How LTE Laid the Groundwork for 5G: A Technical Evolution Explained
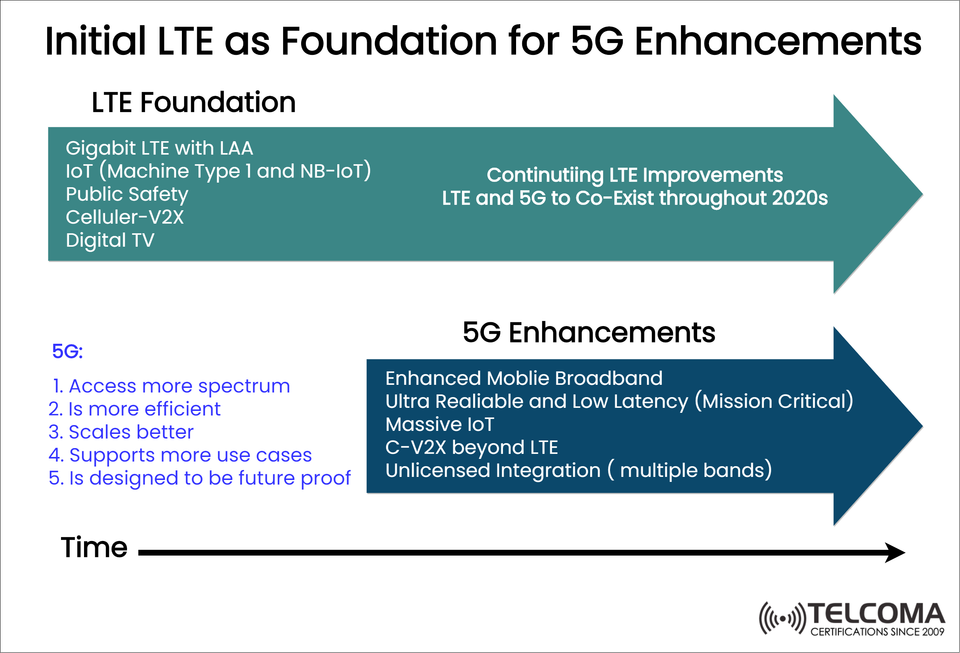

📶 Initial LTE as a Base for 5G Enhancements
As we see 5G deployment on a large scale around the globe, it is important to understand how Long Term Evolution (LTE) provided the framework for this transformation. 5G is not a replacement of LTE as much as it is an evolution built on the solid framework of LTE. 5G is designed to extend capabilities and add layers to services and use cases.
This blog breaks down how LTE provided the technical and architectural framework to allow LTE to flow into ultra-fast, scalable, and future-proof mobile networks.
🧱 LTE: The Base Layer of 5G
LTE was not just a staging platform; LTE was created as a platform to progress. Many of the features that LTE offered have directly resulted in many of the features seen currently as part of 5G and with early 5G displays.
Key Technologies in LTE that Contribute to 5G:
Gigabit LTE with LAA (Licensed Assisted Access)
Uses unlicensed spectrum to provide additional capacity along with throughput.
Support for IoT (Machine Type Communication & NB-IoT)
Initial roots of massive IoT in 5G would not have been possible.
Public Safety Communications
Mission critical communications that have driven ultra-reliable communication with low-latency communication in 5G.
Cellular V2X (Vehicle to Everything)
Already evolving beyond LTE to C-V2X as part of 5G.
Digital TV Broadcasting
Providing another piece of the puzzle for 5G broadcast.
📈 5G: Enhancing LTE
5G does not come about in isolation. 5G builds on the research and development breakthroughs of LTE with additional capabilities and flexibility to accommodate existing and new use cases.
The Advantages of 5G Compared to LTE:
More Spectrum
High-band mmWave and mid-band C-Band
Efficiency
Beamforming, Massive MIMO, network slicing
Scale
Capability to support billions of connected devices and sensors
Use Cases
Smart factories, autonomous vehicles, AR/VR, etc.
