensuring that every shipped product meets both industry and safety standards, without any manual record inconsistencies.
- Meeting Regulatory Standards
Following regulations in manufacturing means sticking to strict safety, environmental, and ethical guidelines. Blockchain simplifies this by automating compliance checks.
Key Advantages:
Logs every compliance-related event — from material sourcing to emissions data and labor practices.
Facilitates instant audits through blockchain explorers.
Automates certification processes utilizing smart contracts that only trigger when all criteria are met.
For instance, if a batch of components passes both safety and environmental evaluations, the blockchain automatically marks it as compliant, cutting out paperwork and delays.
How Blockchain Works with Telecom and IoT
Blockchain truly shines when combined with telecom and IoT infrastructure. With 5G connectivity, IoT devices on the production floor can gather and verify data in real time, directly feeding it into blockchain records.
Complementary Technologies:
Technology Function in Manufacturing Block chain Benefit 5G High-speed, low-latency data transfer Real-time blockchain updates IoT Sensors Data gathering and monitoring of equipment Permanent data logging Edge Computing Local data processing Streamlined blockchain validation AI/ML Predictive analytics Smart contract-based automation
This combination promises secure, transparent, and automated manufacturing operations, forming the backbone of future Industry 4.0 and 5G-enabled factories.
Challenges and Considerations
Even with its benefits, bringing blockchain into manufacturing comes with its own challenges:
Scalability and latency issues in high-output environments
Complexity of integration with existing ERP and MES systems
Regulatory uncertainties for international use
Energy consumption associated with certain consensus methods
Fortunately, ongoing innovations like permissioned blockchains, consortium networks, and proof-of-stake (PoS) models are effectively tackling these challenges.
Conclusion: The Future of Blockchain in Manufacturing
Blockchain is reshaping the manufacturing landscape by enhancing trust, traceability, and transparency at every stage — from sourcing materials to delivering finished products.
As industries shift toward smart, interconnected ecosystems backed by 5G, IoT, and AI, blockchain acts as the trust layer that brings all these technologies together.
By incorporating blockchain into manufacturing processes, professionals in telecom and tech can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, accountability, and security — paving the way for Industry 5.0, where humans and machines collaborate in transparent digital environments.