Future-Proofed Architecture
Modular, cloud-native architecture to enhance as 5G-Advanced and other iterations of the framework develop
🚀 5G Enhancements: Foundation laid by LTE
As shown in the figure, a whole set of 5G enhancements capable of transforming 5G networks build upon the foundation set by LTE:
Enhancement Definition
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) High-speed, gigabit-level data services powered by Gigabit LTE & carrier aggregation
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC) Mission critical applications such as tele-surgery, autonomous driving
Massive IoT Scalable and extensible connections to millions of low-power devices
C-V2X Beyond LTE In Vehicle-to-Everything communication utilizing the 5G sidelink and edge compute
Multi-band use with unlicensed Multiple licensed bands and an unlicensed band from a single physical interface.
🔄 Coexisting LTE and 5G... Why is this Important?
Operators are not turning off LTE right away. In most cases, LTE continues to be an anchor layer in non-standalone (NSA) 5G deployments. This use of LTE in conjunction with 5G provides:
Low cost characteristics for 5G deployment
Trusted fallback locations with low 5G coverage
Pathway for legacy devices and applications to evolve
Every operator in North America will likely utilize LTE in some manner through the 2020s, especially in rural and less developed regions where 5G is still deploying.
🧭 Recommendations
For Network Engineers:
Create plans for two-mode networks (LTE + 5G) to capitalize on transitional periods.
Upgrade LTE infrastructure (e.g. Gigabit LTE) to maximize on 5G NSA upgrade.
For Business Managers:
Leverage LTE's footprint to deliver early 5G business use cases.
Create solutions that organically transition from LTE-based IoT to 5G Massive IoT.
For Developers:
Design applications that can operate on both LTE and 5G, especially for low-latency or mission-critical services.
• LTE-to-5G: A Strategic Migration Plan
For telecom professionals and technology leaders looking for guidance, here is a recommended strategy for migrating from LTE to 5G:
Phase Focus Areas
Phase 1 (Present) Use Gigabit LTE, implement NSA 5G, upgrade LTE core and backhaul
Phase 2 (Mid-Term) Implement SA 5G coverage, integrate URLLC, use dual LTE/5G IoT platforms
Phase 3 (Long-Term) Optimize for 5G-Advanced, begin retiring LTE (i.e., dense urban locations)
• The Bottom Line
LTE's success isn't just historical—it's foundational.
Carrier-grade LTE performance, IoT capabilities, and a multitude of other applications serve as a robust, flexible, and upgradeable foundation.
5G will not drive LTE into extinction overnight—it will build upon it.
The transition must be a deliberate strategy with interoperability and coexistence as key elements.
Investments in LTE are just as relevant today as they were when made, and they can directly impact how successful you will be with your 5G initiatives tomorrow.
The road to your 5G destination, full and complete maturity, passes through LTE, and understanding both will be essential in deploying fiber future-proof networks.
• Utilizing LTE with 5G: The Operational Strategy
The operational strategy will need to bring LTE and 5G capabilities together to make the most out of your network rationale. Integrating LTE and 5G should not just be technological; it also must be operational and are interrelated strategy components known as properly integrating LTE and 5G capabilities.
🧑💼 Who Should Take Action Right Now—and How?
🏗️ Telecom Infrastructure Providers:
Upgrade LTE base stations with 5G-compatible hardware.
Use dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) to enable LTE and 5G in the same band.
📱 Devices OEMs and Chipset Suppliers:
Keep developing dual-mode LTE/5G devices.
Optimize RF components for sub-6 GHz and mmWave.
🏭 Enterprise Networks:
Start deploying private LTE in preparation for private 5G.
Plan industrial use cases leveraging LTE URLLC features now with a migration path to 5G NR.
🧑💻 Developers & Startups:
Create applications that can leverage both LTE and 5G by using network-aware SDKs.
Innovate around NB-IoT/M1 as these transition into 5G Massive IoT.
🗂 Related Topics to Explore
To build your awareness and to feed your curiosity, look to learn about:
📘 [5G Core vs LTE Core: Ins and Outs of their architectural differences]
📡 [What is Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS)? A user-friendly explanation]
🚙 [From LTE-V to 5G-V2X - The evolution of vehicle connectivity]
🌍 [5G deployments in emerging markets - leveraging LTE infrastructure]
🧪 [Testing methods for dual LTE/5G networks]
